Abstract
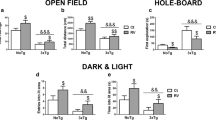
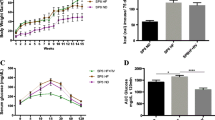
Resveratrol is a polyphenol that is mainly found in grapes and red wine and has been reported to be a caloric restriction (CR) mimetic driven by Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) activation. Resveratrol increases metabolic rate, insulin sensitivity, mitochondrial biogenesis and physical endurance, and reduces fat accumulation in mice. In addition, resveratrol may be a powerful agent to prevent age-associated neurodegeneration and to improve cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Moreover, different findings support the view that longevity in mice could be promoted by CR. In this study, we examined the role of dietary resveratrol in SAMP8 mice, a model of age-related AD. We found that resveratrol supplements increased mean life expectancy and maximal life span in SAMP8 and in their control, the related strain SAMR1. In addition, we examined the resveratrol-mediated neuroprotective effects on several specific hallmarks of AD. We found that long-term dietary resveratrol activates AMPK pathways and pro-survival routes such as SIRT1 in vivo. It also reduces cognitive impairment and has a neuroprotective role, decreasing the amyloid burden and reducing tau hyperphosphorylation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal B, Baur J (2011) Resveratrol and life extension. Ann NY Acad Sci 1215:138–143
Araki T, Sasaki Y, Milbrandt J (2004) Increased nuclear NAD biosynthesis and SIRT1 activation prevent axonal degeneration. Science 305:1010–1013
Banks WA, Morley JE, Farr SA, Price TO, Ercal N, Vidaurre I, Schally AV (2010) Effects of a growth hormone-releasing hormone antagonist on telomerase activity, oxidative stress, longevity, and aging in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:22272–22277
Barger JL, Kayo T, Vann JM, Arias EB, Wang J, Hacker TA, Wang Y, Raederstorff D, Morrow JD, Leeuwenburgh C, Allison DB, Saupe KW, Cartee GD, Weindruch R, Prolla TA (2008) A low dose of dietary resveratrol partially mimics caloric restriction and retards aging parameters in mice. PLoS One 3:e2264
Baur JA, Sinclair DA (2006) Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:493–506
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K, Pistell PJ, Poosala S, Becker KG, Boss O, Gwinn D, Wang M, Ramaswamy S, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Lakatta EG, Le Couteur D, Shaw RJ, Navas P, Puigserver P, Ingram DK, de Cabo R, Sinclair DA (2006) Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 444:337–342
Bayod S, Del Valle J, Canudas AM, Lalanza JF, Sanchez-Roige S, Camins A, Escorihuela RM, Pallàs M (2011) Long-term treadmill exercise induces neuroprotective molecular changes in rat brain. J Appl Physiol 111:1380–1390
Beher D, Wu J, Cumine S, Kim KW, Lu SC, Atangan L, Wang M (2009) Resveratrol is not a direct activator of SIRT1 enzyme activity. Chem Biol Drug Des 74:619–624
Canudas AM, Gutierrez-Cuesta J, Rodríguez MI, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Sureda FX, Camins A, Pallàs M (2005) Hyperphosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau in senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM). Mech Ageing Dev 126:1300–1304
Chang J, Rimando A, Pallas M, Camins A, Porquet D, Reeves J, Shukitt-Hale B, Smith MA, Joseph JA, Casadesus G (2012) Low-dose pterostilbene, but not resveratrol, is a potent neuromodulator in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(9):2062–2071
