Abstract
Purpose
This study assessed changes in soil potassium (K) pools, soil K-bearing minerals, and crop yields without K-fertilizer application for 25 years on the North China Plains.
Materials and methods
Two long-term field experiments (over 25 years) in a wheat-maize rotation system were conducted: Experiment 1 was a randomized complete block experiment of three rates of fertilizer nitrogen (N: 0, 270, 540 kg ha−1 year−1) and phosphorus (P: 0, 36, 72 kg ha−1 year−1). Experiment 2 had an orthogonal treatment structure with three rates of N and P fertilizers and straw (0, 112.5, 187.5 kg N ha−1 year−1; 0, 40, 80 kg P ha−1 year−1; and 0, 2250, 4500 kg straw ha−1 year−1). The three different tillage methods were as follows: T1, conventional tillage with straw incorporation; T2, conventional tillage with straw cover on soil surface; and M, minimum tillage. Three replicates were designed for each treatment in both experiments. Different forms of K, including total K, mineral K (MK), slowly available K (SK), and rapidly available K (RK), were quantified by standard methods. Crop yield was calculated based on random quadrants’ data.
Results and discussion
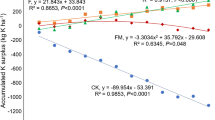
The results from both experiments indicated that the depletion of RK promoted the conversion of MK to SK by K release from hydromica. Crop yields in all the treatments with P fertilizer were significantly higher than those in N alone and CK treatments in both long-term experiments, suggesting that P fertilizer had a greater contribution in improving crop yield than N fertilizer after long-term lack of K fertilization. The average values of different forms of K and crop yield in exp. 2 were clearly higher than those in exp. 1. After 11 years of high rates of straw without chemical K fertilization, the average soil RK peaked. However, 5 years later, it showed a negative K budget and crop yield began to decline.
Conclusions
For over 25 years, fertilization and tillage managements had little impact on soil TK and MK contents because of the high feldspar and hydromica contents in the soil. The weathering of K-bearing minerals and fertilization significantly changed soil SK and RK contents, and hydromica was the main source of SK. P fertilizer was more important in increasing crop yield than N fertilizer and straw with long-term zero K inputs. To maintain high crop yield (12.02–13.82 t ha−1 year−1, the total yield of summer maize and winter wheat) and improve the fertilizer utilization efficiency, 150–228 kg K ha−1 should be applied alongside 187.5 kg N ha−1 year−1, 80 kg P ha−1 year−1, and 4500 kg straw ha−1 year−1 every 16 years in this production system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz I, Mahmood T, Islam KR (2013) Effect of long term no-till and conventional tillage practices on soil quality. Soil Till Res 131:28–35
Bajwa MI (1994) Soil potassium status, potassium fertilizer usage and recommendation potash in Pakistan. Potash Rev 20th Suit 3:128
Dai X, Ouyang Z, Li Y, Wang H (2013) Variation in yield gap induced by nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer in North China Plain. PLoS One 8:e82147
Darunsontaya T, Suddhiprakarn A, Kheoruenromne I, Prakongkep N, Gilkes RJ (2012) The forms and availability to plants of soil potassium as related to mineralogy for upland Oxisols and Ultisols from Thailand. Geoderma 170:11–24
Divito GA, Sadras VO (2014) How do phosphorus, potassium and sulphur affect plant growth and biological nitrogen fixation in crop and pasture legumes? A meta-analysis. Field Crop Res 156:161–171
Gong ZT, Zhang GL, Chen ZC (2007) Pedogenesis and soil taxonomy. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Haliniarz M, Bujak K, Gaweda D, Kwiatkowski C (2013) Response of spring wheat to reduced tillage systems and to different levels of mineral fertilization. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum: Agriculture 12:13–24
Johnston AE, Goulding KWT (1990) The use of plant and soil analysis to predict the potassium supplying capacity of soil. Proceedings 22nd Colloquim of the Interna-tional Potash Institute, Berne
