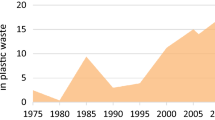
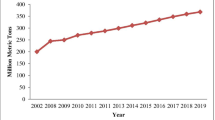
Abstract
Recycling construction waste in urban cities has attracted wide attention in the government department and building industry worldwide owing to numerous benefits in economics, the environment, and society for sustainable development. Most of the research was focused on the scope of first-tier/new first-tier cities. At the same time, less attention has been paid to second-tier cities, which should be further considered because of their significant potential for increasing construction waste. Jinan is one of the pilot cities for construction waste treatment in China. This city has been chosen as the case in this study to explore critical restrictive factors for developing the construction waste recycling industry (CWRI) in second-tier cities with the adoption of combined methods of the DEMATEL-ISM-EWM. It was revealed by the results that (1) the government is the main stakeholder. In addition, the legislation, management system, incentive/support for stakeholders, and technical standards were closely associated with CWRI development in Jinan. Low landfill fees and natural ore tax rates are unique and vital restrictive factors that should receive more attention. (2) Other key restrictive factors that should be given priority were (i) the lack of green design for designers, (ii) poor classification and management of construction waste for constructors on site, (iii) tight operating funds and insufficient publicity for recycling enterprises, and (iv) insufficient research funds for research institutions. Finally, a comparison of the similarities and differences of the restrictive factors on CWRI development between second-tier and first-tier/new first-tier cities was conducted, and a series of reasonable suggestions were provided, considering the perspective of stakeholders. The research will offer a valuable reference for industry practitioners and academics interested in CWRI.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adams MP, Fu TF, Cabrera AG, Morales M, Ideker JH, Isgor OB (2016) Cracking susceptibility of concrete made with coarse recycled concrete aggregates. Constr Build Mater 102:803–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.11.022
Agi MA, Nishant R (2017) Understanding influential factors on implementing green supply chain management practices: an interpretive structural modelling analysis. J Environ Manag 188:351–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.11.081
Ajayi SO, Oyedele LO (2017) Policy imperatives for diverting construction waste from landfill: experts’ recommendations for UK policy expansion. J Clean Prod 147:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.075
Ajayi SO, Oyedele LO, Akinade OO, Bilal M, Alaka HA, Owolabi HA, Kadiri KO (2017) Attributes of design for construction waste minimization: a case study of waste-to-energy project. Renew Sust Energ Rev 73:1333–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.084
Akhtar A, Sarmah AK (2018) Construction and demolition waste generation and properties of recycled aggregate concrete: a global perspective. J Clean Prod 186:263–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.085
Au L, Ahn S, Kim T (2018) System dynamic analysis of impacts of government charges on disposal of construction and demolition waste: a Hong Kong case study. Sustainability 10(4):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041077
Azevedo SG, Sequeira T, Santos M, Mendes L (2019) Biomass-related sustainability: a review of the literature and interpretive structural modeling. Energy 171:1107–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.01.068
Bao Z, Lu W (2020) Developing efficient circularity for construction and demolition waste management in fast emerging economies: Lessons learned from Shenzhen, China. Sci Total Environ 724:138264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138264
Bao Z, Lee WMW, Lu W (2020) Implementing on-site construction waste recycling in Hong Kong: barriers and facilitators. Sci Total Environ 747:141091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141091
Chen S, Liu YY, Lin J, Shi XD, Jiang KJ, Zhao GL (2021) Coordinated reduction of CO2 emissions and environmental impacts with integrated city-level LEAP and LCA method: a case study of Jinan, China. Adv Clim Chang Res 12:848–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accre.2021.08.008
Chen P, Cai B, Wu M, Zhao Y (2022) Obstacle analysis of application of blockchain technology in power data trading based on improved DEMATEL–ISM method under fuzzy environment. Energy Rep 8:4589–4607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.03.043
Fu K, Xia J-b, Zhang X-y, Shen J (2017) System structural analysis of communication networks based on DEMATEL-ISM and entropy. J Cent South Univ 24:1594–1601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3564-z
Gálvez-Martos JL, Styles D, Schoenberger H, Zeschmar-Lahl B (2018) Construction and demolition waste best management practice in Europe. Resour Conserv Recy 136:166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.04.016
