Abstract
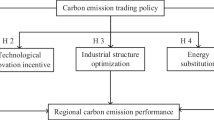
It will contribute to ameliorating the national carbon trading system and further benefit the realization of China’s carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals through in-depth study and summarize the effectiveness of carbon trading policy implementation in pilot areas. Based on the multi-phase difference-in-differences approach and synthetic control method, this paper utilizes China’s provincial panel data from 2006 to 2020 to comprehensively assess the Porter effect (including the economic and green innovation effects) and carbon mitigation effect of carbon trading policy from the overall and local perspectives. Then the robustness test and mechanism analysis are carried out. The findings show that: (1) from the overall effect, the carbon trading policy brings a noticeable carbon mitigation effect and Porter effect, and the intensity of the impact keeps changing over time; (2) there is significant heterogeneity in the local effects of this policy on the eight pilot provinces and cities, with only Chongqing obtaining both the Porter effect and the carbon mitigation effect, while the rest of the regions do not yield the triple dividend of economic, environmental, and green innovation simultaneously; (3) there are much more prominent environment and green innovation effects in the developed regions, while the underdeveloped ones have better economic development and no green innovation effect; (4) the policy can bring environmental and economic dividends through energy structure optimization. However, due to the carbon rebound effect, stimulating green innovation pathways can only boost the economy while carbon emissions increase instead. The research conclusions can provide the decision support and policy direction for policies related to China’s carbon market.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abadie A, Diamond A, Hainmueller J (2010) Synthetic control methods for comparative case studies: estimating the effect of california’s tobacco control program. J Am Stat Assoc 105:493–505. https://doi.org/10.1198/jasa.2009.ap08746
Alexeeva V, Anger N (2015) The globalization of the carbon market: welfare and competitiveness effects of linking emissions trading schemes. Mitig Adapt Strat Glob Change 21:905–930
Behera P, Sethi N (2022) Nexus between environment regulation, FDI, and green technology innovation in OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:52940–52953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19458-7
Cai K, Sun C, Wang H, Song Q, Wang C, Wang P (2022) The potential challenge for the effective GHG emissions mitigation of urban energy consumption: a case study of Macau. Environ Impact Assess Rev 93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106717
Chen, S., Shi, A., Wang, X. (2020) Carbon emission curbing effects and influencing mechanisms of China’s emission trading scheme: the mediating roles of technique effect, composition effect and allocation effect. Journal of Cleaner Production 264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121700
Chen Z, Zhang X, Chen F (2021) Do carbon emission trading schemes stimulate green innovation in enterprises? Evidence from China. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120744
Cui L-B, Fan Y, Zhu L, Bi Q-H (2014) How will the emissions trading scheme save cost for achieving China’s 2020 carbon intensity reduction target? Appl Energy 136:1043–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.05.021
Cui Q, Wei Y-M, Li Y (2016) Exploring the impacts of the EU ETS emission limits on airline performance via the dynamic environmental DEA approach. Appl Energy 183:984–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.09.048
Dong F, Dai Y, Zhang S, Zhang X, Long R (2019) Can a carbon emission trading scheme generate the Porter effect? Evidence from pilot areas in China. Sci Total Environ 653:565–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.395
Dong F, Long R, Yu B, Wang Y, Li J, Wang Y, Dai Y, Yang Q, Chen H (2018) How can China allocate CO2 reduction targets at the provincial level considering both equity and efficiency? Evidence from its Copenhagen Accord pledge. Resour Conserv Recycl 130:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.11.011
Dong F, Li Y, Gao Y, Zhu J, Qin C, Zhang X (2022) Energy transition and carbon neutrality: exploring the non-linear impact of renewable energy development on carbon emission efficiency in developed countries. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.106002
Duan M, Tian Z, Zhao Y, Li M (2017) Interactions and coordination between carbon emissions trading and other direct carbon mitigation policies in China. Energy Res Soc Sci 33:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2017.09.008