Jouany C, Colomb B, Bosc M (1996) Long-term effects of potassium fertilization on yields and fertility status of calcareous soils of south-west France. Eur J Agrono 5:287–294
Kirkman JH, Basker A, Surapaneni A, MacGregor AN (1994) Potassium in the soils of New Zealand—a review. New Zeal J Agric Res 37:207–227
Kuntz M, Alfred B, Andreas G, Scholberg JM, Mäder P, Pfiffner L (2013) Influence of reduced tillage on earthworm and microbial communities under organic arable farming. Pedobiologia 56:251–260
Lal R (2013) Enhancing ecosystem services with no-till. Renew Agric Food Syst 28:102–114
Li J, Lu J, Li X, Ren T, Cong R, Zhou L (2014) Dynamics of potassium release and adsorption on rice straw residue. PLoS One 9(2):e90440
Liu RL, Jin JY, Wu RG, Liang MZ (1999) Study on K balance and effect of K fertilizer in soil-crop system in North China: I. Soil K balance and regulation in the main cropping system. Soil Fert 6:3–11 (in Chinese)
Liu SP, Nie XT, Zhang HC, Dai QG, Huo ZY, Xu K (2006) Effects of tillage and straw returning on soil fertility and grain yield in a wheat-rice double cropping system. Soc Agric Eng 22:48–51 (in Chinese)
Liu D, Lian B, Dong H (2012) Isolation of Paenibacillus sp. and assessment of its potential for enhancing mineral weathering. Geomicrobiol J 29:413–421
Lyons JM, Wheaton TA, Pratt HK (1964) Relationship between the physical nature of mitochondrial membranes and chilling sensitivity in plants. Plant Physiol 39:262–268
Maltas A, Charles R, Jeangros B, Sinaj S (2013) Effect of organic fertilizers and reduced-tillage on soil properties, crop nitrogen response and crop yield: results of a 12-year experiment in Changins, Switzerland. Soil Till Res 126:11–18
Matson PA, Naylor R, Ortiz-Monasterio I (1998) Integration of environmental, agronomic, and economic aspects of fertilizer management. Science 280:112–115
Mbuthia LW, Veronica A-M, Jennifer D, Sean S, Donald T, Evah O, Molefi M, Forbes W, Neal E (2015) Long term tillage, cover crop, and fertilization effects on microbial community structure, activity: implications for soil quality. Soil Biol Biochem 89:24–34
Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP (2014) Does a rhizospheric microorganism enhance K availability in agricultural soils? Microb Res 169:337–347
Najafi-Ghiri M, Abtahi A (2013) Potassium fixation in soil size fractions of arid soils. Soil Water Res 8:49–55
Niu LA, Hao JM, Niu XS (1998) Study on the effects of straw returning and N and P fertilizer application. Soil Fert 6:32–35 (in Chinese)
Niu JF, Zhang WF, Chen XP, Li CJ, Zhang FS, Jiang LH, Liu ZH, Xiao K, Assaraf M, Imas P (2011a) Potassium fertilization on maize under different production practices in the North China Plain. Agrono J 103:822–829
Niu LA, Hao JM, Zhang BZ, Niu XS (2011b) Influences of long-term fertilizer and tillage management on soil fertility of the North China Plain. Pedosphere 21:813–820
Niu JF, Zhang WF, Ru S, Chen XP, Xiao K, Zhang X, Zhang FS (2013) Effects of potassium fertilization on winter wheat under different production practices in the North China Plain. Field Crop Res 140:69–76
Parmar P, Sindhu SS (2013) Potassium solubilization by rhizosphere bacteria: influence of nutritional and environmental conditions. J Microbiol Res 3:25–31
Pettigrew WT (2008) Potassium influences on yield and quality production for maize, wheat, soybean and cotton. Physiol Plantarum 133:670–681
Pratt PF (1965) Potassium. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of Soil Analysis Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. Am Soc Agron Madison Wisc, pp 1018–1035
Qiu SJ, Xie JC, Zhao SC, Xu XP, Whang XF, Zhou W, He P, Johnston AM, Christie P, Jin JY (2014) Long-term effects of potassium fertilization on yield, efficiency, and soil fertility status in a rain-fed maize system in northeast China. Field Crop Res 163:1–9
Römheld V, Kirkby EA (2010) Research on potassium in agriculture: needs and prospects. Plant Soil 335:155–180
Sharma U, Paliyal SS (2015) Forms of soil potassium as influenced by long term application of chemical fertilizers and organics in rainfed maize-wheat cropping system. J Krishi Vigyan 3:48–53