Chen J, Zhou Y, Mueller-Steiner S, Chen LF, Kwon H, Yi S, Mucke L, Gan L (2005) SIRT1 protects against microglia-dependent amyloid-beta toxicity through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling. J Biol Chem 280:40364–40374
Chung S, Yao H, Caito S, Hwang JW, Arunachalam G, Rahman I (2010) Regulation of SIRT1 in cellular functions: role of polyphenols. Arch Biochem Biophys 501(1):79–90
Cohen HY, Miller C, Bitterman KJ, Wall NR, Hekking B, Kessler B, Howitz KT, Gorospe M, de Cabo R, Sinclair DA (2004) Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 305:390–392
Colman RJ, Anderson RM, Johnson SC, Kastman EK, Kosmatka KJ, Beasley TM, Allison DB, Cruzen C, Simmons HA, Kemnitz JW, Weindruch R (2009) Caloric restriction delays disease onset and mortality in rhesus monkeys. Sci 325(5937):201–4
Del Valle J, Duran-Vilaregut J, Manich G, Casadesús G, Smith MA, Camins A, Pallàs M, Pelegrí C, Vilaplana J (2010) Early amyloid accumulation in the hippocampus of SAMP8 mice. J Alzheimers Dis 19:1303–1315
Del Valle J, Duran-Vilaregut J, Manich G, Pallàs M, Camins A, Vilaplana J, Pelegrí C (2011) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy, blood–brain barrier disruption and amyloid accumulation in SAMP8 mice. Neurodegener Dis 8:421–429
Donmez G, Wang D, Cohen DE, Guarente L (2010) SIRT1 suppresses β-Amyloid production by activating the α-secretase gene ADAM10. Cell 142:320–332
Flood JF, Morley JE (1998) Learning and memory in the SAMP8 mouse. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 22:1–20
Gan L (2007) Therapeutic potential of sirtuin-activating compounds in Alzheimer’s disease. Drug News Perspect 20:233–239
Greco SJ, Hamzelou A, Johnston JM, Smith MA, Ashford JW, Tezapsidis N (2011) Leptin boosts cellular metabolism by activating AMPK and the sirtuins to reduce tau phosphorylation and β-amyloid in neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414:170–174
Gutierrez-Cuesta J, Tajes M, Jiménez A, Coto-Montes A, Camins A, Pallàs M (2008) Evaluation of potential pro-survival pathways regulated by melatonin in a murine senescence model. J Pineal Res 45:497–505
Halagappa VK, Guo Z, Pearson M, Matsuoka Y, Cutler RG, Laferla FM, Mattson MP (2007) Intermittent fasting and caloric restriction ameliorate age-related behavioral deficits in the triple-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 26:212–220
Ho L, Chen LH, Wang J, Zhao W, Talcott ST, Ono K, Teplow D, Humala N, Cheng A, Percival SS, Ferruzzi M, Janle E, Dickstein DL, Pasinetti GM (2009) Heterogeneity in red wine polyphenolic contents differentially influences Alzheimer’s disease-type neuropathology and cognitive deterioration. J Alzheimers Dis 16:59–72
Howitz KT, Bitterman KJ, Cohen HY, Lamming DW, Lavu S, Wood JG, Zipkin RE, Chung P, Kisielewski A, Zhang LL, Scherer B, Sinclair DA (2003) Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 425:191–196
Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C, Harigaya Y, Younkin S, Yang F, Cole G (1996) Correlative memory deficits, Abeta elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science 274:99–102
Hu YY, He SS, Wang X, Duan QH, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wang J (2002) Levels of nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated tau in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients: an ultrasensitive bienzyme-substrate-recycle enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Pathol 160:1269–1278
Julien C, Tremblay C, Emond V, Lebbadi M, Salem N Jr, Bennett DA, Calon F (2009) Sirtuin 1 reduction parallels the accumulation of tau in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:48–58
