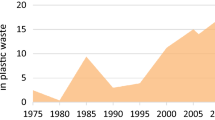
Abstract
Peru suffers from poor solid waste and coastal management, as well as evidenced plastic pollution in various forms. However, studies in Peru focusing on small plastic debris (i.e., meso- and microplastics) are still limited and inconclusive. Thus, the present study investigated the abundance, characteristics, seasonality, and distribution of small plastic debris along the coast of Peru. The abundance of small plastic debris is predominantly driven by specific locations, where a source of contamination is present, rather than presenting seasonal patterns. Meso- and microplastics were strongly correlated in both seasons (summer and winter), suggesting meso-plastic constantly breaking down as microplastic sources. Additionally, heavy metals (e.g., Cu, Pb) were found in low concentrations (mean concentrations < 0.4%) on the surface of some mesoplastics. Here, we provided a baseline on the multiple factors involving small plastic debris on the Peruvian coast and preliminarily identify associated contaminants.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available on request.
References
Abelouah MR, Ben-Haddad M, Hajji S, De-la-Torre GE, Aziz T, Oualid JA, Banni M, Alla AA (2022) Floating microplastics pollution in the Central Atlantic Ocean of Morocco: Insights into the occurrence, characterization, and fate. Mar Pollut Bull 182:113969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113969
Abelouah MR, Romdhani I, Ben-Haddad M, Hajji S, De-la-Torre GE, Gaaied S, Barra I, Banni M, Alla AA (2023) Binational survey using Mytilus galloprovincialis as a bioindicator of microplastic pollution: Insights into chemical analysis and potential risk on humans. Sci Total Environ 161894. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2023.161894
Akkajit P, Tipmanee D, Cherdsukjai P, Suteerasak T, Thongnonghin S (2021) Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in beach sediments along Phuket coastline. Mar Pollut Bull 169:112496. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2021.112496
Alvarez-Zeferino JC, Ojeda-Benítez S, Cruz-Salas AA, Martínez-Salvador C, Vázquez-Morillas A (2020) Microplastics in Mexican beaches. Resour Conserv Recycl 155:104633. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RESCONREC.2019.104633
Andrady AL (2022) Weathering and fragmentation of plastic debris in the ocean environment. Mar Pollut Bull 180:113761. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2022.113761
Andrady AL, Barnes PW, Bornman JF, Gouin T, Madronich S, White CC, Zepp RG, Jansen MAK (2022) Oxidation and fragmentation of plastics in a changing environment; from UV-radiation to biological degradation. Sci Total Environ 158022. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.158022
Ben-Haddad M, Abelouah MR, Hajji S, De-la-Torre GE, Oualid HA, Rangel-Buitrago N, Ait Alla A (2022) The wedge clam Donax trunculus L., 1758 as a bioindicator of microplastic pollution. Mar Pollut Bull 178:113607. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2022.113607
Benson NU, Agboola OD, Fred-Ahmadu OH, De-la-Torre GE, Oluwalana A, Williams A (2022) Micro(nano)plastics Prevalence, Food Web Interactions and Toxicity Assessment in Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Front Mar Sci 9:851281. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMARS.2022.851281
Bosker T, Guaita L, Behrens P (2018) Microplastic pollution on Caribbean beaches in the Lesser Antilles. Mar Pollut Bull 133:442–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.060
Claessens M, Meester SD, Landuyt LV, Clerck KD, Janssen CR (2011) Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2199–2204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.06.030
Dalla Fontana G, Mossotti R, Montarsolo A (2020) Assessment of microplastics release from polyester fabrics: The impact of different washing conditions. Environ Pollut 264:113960. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2020.113960
Dehaut A, Hermabessiere L, Duflos G (2019) Current frontiers and recommendations for the study of microplastics in seafood. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 116:346–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.11.011
De-la-Torre GE, Dioses-Salinas DC, Castro JM, Antay R, Fernández NY, Espinoza-Morriberón D, Saldaña-Serrano M (2020) Abundance and distribution of microplastics on sandy beaches of Lima, Peru. Mar Pollut Bull 151:110877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110877