Gani A, Bhanot N, Talib F, Asjad M (2022) An integrated DEMATEL-MMDE-ISM approach for analyzing environmental sustainability indicators in MSMEs. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:2035–2051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15194-6
Ghaffar SH, Burman M, Braimah N (2020) Pathways to circular construction: an integrated management of construction and demolition waste for resource recovery. J Clean Prod 244:118710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118710
Guo F, Wang J, Song Y (2022) How to promote sustainable development of construction and demolition waste recycling systems: production subsidies or consumption subsidies? Sustain Prod Consump 32:407–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.05.002
Han R (2020) Research on resource utilization of construction waste in Jinan. ShanDong Jianzhu University, Thesis
He L, Yuan H, Wu H (2022) Collaborative mechanism for promoting the cross-regional management of construction and demolition waste. J Clean Prod 372:133706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133706
Hu S, Ren F, Jia J, Cui C, Guo C, Cui N, Ma L, Si H, Lu T, Liu G, Zhang B, Liu J (2022) Exploring the environmental properties and resource utilization of construction waste in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-23327-8
Huang B, Wang X, Kua H, Geng Y, Bleischwitz R, Ren JZ (2018) Construction and demolition waste management in China through the 3R principle. Resour Conserv Recy 129:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.029
Islam R, Nazifa TH, Yuniarto A, Shanawaz UASM, Salmiati S, Shahid S (2019) An empirical study of construction and demolition waste generation and implication of recycling. Waste Manag 95:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.05.049
Jangre J, Prasad K, Patel D (2022) Analysis of barriers in e-waste management in developing economy: an integrated multiple-criteria decision-making approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:72294–72308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-21363-y
Jin RY, Li B, Zhou TY, Wanatowski D, Piroozfar P (2017) An empirical study of perceptions towards construction and demolition waste recycling and reuse in China. Resour Conserv Recy 126:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.07.034
Kang K, Besklubova S, Dai Y, Zhong RY (2022) Building demolition waste management through smart BIM: a case study in Hong Kong. Waste Manag 143:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.02.027
Kim J (2021) Construction and demolition waste management in Korea: recycled aggregate and its application. Clean Technol Environ 23:2223–2234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02177-x
Kumar A, Dixit G (2018) An analysis of barriers affecting the implementation of e-waste management practices in India: a novel ISM-DEMATEL approach. Sustain Prod Consump 14:36–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2018.01.002
Li Y (2017) Restrictive factors and countermeasures of construction waste recycling research on strategy – based on social network analysis method. Shenzhen University, Thesis
Li JR, Yao Y, Zuo J, Li JG (2020) Key policies to the development of construction and demolition waste recycling industry in China. Waste Manag 108:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.04.016
Liang Y, Wang H, Zhao X (2022) Analysis of factors affecting economic operation of electric vehicle charging station based on DEMATEL-ISM. Comput Ind Eng 163:107818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107818
Liu JK, Teng Y, Wang D, Gong EQ (2020a) System dynamic analysis of construction waste recycling industry chain in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:37260–37277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06739-x
Liu JK, Yi YQ, Wang XT (2020b) Exploring factors influencing construction waste reduction: a structural equation modeling approach. J Clean Prod 276:123185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020b.123185
Liu B, Zhang L, Wang Q (2021a) Demand gap analysis of municipal solid waste landfill in Beijing: based on the municipal solid waste generation. Waste Manag 134:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.08.007
Liu JK, Wu P, Jiang YH, Wang XT (2021b) Explore potential barriers of applying circular economy in construction and demolition waste recycling. J Clean Prod 326:129400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021b.129400
Liu RJ, Tang FC, Wang YH, Zheng SF (2021c) A modified NK algorithm based on BP neural network and DEMATEL for evolution path optimization of urban innovation ecosystem. Compl Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-021-00284-2
Liu JK, Chen YX, Wang XT (2022) Factors driving waste sorting in construction projects in China. J Clean Prod 336:130397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130397
Lockrey S, Nguyen H, Crossin E, Verghese K (2016) Recycling the construction and demolition waste in Vietnam: opportunities and challenges in practice. J Clean Prod 133:757–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.175
Lu SY (2021) The development research on the construction waste resource industry in PPP pattern. Earth Environ Sci 634:012090. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/634/1/012090