Kim D, Nguyen MD, Dobbin MM, Fischer A, Sananbenesi F, Rodgers JT, Delalle I, Baur JA, Sui G, Armour SM, Puigserver P, Sinclair DA, Tsai LH (2007) SIRT1 deacetylase protects against neurodegeneration in models for Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J 26:3169–3179
Ladiwala AR, Lin JC, Bale SS, Marcelino-Cruz AM, Bhattacharya M, Dordick JS, Tessier PM (2010) Resveratrol selectively remodels soluble oligomers and fibrils of amyloid Abeta into off-pathway conformers. J Biol Chem 285:24228–24237
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P, Elliott P, Geny B, Laakso M, Puigserver P, Auwerx J (2006) Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 127:1109–11022
Lichtenthaler SF (2011) Alpha-secretase in Alzheimer’s disease: molecular identity, regulation and therapeutic potential. J Neurochem 116:10–21
Manich G, Mercader C, del Valle J, Duran–Vilaregut J, Camins A, Pallàs M, Vilaplana J, Pelegri C (2011) Characterization of amyloid-β granules in the hippocampus of SAMP8 mice. J Alzheimers Dis 25:535–546
Marambaud P, Zhao H, Davies P (2005) Resveratrol promotes clearance of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptides. J Biol Chem 280:37377–37382
Markesbery WR (1997) Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med 23:134–147
Markowska AL, Spangler EL, Ingram DK (1998) Behavioral assessment of the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM P8 and R1). Physiol Behav 64:15–26
Mattison JA, Roth GS, Beasley TM, Tilmont EM, Handy AM, Herbert RL, Longo DL, Allison DB, Young JE, Bryant M, Barnard D, Ward WF, Qi W, Ingram DK, de Cabo R (2012) Impact of caloric restriction on health and survival in rhesus monkeys from the NIA study. Nature 489:318–321
Miller RA, Harrison DE, Astle CM, Baur JA, Boyd AR, de Cabo R, Fernandez E, Flurkey K, Javors MA, Nelson JF, Orihuela CJ, Pletcher S, Sharp ZD, Sinclair D, Starnes JW, Wilkinson JE, Nadon NL, Strong R (2011) Rapamycin, but not resveratrol or simvastatin, extends life span of genetically heterogeneous mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 66:191–201
Miyamoto M, Kiyota Y, Yamazaki N, Nagaoka A, Matsuo T, Nagawa Y, Takeda T (1986) Age-related changes in learning and memory in the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM). Physiol Behav 38:399–406
Miyamoto M, Kiyota Y, Nishiyama M, Nagaoka A (1992) Senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM): age-related reduced anxiety-like behavior in the SAM-P/8 strain. Physiol Behav 51:979–985
Morley JE, Kumar VB, Bernardo AE, Farr SA, Uezu K, Tumosa N, Flood JF (2000) Beta-amyloid precursor polypeptide in SAMP8 mice affects learning and memory. Peptides 21:1761–1767
Morley JE, Farr SA, Flood JF (2002) Antibody to amyloid beta protein alleviates impaired acquisition, retention, and memory processing in SAMP8 mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 78:125–138
Morley JE, Farr SA, Kumar VB, Armbrecht HJ (2012) The SAMP8 mouse: a model to develop therapeutic interventions for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 18:1123–1130
Ono K, Condron MM, Ho L, Wang J, Zhao W, Pasinetti GM, Teplow DB (2008) Effects of grape seed-derived polyphenols on amyloid beta-protein self-assembly and cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 283:32176–32187
Oomen CA, Farkas E, Roman V, van der Beek EM, Luiten PGM, Meerlo P (2009) Resveratrol preserves cerebrovascular density and cognitive function in aging mice. Front Ag Neurosci 1:4. doi:10.3389/neuro.24.004.2009
Pacholec M, Bleasdale JE, Chrunyk B, Cunningham D, Flynn D, Garofalo RS, Griffith D, Griffor M, Loulakis P, Pabst B, Qiu X, Stockman B, Thanabal V, Varghese A, Ward J, Withka J, Ahn K (2010) SRT1720, SRT2183, SRT1460, and resveratrol are not direct activators of SIRT1. J Biol Chem 285:8340–8351