Fan F, Zhang X (2021) Transformation effect of resource-based cities based on PSM-DID model: an empirical analysis from China. Environmental Impact Assessment Review 91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106648
Fan Y, Wu J, Xia Y, Liu J-Y (2016) How will a nationwide carbon market affect regional economies and efficiency of CO2 emission reduction in China? China Econ Rev 38:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2015.12.011
Fang G, Tian L, Liu M, Fu M, Sun M (2018) How to optimize the development of carbon trading in China—enlightenment from evolution rules of the EU carbon price. Appl Energy 211:1039–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.12.001
Forbes KF, Zampelli EM (2019) Wind energy, the price of carbon allowances, and CO2 emissions: evidence from Ireland. Energy Policy 133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.07.007
Gao Y, Li M, Xue J, Liu Y (2020) Evaluation of effectiveness of China’s carbon emissions trading scheme in carbon mitigation. Energy Economics 90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104872
Gulbrandsen LH, Stenqvist C (2013) The limited effect of EU emissions trading on corporate climate strategies: comparison of a Swedish and a Norwegian pulp and paper company. Energy Policy 56:516–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.01.014
Hao Y, Deng Y, Lu Z-N, Chen H (2018) Is environmental regulation effective in China? Evidence from city-level panel data. J Clean Prod 188:966–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.003
Hong Y (2021) Basic practices and reflections of developed provinces in taking the lead to high-income stage[J]. Theoretical Inquiry 05:112–120. In China
Hu J, Pan X, Huang Q (2020a) Quantity or quality? The impacts of environmental regulation on firms’ innovation–Quasi-natural experiment based on China’s carbon emissions trading pilot. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120122
Huang W. et al. (2022) Review of recent progress of emission trading policy in China. Journal of Cleaner Production 349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131480
Li G, Masui T (2019) Assessing the impacts of China’s environmental tax using a dynamic computable general equilibrium model. J Clean Prod 208:316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.016
Lin B, Jia Z (2017) The impact of emission trading scheme (ETS) and the choice of coverage industry in ETS: a case study in China. Appl Energy 205:1512–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.098
Lin B, Jia Z (2019) What will China’s carbon emission trading market affect with only electricity sector involvement? A CGE based study. Energy Econ 78:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.11.030
Liu J, Duan Y, Zhong S (2022) Does green innovation suppress carbon emission intensity? New evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21621-z
Liu Z, Guan D, Wei W (2018) Accounting for carbon dioxide emission data in China. Scientia Sinica Terrae 48:878–887 (In China)
Louçã F (2014) The elusive concept of innovation for Schumpeter, Marschak and the early econometricians. Res Policy 43:1442–1449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2014.02.002
Lv M, Bai M (2021) Evaluation of China’s carbon emission trading policy from corporate innovation. Finance Research Letters 39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2020.101565
Porter ME, van der Linde C (1995) Toward a new conception of the environment competitiveness relationship. J Econ Perspect 9(4):97–118
Ren F, Long D (2021) Carbon emission forecasting and scenario analysis in Guangdong province based on optimized fast learning network. Journal of Cleaner Production 317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128408
Segura S, Ferruz L, Gargallo P, Salvador M (2018) Environmental versus economic performance in the EU ETS from the point of view of policy makers: a statistical analysis based on copulas. J Clean Prod 176:1111–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.218
Shan HJ (2008) Re-estimation of capital stock K in China:1952–2006[J]. Quant Econ Tech Econ Res 25(10):17–31 (In China)
Shakil M, Mahmood N, Tasnia M, Munim Z (2019) Do environmental, social and governance performance affect the financial performance of banks? A cross-country study of emerging market banks. Manag. Environ. Qual. 30 (6), 1331e1344. 10.1 108/MEQ-08–2018–0155
Villoria-Sáez P, Tam VWY, Río Merino Md, Viñas Arrebola C, Wang X (2016) Effectiveness of greenhouse-gas emission trading schemes implementation: a review on legislations. J Clean Prod 127:49-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.03.148
Wang C, Shi Y, Zhang L, Zhao X, Chen H (2021) The policy effects and influence mechanism of China’s carbon emissions trading scheme. Air Qual Atmos Health 14:2101–2114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-021-01081-z