De-la-Torre GE, Dioses-Salinas DC, Pérez-Baca BL, Millones Cumpa LA, Pizarro-Ortega CI, Torres FG, Gonzales KN, Santillán L (2021) Marine macroinvertebrates inhabiting plastic litter in Peru. Mar Pollut Bull 167:112296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112296
De-la-Torre GE, Dioses-Salinas DC, Dobaradaran S, Spitz J, Keshtkar M, Akhbarizadeh R, Abedi D, Tavakolian A (2022a) Physical and chemical degradation of littered personal protective equipment (PPE) under simulated environmental conditions. Mar Pollut 178:113587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113587
De-la-Torre GE, Dioses-Salinas DC, Pizarro-Ortega CI, Fernández Severini MD, Forero-López AD, Mansilla R, Ayala F, Jimenez Castillo LM, Castillo-Paico E, Torres DA, Mendoza-Castilla LM, Meza-Chuquizuta C, Vizcarra JK, Mejía M, Valdivia De La Gala JJ, Sayra Ninaja EA, Siles Calisaya DL, Flores-Miranda WE, Eras Rosillo JL, Espinoza-Morriberón D, Gonzales KN, Torres FG, Rimondino GN, Ben-Haddad M, Dobaradaran S, Aragaw TA, Santillán L (2022b) Binational survey of personal protective equipment (PPE) pollution driven by the COVID-19 pandemic in coastal environments: Abundance, distribution, and analytical characterization. J Hazard Mater 426:128070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.128070
De-la-Torre GE, Pizarro-Ortega CI, Dioses-Salinas DC, Castro Loayza J, Smith Sanchez J, Meza-Chuquizuta C, Espinoza-Morriberón D, Rakib MRJ, Ben-Haddad M, Dobaradaran S (2022c) Are we underestimating floating microplastic pollution? A quantitative analysis of two sampling methodologies. Mar Pollut Bull 178:113592. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2022.113592
De-la-Torre GE, Pizarro-Ortega CI, Dioses-Salinas DC, Rakib MRJ, Ramos W, Pretell V, Ribeiro VV, Castro ÍB, Dobaradaran S (2022) First record of plastiglomerates, pyroplastics, and plasticrusts in South America. Sci Total Environ 833:155179. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.155179
De-la-Torre GE, Dobaradaran S, Urizar Garfias Reyes DF, Dioses-Salinas DC (2023) Micro- and Nanoplastics in Foods, Second Edi. ed, Reference Module in Food Science. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-822521-9.00112-x
Delvalle de Borrero D, Fábrega Duque J, Olmos J, Garcés-Ordóñez O, Amaral SSG do, Vezzone M, Sá Felizardo JP de, Meigikos Anjos R dos (2020) Distribution of Plastic Debris in the Pacific and Caribbean Beaches of Panama. Air, Soil Water Res 13. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622120920268/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/10.1177_1178622120920268-FIG1.JPEG
Deng H, Su L, Zheng Y, Du F, Liu QX, Zheng J, Zhou Z, Shi H (2021) Crack Patterns of Environmental Plastic Fragments. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.1C08100/SUPPL_FILE/ES1C08100_SI_001.PDF
Dioses-Salinas DC, Pizarro-Ortega CI, De-la-Torre GE (2020) A methodological approach of the current literature on microplastic contamination in terrestrial environments: Current knowledge and baseline considerations. Sci Total Environ 730:139164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139164
Dobaradaran S, Schmidt TC, Nabipour I, Khajeahmadi N, Tajbakhsh S, Saeedi R, Javad Mohammadi M, Keshtkar M, Khorsand M, Faraji Ghasemi F (2018) Characterization of plastic debris and association of metals with microplastics in coastline sediment along the Persian Gulf. Waste Manag 78:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2018.06.037
Fajković H, Cukrov N, Frančišković-Bilinski S, Huljek L, Kostanjšek I, Kwokal Ž, Matekalo R, Pikelj K, Cuculić V (2022) Correlation of metals and degraded marine (micro)plastic litter in geologically similar coastal areas with different anthropogenic characteristics. Mar Pollut Bull 183:114041. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2022.114041
Fernández Severini MD, Villagran DM, Buzzi NS, Sartor GC (2019) Microplastics in oysters (Crassostrea gigas) and water at the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Southwestern Atlantic): An emerging issue of global concern. Reg Stud Mar Sci 32:100829. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSMA.2019.100829