Lu WS, Lee WM.W, Bao ZK, Chi B, Webster C (2020) Cross-jurisdictional construction waste material trading: learning from the smart grid. J Clean Prod 277:123352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123352
Luciano A, Cutaia L, Altamura P, Penalvo E (2022) Critical issues hindering a widespread construction and demolition waste (CDW) recycling practice in EU countries and actions to undertake: the stakeholder's perspective. Sustain Chem Pharm 29:100745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100745
Ma L, Zhang L (2020) Evolutionary game analysis of construction waste recycling management in China. Resour Conserv Recy 161:104863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104863
Ma M, Tam VWY, Le KN, Li W (2020) Challenges in current construction and demolition waste recycling: a China study. Waste Manag 118:610–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.09.030
Manoharan S, Kumar Pulimi VS, Kabir G, Ali SM (2022) Contextual relationships among drivers and barriers to circular economy: an integrated ISM and DEMATEL approach. Sustain Oper Comput 3:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susoc.2021.09.003
Mohammed M, Shafiq N, Elmansoury A, Al-Mekhlafi Al-BA, Rached EF, Zawawi NA, Haruna A, Rafindadi AD, Ibrahim MB (2021) Modeling of 3R (reduce, reuse and recycle) for sustainable construction waste reduction: a partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sustainability 13(19):10660. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910660
Mukherjee Basu A, Punjabi S (2020) Participation in solid waste management: lessons from the advanced locality management (ALM) programme of Mumbai. J Urban Manag 9:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jum.2019.11.002
Powell JT, Jain P, Smith J, Townsend TG, Tolaymat TM (2015) Does disposing of construction and demolition debris in unlined landfills impact groundwater quality? Evidence from 91 landfill sites in Florida. Environ Sci Technol 49:9029–9036. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01368
Raj T, Shankar R, Suhaib M (2008) An ISM approach for modelling the enablers of flexible manufacturing system: the case for India. Int J Prod Res 46:6883–6912. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207540701429926
Reich MC (2005) Economic assessment of municipal waste management systems—case studies using a combination of life cycle assessment (LCA) and life cycle costing (LCC). J Clean Prod 13:253–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.02.015
Shakeri H, Khalilzadeh M (2020) Analysis of factors affecting project communications with a hybrid DEMATEL-ISM approach (a case study in Iran). Heliyon 6:e04430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04430
Sharma BK, Chandel MK (2021) Life cycle cost analysis of municipal solid waste management scenarios for Mumbai, India. Waste Manag 124:293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.02.002
Shi QW, Ren H, Ma XR, Xiao YQ (2019) Site selection of construction waste recycling plant. J Clean Prod 227:533–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.252
Shooshtarian S, Caldera S, Maqsood T, Ryley T, Wong PSP, Zaman A (2022) Analysis of factors influencing the creation and stimulation of the Australian market for recycled construction and demolition waste products. Sustain Prod Consump 34:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.09.005
Sukholthaman P, Shirahada K, Sharp A (2017) Toward effective multi-sector partnership: a case of municipal solid waste management service provision in Bangkok, Thailand. Kasetsart J Soc Sci 38:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjss.2017.05.004
Tu M (2021) Research on the management of construction waste in Jinan City. Donghua University, Thesis
Wang R (2016) Research on the key success factors of Xi’an construction waste recycling. Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Thesis
Wang M (2021) Research on the restrictive factors and countermeasures of popularization of prefabricated buildings in Anhui Province. Anhui Jianzhu University, Thesis
Wang H, Pan X, Zhang S, Zhang P (2021a) Simulation analysis of implementation effects of construction and demolition waste disposal policies. Waste Manag 126:684–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.03.056
Wang Y, Shi Y, Zhou J, Zhao J, Maraseni T, Qian G (2021b) Implementation effect of municipal solid waste mandatory sorting policy in Shanghai. J Environ Manage 298:113512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113512
Wang QZ, Jiang TC, Liu L, Zhang SC, Kildunne A, Miao ZH (2022) Building a whole process policy framework promoting construction and demolition waste utilization in China. Waste Manag Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X221126393
Wu HY, Duan HB, Zheng L, Wang JY, Niu YN, Zhang GM (2016) Demolition waste generation and recycling potentials in a rapidly developing flagship megacity of South China: prospective scenarios and implications. Constr Build Mater 113:1007–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.130