Wang H, Chen Z, Wu X, Nie X (2019) Can a carbon trading system promote the transformation of a low-carbon economy under the framework of the porter hypothesis? —Empirical analysis based on the PSM-DID method. Energy Policy 129:930–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.03.007
Wang K, Wei Y-M, Huang Z (2016) Potential gains from carbon emissions trading in China: a DEA based estimation on abatement cost savings. Omega 63:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2015.09.011
Wang K, Zhao B, Fan T, Zhang J (2022) Economic growth targets and carbon emissions: evidence from China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138053
Wei Y, Xu D, Zhang K, Cheng J (2021) Research on the innovation incentive effect and heterogeneity of the market-incentive environmental regulation on mineral resource enterprises. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:58456–58469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14788-4
Xian Y, Wang K, Wei Y-M, Huang Z (2019) Would China’s power industry benefit from nationwide carbon emission permit trading? An optimization model-based ex post analysis on abatement cost savings. Appl Energy 235:978–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.11.011
Xian Y, Wang K, Wei YM, Huang Z (2020) Opportunity and marginal abatement cost savings from China’s pilot carbon emissions permit trading system: simulating evidence from the industrial sectors. J Environ Manage 271, 110975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110975
Xu W, Xu Z, Liu C (2020) Energy structure, ecological environment and economic development–threshold effect and heterogeneity analysis[J]. Stat Inform Forum 35(10):81–89 (In China)
Yang Y, Zhao T, Wang Y, Shi Z (2015) Research on impacts of population-related factors on carbon emissions in Beijing from 1984 to 2012. Environ Impact Assess Rev 55:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2015.06.007
Yi L, Bai N, Yang L, Li Z, Wang F (2020) Evaluation on the effectiveness of China’s pilot carbon market policy. J Clean Prod 246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119039
Zaklan A, Wachsmuth J, Duscha V (2021) The EU ETS to 2030 and beyond: adjusting the cap in light of the 1.5°C target and current energy policies. Climate Policy 21:778–791. https://doi.org/10.1080/14693062.2021.1878999
Zhang H, Duan M, Deng Z (2019a) Have China’s pilot emissions trading schemes promoted carbon emission reductions?– the evidence from industrial sub-sectors at the provincial level. J Clean Prod 234:912–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.247
Zhang K, Xu D, Li S, Zhou N, Xiong J (2019b) Has China’s pilot emissions trading scheme influenced the carbon intensity of output? Int J Environ Res Public Health 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101854
Zhang W, Zhang N, Yu Y (2019c) Carbon mitigation effects and potential cost savings from carbon emissions trading in China’s regional industry. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 141:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.12.014
Zhang W, Li G, Guo F (2022) Does carbon emissions trading promote green technology innovation in China? Applied Energy 315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119012
Zheng Y, Sun X, Zhang C, Wang D, Mao J. Can emission trading scheme improve carbon emission performance? Evidence From China. Frontiers in Energy Research 9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2021.759572
Zhou D, Liang X, Zhou Y, Tang K (2020) Does emission trading boost carbon productivity? Evidence from China's Pilot Emission Trading Scheme. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155522
Zhu J, Fan Y, Deng X, Xue L (2019) Low-carbon innovation induced by emissions trading in China. Nat Commun 10:4088. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12213-6
Zhu X (2022) Have carbon emissions been reduced due to the upgrading of industrial structure? Analysis of the mediating effect based on technological innovation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:54890–54901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19722-w
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Hebei Social Science Fund (HB17GL068) .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Feng Ren: conceptualization, methodology, software, writing—review and editing. Xiaolin Liu: data curation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Baojing Gu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, F., Liu, X. Evaluation of carbon emission reduction effect and porter effect of China’s carbon trading policy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 46527–46546 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25593-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25593-6