Garcés-Ordóñez O, Castillo-Olaya VA, Granados-Briceño AF, Blandón García LM, Espinosa Díaz LF (2019) Marine litter and microplastic pollution on mangrove soils of the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta, Colombian Caribbean. Mar Pollut Bull 145:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.058
Ghaffari S, Bakhtiari AR, Ghasempouri SM, Nasrolahi A (2019) The influence of human activity and morphological characteristics of beaches on plastic debris distribution along the Caspian Sea as a closed water body. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:25712–25724. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-019-05790-Y
Hajiouni S, Mohammadi A, Ramavandi B, Arfaeinia H, De-la-Torre GE, Tekle-Röttering A, Dobaradaran S (2022) Occurrence of microplastics and phthalate esters in urban runoff: A focus on the Persian Gulf coastline. Sci Total Environ 806:150559. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.150559
Hajji S, Ben-Haddad M, Abelouah MR, De-la-Torre GE, Alla AA (2023) Occurrence, characteristics, and removal of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants located on the Moroccan Atlantic: The case of Agadir metropolis. Sci Total Environ 862:160815. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.160815
Hartmann NB, Hüffer T, Thompson RC, Hassellöv M, Verschoor A, Daugaard AE, Rist S, Karlsson T, Brennholt N, Cole M, Herrling MP, Hess MC, Ivleva NP, Lusher AL, Wagner M (2019) Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ Sci Technol 53:1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.8B05297/ASSET/IMAGES/ACS.EST.8B05297.SOCIAL.JPEG_V03
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Thiel M (2013) Distribution and abundance of small plastic debris on beaches in the SE Pacific (Chile): A study supported by a citizen science project. Mar Environ Res 87–88:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.02.015
Joo SH, Liang Y, Kim M, Byun J, Choi H (2021) Microplastics with adsorbed contaminants: Mechanisms and Treatment. Environ Challenges 3:100042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100042
Karlsson TM, Arneborg L, Broström G, Almroth BC, Gipperth L, Hassellöv M (2018) The unaccountability case of plastic pellet pollution. Mar Pollut Bull 129:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.041
Kashfi FS, Ramavandi B, Arfaeinia H, Mohammadi A, Saeedi R, De-la-Torre GE, Dobaradaran S (2022) Occurrence and exposure assessment of microplastics in indoor dusts of buildings with different applications in Bushehr and Shiraz cities, Iran. Sci Total Environ 829:154651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154651
Kühn S, van Franeker JA (2020) Quantitative overview of marine debris ingested by marine megafauna. Mar Pollut Bull 151:110858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110858
Kutralam-Muniasamy G, Pérez-Guevara F, Elizalde-Martínez I, Shruti VC (2020) Review of current trends, advances and analytical challenges for microplastics contamination in Latin America. Environ Pollut 267:115463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115463
Li Y, Lu Z, Zheng H, Wang J, Chen C (2020) Microplastics in surface water and sediments of Chongming Island in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ Sci Eur 32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-0297-7
Lin WH, Kuo J, Lo SL (2021) Effect of light irradiation on heavy metal adsorption onto microplastics. Chemosphere 285:131457. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.131457
Liu Q, Wu H, Chen J, Guo B, Zhao X, Lin H, Li W, Zhao Xin, Lv S, Huang C (2022a) Adsorption mechanism of trace heavy metals on microplastics and simulating their effect on microalgae in river. Environ Res 214:113777. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2022.113777
Liu S, Huang JH, Zhang W, Shi LX, Yi KX, Yu HB, Zhang CY, Li SZ, Li JN (2022b) Microplastics as a vehicle of heavy metals in aquatic environments: A review of adsorption factors, mechanisms, and biological effects. J Environ Manag 302:113995. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.113995
Lozoya JP, Teixeira de Mello F, Carrizo D, Winstein F, Olivera Y, Cedrés F, Pereira M, Fossati M (2016) Plastics and microplastics on recreational beaches in Punta del Este (Uruguay): Unseen critical residents? Environ Pollut 218:931–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.041
Manullang CY (2019) The abundance of Plastic Marine Debris on Beaches in Ambon Bay. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 253:012037. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/253/1/012037