Pallas M, Camins A, Smith MA, Perry G, Lee HG, Casadesus G (2008) From aging to Alzheimer’s disease: unveiling “the switch” with the senescence-accelerated mouse model (SAMP8). J Alzheimers Dis 15:615–624
Park H, Kam TI, Kim Y, Choi H, Gwon Y, Kim C, Koh JY, Jung YK (2012a) Neuropathogenic role of adenylate kinase-1 in Aβ-mediated tau phosphorylation via AMPK and GSK3β. Hum Mol Genet 21:2725–2737
Park SJ, Ahmad F, Philp A, Baar K, Williams T, Luo H, Ke H, Rehmann H, Taussig R, Brown AL, Kim MK, Beaven MA, Burgin AB, Manganiello V, Chung JH (2012b) Resveratrol ameliorates aging-related metabolic phenotypes by inhibiting cAMP phosphodiesterases. Cell 148:421–433
Park SK, Kim K, Page GP, Allison DB, Weindruch R, Prolla TA (2009) Gene expression profiling of aging in multiple mouse strains: identification of aging biomarkers and impact of dietary antioxidants. Aging Cell 8:484–495
Parker JA, Arango M, Abderrahmane S, Lambert E, Tourette C, Catoire H, Néri C (2005) Resveratrol rescues mutant polyglutamine cytotoxicity in nematode and mammalian neurons. Nat Genet 37:349–350
Pearson KJ, Baur JA, Lewis KN, Peshkin L, Price NL, Labinskyy N, Swindell WR, Kamara D, Minor RK, Perez E, Jamieson HA, Zhang Y, Dunn SR, Sharma K, Pleshko N, Woollett LA, Csiszar A, Ikeno Y, Le Couteur D, Elliott PJ, Becker KG, Navas P, Ingram DK, Wolf NS, Ungvari Z, Sinclair DA, de Cabo R (2008) Resveratrol delays age-related deterioration and mimics transcriptional aspects of dietary restriction without extending life span. Cell Metab 8:157–168
Perry G, Castellani RJ, Hirai K, Smith MA (1998) Reactive oxygen species mediate cellular damage in Alzheimer disease. J Alzheimers Dis 1:45–55
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ, Duarte FV, Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, Agarwal B, Ye L, Ramadori G, Teodoro JS, Hubbard BP, Varela AT, Davis JG, Varamini B, Hafner A, Moaddel R, Rolo AP, Coppari R, Palmeira CM, de Cabo R, Baur JA, Sinclair DA (2012) SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab 15:675–690
Rodríguez MI, Escames G, López LC, López A, García JA, Ortiz F, Sánchez V, Romeu M, Acuña-Castroviejo D (2008) Improved mitochondrial function and increased life span after chronic melatonin treatment in senescent prone mice. Exp Gerontol 43:749–756
Ruderman NB, Xu XJ, Nelson L, Cacicedo JM, Saha AK, Lan F, Ido Y (2010) AMPK and SIRT1: a long-standing partnership? Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 298:E751–E760
Saunders LR, Sharma AD, Tawney J, Nakagawa M, Okita K, Yamanaka S, Willenbring H, Verdin E (2010) miRNAs regulate SIRT1 expression during mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation and in adult mouse tissues. Aging 2:415–431
Selman C, McLaren JS, Mayer C, Duncan JS, Collins AR, Duthie GG, Redman P, Speakman JR (2008) Lifelong alpha-tocopherol supplementation increases the median life span of C57BL/6 mice in the cold but has only minor effects on oxidative damage. Rejuvenation Res 11:83–96
Shih PH, Chan YC, Liao JW, Wang MF, Yen GC (2010) Antioxidant and cognitive promotion effects of anthocyanin-rich mulberry (Morus atropurpurea L.) on senescence-accelerated mice and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. J Nutr Biochem 21:598–605
Smith MA, Sayre LM, Monnie VM, Perry G (1995) Radical AGEing in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci 18:172–176
Sohal RS, Svensson I, Sohal BH, Brunk UT (1989) Superoxide anion radical production in different animal species. Mech Ageing Dev 49:129–135