Wu H, Zuo J, Zillante G, Wang J, Yuan H (2019a) Construction and demolition waste research: a bibliometric analysis. Archit Sci Rev 62:354–365. https://doi.org/10.1080/00038628.2018.1564646
Wu ZZ, Yu ATW, Poon CS (2019b) An off-site snapshot methodology for estimating building construction waste composition - a case study of Hong Kong. Environ Impact Asses 77:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2019.03.006
Wu ZZ, Yu ATW, Wang H, Wei YG, Huo XS (2019c) Driving factors for construction waste minimization: empirical studies in Hong Kong and Shenzhen. J Green Build 14:155–167. https://doi.org/10.3992/1943-4618.14.4.155
Wu ZZ, Yu ATW, Poon CS (2020) Promoting effective construction and demolition waste management towards sustainable development: a case study of Hong Kong. Sustain Dev 28:1713–1724. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2119
Wu ZZ, Zhang Y, Chen QH, Wang H (2021) Attitude of Chinese public towards municipal solid waste sorting policy: a text mining study. Sci Total Environ 756:142674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142674
Wu ZZ, Yang KJ, Xue H, Zuo J, Li SH (2022) Major barriers to information sharing in reverse logistics of construction and demolition waste. J Clean Prod 350:131331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131331
Xiong TT (2018) Research on the driving factors of the development of construction waste recycling industry in Chongqing. Chongqing University, Thesis
Yeheyis M, Hewage K, Alam MS et al (2012) An overview of construction and demolition waste management in Canada: a lifecycle analysis approach to sustainability. Clean Technol Envir 15:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0481-6
Yu A T W, Wong I, Wu Z, Poon C-S (2021) Strategies for effective waste reduction and management of building construction projects in highly urbanized cities—a case study of Hong Kong. Buildings 11(5):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11050214
Yu S, Awasthi AK, Ma W, Wen M, Di Sarno L, Wen C, Hao JL (2022a) In support of circular economy to evaluate the effects of policies of construction and demolition waste management in three key cities in Yangtze River Delta. Sustain Chem Pharm 26:100625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100625
Yu SW, Awasthi AK, Ma WT, Wen MK, Sarno LD, Wen CH, Hao JL (2022b) In support of circular economy to evaluate the effects of policies of construction and demolition waste management in three key cities in Yangtze River Delta. Sustain Chem Pharm 26:100625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100625
Yuan HP (2013) A SWOT analysis of successful construction waste management. J Clean Prod 39:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.08.016
Yuan HP (2017) Barriers and countermeasures for managing construction and demolition waste: a case of Shenzhen in China. J Clean Prod 157:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.137
Yuan HP, Shen LY (2011) Trend of the research on construction and demolition waste management. Waste Manag 31:670–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.10.030
Zhang RR (2020) Reasearch on the dynamic mechanism of Jinan construction waste recycling industry development. ShanDong Jianzhu University, Thesis
Zhang L, Sun X, Xue H (2019) Identifying critical risks in Sponge City PPP projects using DEMATEL method: a case study of China. J Clean Prod 226:949–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.067
Zhao W, Leeftink RB, Rotter VS (2010) Evaluation of the economic feasibility for the recycling of construction and demolition waste in China—the case of Chongqing. Resour Conserv Recy 54:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.09.003
Zhao W, Ren H, Rotter VS (2011) A system dynamics model for evaluating the alternative of type in construction and demolition waste recycling center – the case of Chongqing, China. Resour Conserv Recy 55:933–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2011.04.011
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the editor and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This study is supported by the Shandong Province Social Science Foundation of China (Grant number 21CGLJ26), Shandong Province Science Foundation of China (Grant number ZR202103070032), Shandong Jianzhu University doctoral foundation project (X19009S), and Shandong Housing and Urban–Rural Development Department (Grant number 2018-R1-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yunhong Wei designed the paper framework and wrote the manuscript. Lin Zhang and Yunhong Wei were responsible for manuscript revision and improvements. Peidong Sang contributed to the conception of the study and helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This is not applicable.
Consent for publication
This is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher'snote
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Zhang, L. & Sang, P. Exploring the restrictive factors for the development of the construction waste recycling industry in a second-tier Chinese city: a case study from Jinan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 46394–46413 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25565-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25565-w