Maynard IFN, Bortoluzzi PC, Nascimento LM, Madi RR, Cavalcanti EB, Lima ÁS, de Jeraldo V, L.S., Marques, M.N., (2021) Analysis of the occurrence of microplastics in beach sand on the Brazilian coast. Sci Total Environ 771:144777. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.144777
Mohammadi A, Malakootian M, Dobaradaran S, Hashemi M, Jaafarzadeh N (2022) Occurrence, seasonal distribution, and ecological risk assessment of microplastics and phthalate esters in leachates of a landfill site located near the marine environment: Bushehr port, Iran as a case. Sci Total Environ 842:156838. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.156838
Monteiro RCP, de Ivar Sul JA, Costa MF (2018) Plastic pollution in islands of the Atlantic Ocean. Environ Pollut 238:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2018.01.096
Moore RC, Loseto L, Noel M, Etemadifar A, Brewster JD, MacPhee S, Bendell L, Ross PS (2020) Microplastics in beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) from the Eastern Beaufort Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110723
Nakashima E, Isobe A, Kako S, Itai T, Takahashi S (2012) Quantification of toxic metals derived from macroplastic litter on Ookushi Beach, Japan. Environ Sci Technol 46:10099–10105. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES301362G/SUPPL_FILE/ES301362G_SI_001.PDF
Olivo E, Vaccaro C, Jimenez-Cárdenas V, Luna-Acosta A, David Gómez-Méndez L (2022) Differential Presence of Microplastics and Mesoplastics in Coral Reef and Mangrove Fishes in Isla Grande, Colombia. Microplastics 1:477–493. https://doi.org/10.3390/MICROPLASTICS1030034
Orona-Návar C, García-Morales R, Loge FJ, Mahlknecht J, Aguilar-Hernández I, Ornelas-Soto N (2022) Microplastics in Latin America and the Caribbean: A review on current status and perspectives. J Environ Manag 309:114698. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2022.114698
Pan K, Wang WX (2012) Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2011.03.013
Pazos RS, Bauer DE, Gómez N (2018) Microplastics integrating the coastal planktonic community in the inner zone of the Río de la Plata estuary (South America). Environ Pollut 243:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.064
Pedrotti ML, Petit S, Elineau A, Bruzaud S, Crebassa JC, Dumontet B, Martí E, Gorsky G, Cózar A (2016) Changes in the Floating Plastic Pollution of the Mediterranean Sea in Relation to the Distance to Land. PLoS One 11:e0161581. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0161581
Purca S, Henostroza A (2017) Presencia de microplásticos en cuatro playas arenosas de Per. Rev Peru Biol 24:101–106. https://doi.org/10.15381/rpb.v24i1.12724
Rakib MRJ (2023) Spatiotemporal trends and characteristics of microplastic contamination in a large river-dominated estuary. Environ Sci Process Impacts. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00014A
Rakib MRJ, Sarker A, Ram K, Uddin MG, Walker TR, Chowdhury T, Uddin J, Khandaker MU, Rahman MM, Idris AM (2023) Microplastic Toxicity in Aquatic Organisms and Aquatic Ecosystems: a Review. Water Air Soil Pollut 234. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11270-023-06062-9
Rodríguez C, Fossatti M, Carrizo D, Sánchez-García L, de Mello F, Weinstein F, Lozoya JP (2020) Mesoplastics and large microplastics along a use gradient on the Uruguay Atlantic coast: Types, sources, fates, and chemical loads. Sci Total Environ 721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137734
Sá B, Pais J, Antunes J, Pequeno J, Pires A, Sobral P (2022) Seasonal Abundance and Distribution Patterns of Microplastics in the Lis River, Portugal. Sustainability 14:2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042255
Sarkar DJ, Sarkar SD, Das BD, Sahoo BK, Das A, Nag SK, Manna RK, Behera BK, Samanta S (2021) Occurrence, fate and removal of microplastics as heavy metal vector in natural wastewater treatment wetland system. Water Res 192:116853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.116853
Singh HB, Bharati, KA (2014) Enumeration of dyes, in: Singh HB, Bharati KA (Eds.), Handbook of Natural Dyes and Pigments. Woodhead Publishing India, pp. 33–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-93-80308-54-8.50006-X