Sheldrick WF, Syers JK, Lingard J (2003) Soil nutrient audits for China to estimate nutrient balances and output/input relationships. Agric Ecosyst Environ 94:341–354
Sheng XF (2005) Growth promotion and increased potassium uptake of cotton and rape by a potassium releasing strain of Bacillus edaphicus. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1918–1922
Srinivasarao C, Kundu S, Ramachandrappa BK, Reddy S, Lal R, Venkateswarlu B, Naik RP (2014) Potassium release characteristics, potassium balance, and fingermillet (Eleusine coracana G.) yield sustainability in a 27-year long experiment on an Alfisol in the semi-arid tropical India. Plant Soil 374:315–330
Sun L, Li C, He P, Liu M, Hu J (2011) Long-term application of K fertilizer and straw returning improve crop yield, absorptive capacity of K, and soil nutrient natural supplying capacity in North China. Front Agric China 5:563–569
Takahashi S, Anwar MR (2007) Wheat grain yield, phosphorus uptake and soil phosphorus fraction after 23 years of annual fertilizer application to an Andosol. Field Crop Res 101:160–171
Tan DS, Jin JY, Huang SW, Li ST, He P (2007) Effect of long-term application of K fertilizer and wheat straw to soil on crop yield and soil K under different planting systems. Agric Sci China 6:200–207
Tan DS, Jin JY, Jiang LH, Huang SW, Liu ZH (2012) Potassium assessment of grain producing soils in North China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 148:65–71
Triplett GB, Dick WA (2008) No-tillage crop production: a revolution in agriculture! Agrono J 100:S153–S165
Wang Y, Wang E, Wang D, Huang S, Ma Y, Smith CJ, Wang L (2010) Crop productivity and nutrient use efficiency as affected by long-term fertilisation in North China Plain. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 86:105–119
Welch LF, Scott AD (1961) Availability of nonexchangeable soil potassium to plants as affected by added potassium and ammonium. Soil Sci Soc Am J 25:102–104
Wu LQ, Ma WQ, Zhang CC, Wu L, Zhang WF, Jiang RF, Chen XP (2013) Current potassium-management status and grain-yield response of Chinese maize to potassium application. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 176:441–449
Zhang FS (2008) Research report on fertilizer industry and scientific application of fertilizer. Chinese Agricultural University Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang FS, Jiang RF, Chen XP, Jia LL (2011) Soil testing and fertilization recommendation. China Agricultural University Press, Beijing, pp 15–19 (in Chinese)
Zhao SC, He P, Qiu SJ, Jia LL, Liu MC, Jin JY, Johnston AM (2014) Long-term effects of potassium fertilization and straw return on soil potassium levels and crop yields in north-central China. Field Crop Res 169:116–122
Zhou XF, Feng W, Yang JF, Sun LM, Wang SY, Zhao ZL (2011) The study on the abundance and deficiency indices of phosphorus and potassium of wheat with straw returning in Taihang Mountain Piedmont Plain. Acta Agric Boreali Sin 26:170–174 (in Chinese)
Zikeli S, Gruber S, Teufel CF, Hartung K, Claupein W (2013) Effects of reduced tillage on crop yield, plant available nutrients and soil organic matter in a 12-year long-term trial under organic management. Sustainability 5:3876–3894
Zörb C, Senbayram M, Peiter E (2014) Potassium in agriculture—status and perspectives. J Plant Physiol 171:656–669
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the National Science-Technology Support Plan of China (2015BAD06B01), the National Science Foundation of China (41401266), and the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2015CB150502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Caixian Tang
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 42 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Niu, L., Zhang, Q. et al. Impacts of long-term lack of potassium fertilization on different forms of soil potassium and crop yields on the North China Plains. J Soils Sediments 17, 1607–1617 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1658-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1658-8