Spangler EL, Patel N, Speer D, Hyman M, Hengemihle J, Markowska A, Ingram DK (2002) Passive avoidance and complex maze learning in the senescence accelerated mouse (SAM): age and strain comparisons of SAM P8 and R1. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 57:B61–B68
Takeda T (2009) Senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM) with special references to neurodegeneration models, SAMP8 and SAMP10 mice. Neurochem Res 34:639–659
Takeda T, Hosokawa M, Takeshita S, Irino M, Higuchi K, Matsushita T, Tomita Y, Yasuhira K, Hamamoto H, Shimizu K, Ishii M, Yamamuro T (1981) A new murine model of accelerated senescence. Mech Ageing Dev 17:183–194
Um JH, Park SJ, Kang H, Yang S, Foretz M, McBurney MW, Kim MK, Viollet B, Chung JH (2010) AMP-activated protein kinase-deficient mice are resistant to the metabolic effects of resveratrol. Diabetes 59:554–563
Valenzano DR, Terzibasi E, Genade T, Cattaneo A, Domenici L, Cellerino A (2006) Resveratrol prolongs lifespan and retards the onset of age-related markers in a short-lived vertebrate. Curr Biol 16:296–300
Villalba JM, de Cabo R, Alcain FJ (2012) A patent review of sirtuin activators: an update. Expert Opin Ther Pat 22:355–367
Vingtdeux V, Dreses-Werringloer U, Zhao H, Davies P, Marambaud P (2008) Therapeutic potential of resveratrol in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurosci 9(Suppl 2):S6
Viswanathan M, Kim SK, Berdichevsky A, Guarente L (2005) A role for SIR-2.1 regulation of ER stress response genes in determining C. elegans life span. Dev Cell 9:605–615
Wang J, Ho L, Zhao Z, Seror I, Humala N, Dickstein DL, Thiyagarajan M, Percival SS, Talcott ST, Pasinetti GM (2006) Moderate consumption of Cabernet Sauvignon attenuates Abeta neuropathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 20:2313–2320
Wang J, Ho L, Zhao W, Ono K, Rosensweig C, Chen L, Humala N, Teplow DB, Pasinetti GM (2008) Grape-derived polyphenolics prevent Abeta oligomerization and attenuate cognitive deterioration in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 28:6388–6392
Weindruch R, Walford RL (1988) The retardation of aging and disease by dietary restriction. Charles C Thomas, Springfield
Wood JG, Rogina B, Lavu S, Howitz K, Helfand SL, Tatar M, Sinclair D (2004) Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature 430:686–689
Yagi H, Katoh S, Akiguchi I, Takeda T (1988) Age-related deterioration of ability of acquisition in memory and learning in senescence accelerated mouse: SAM-P/8 as an animal model of disturbances in recent memory. Brain Res 474:86–93
Zang M, Xu S, Maitland-Toolan KA, Zuccollo A, Hou X, Jiang B, Wierzbicki M, Verbeuren TJ, Cohen RA (2006) Polyphenols stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase, lower lipids, and inhibit accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetic LDL receptor-deficient mice. Diabetes 55:2180–2191
Acknowledgments
We thank the Language Advisory Service of the University of Barcelona for revising the manuscript. This study was supported by grants SAF-2009-13093, BFU 2010/22149, SAF-2011-23631, and SAF-2012 from the “Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia,” 2009/SGR00893 from the “Generalitat de Catalunya,” 610RT0405 from the Programa Iberoamericano de Ciencia y Tecnologia para el Desarrollo (CYTED), and the Fundación MAPFRE (Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Porquet, D., Casadesús, G., Bayod, S. et al. Dietary resveratrol prevents Alzheimer’s markers and increases life span in SAMP8. AGE 35, 1851–1865 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9489-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9489-4