Stockin KA, Pantos O, Betty EL, Pawley MDM, Doake F, Masterton H, Palmer EI, Perrott MR, Nelms SE, Machovsky-Capuska GE (2021) Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analysis identifies microplastics in stranded common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) from New Zealand waters. Mar Pollut Bull 173:113084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113084
Stolte A, Forster S, Gerdts G, Schubert H (2015) Microplastic concentrations in beach sediments along the German Baltic coast. Mar Pollut Bull 99:216–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.022
Su L, Xiong X, Zhang Y, Wu C, Xu X, Sun C, Shi H (2022) Global transportation of plastics and microplastics: A critical review of pathways and influences. Sci Total Environ 831:154884. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.154884
Takdastan A, Niari MH, Babaei A, Dobaradaran S, Jorfi S, Ahmadi M (2021) Occurrence and distribution of microplastic particles and the concentration of Di 2-ethyl hexyl phthalate (DEHP) in microplastics and wastewater in the wastewater treatment plant. J Environ Manag 280:111851. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2020.111851
Torres FG, Dioses-Salinas DC, Pizarro-Ortega CI, De-la-Torre GE (2021) Sorption of chemical contaminants on degradable and non-degradable microplastics: Recent progress and research trends. Sci Total Environ 757:143875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143875
Truchet DM, Forero Lopez AD, Ardusso MG, Rimondino GN, Buzzi NS, Malanca FE, Spetter CV, Fernández-Severini MD (2021) Microplastics in bivalves, water and sediments from a touristic sandy beach of Argentina. Mar Pollut Bull 173:113023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113023
Truchet DM, Ardusso MG, Forero-López AD, Rimondino GN, Buzzi NS, Malanca F, Spetter CV, Fernández-Severini MD (2022) Tracking synthetic microdebris contamination in a highly urbanized estuary through crabs as sentinel species: An ecological trait-based approach. Sci Total Environ 837:155631. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.155631
Tziourrou P, Kordella S, Ardali Y, Papatheodorou G, Karapanagioti HK (2021) Microplastics formation based on degradation characteristics of beached plastic bags. Mar Pollut Bull 169:112470. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2021.112470
Vandermeersch G, Van Cauwenberghe L, Janssen CR, Marques A, Granby K, Fait G, Kotterman MJJ, Diogène J, Bekaert K, Robbens J, Devriese L (2015) A critical view on microplastic quantification in aquatic organisms. Environ Res 143:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.07.016
Wang F, Zhang X, Zhang S, Zhang S, Adams CA, Sun Y (2020) Effects of Co-Contamination of Microplastics and Cd on Plant Growth and Cd Accumulation. Toxics 8:36. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8020036
Wang G, Lu J, Li W, Ning J, Zhou L, Tong Y, Liu Z, Zhou H, Xiayihazi N (2021) Seasonal variation and risk assessment of microplastics in surface water of the Manas River Basin, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111477
Zhao JR, Zheng R, Tang J, Sun HJ, Wang J (2022) A mini-review on building insulation materials from perspective of plastic pollution: Current issues and natural fibres as a possible solution. J Hazard Mater 438:129449. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2022.129449
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is thankful to Universidad San Ignacio de Loyola for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gabriel Enrique De-la-Torre: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Software, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Carlos Ivan Pizarro-Ortega: Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Diana Carolina Dioses-Salinas: Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Victor Vasques Ribeiro: Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Damarisch Fernanda Urizar Garfias Reyes: Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Mohamed Ben-Haddad: Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Md. Refat Jahan Rakib: Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Sina Dobaradaran: Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
De-la-Torre, G.E., Pizarro-Ortega, C.I., Dioses-Salinas, D.C. et al. Micro- and mesoplastic pollution along the coast of Peru. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 71396–71408 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27707-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27707-6