Abstract
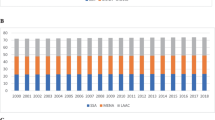
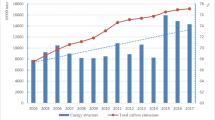
The rising energy demand for information and communication technology (ICT) devices has piqued the interest of scholars and policymakers. Given that ICT devices are ubiquitous, any attempt to mitigate climate change should address the carbon footprint of the ICT sector. The present study examines the direct impact of ICT on the environment and the indirect impact through interaction with energy consumption, financial development, and globalization in SAARC economies from 2000 to 2020. Using econometric approaches robust to cross-sectional dependence, such as the Driscoll-Kraay estimator and the Dumitrescu-Hurlin causality test, the study found that ICT, renewable energy consumption, and globalization significantly reduce CO2 emission, whereas non-renewable energy consumption and financial development significantly increase emission. However, the interaction between financial development and ICT jointly reduces CO2 emissions. Similarly, renewable energy and globalization reduce emissions from increased ICT usage. The study also confirms the validity of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for ICT diffusion. The causality test indicates bidirectional causality between ICT and CO2 emissions. Results suggest that SAARC economies can safely boost ICT and related applications to minimize emissions. They should also use renewable energy and green innovations in telecommunications to reduce their adverse environmental repercussions.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abbas SZ, Kousar A, Razzaq S et al (2018) Energy management in South Asia. Energy Strateg Rev 21:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2018.04.004
Ahmed F, Naeem M, Iqbal M (2017) ICT and renewable energy: a way forward to the next generation telecom base stations. Telecommun Syst 64:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0156-4
Akande A, Cabral P, Casteleyn S (2019) Assessing the gap between technology and the environmental sustainability of European cities. Inf Syst Front 21:581–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-019-09903-3
Allard A, Takman J, Uddin GS, Ahmed A (2018) The N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve: an empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:5848–5861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0907-0
Añón Higón D, Gholami R, Shirazi F (2017) ICT and environmental sustainability: a global perspective. Telemat Informatics 34:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.01.001
Arain H, Han L, Meo MS (2019) Nexus of FDI, population, energy production, and water resources in South Asia: a fresh insight from dynamic common correlated effects (DCCE). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:27128–27137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05903-7
Arshad Z, Robaina M, Botelho A (2020) The role of ICT in energy consumption and environment: an empirical investigation of Asian economies with cluster analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:32913–32932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09229-7
Asongu SA, Nwachukwu JC (2016) The mobile phone in the diffusion of knowledge for institutional quality in sub-Saharan Africa. World Dev 86:133–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2016.05.012
Asongu SA, Le Roux S, Biekpe N (2018) Enhancing ICT for environmental sustainability in sub-Saharan Africa. Technol Forecast Soc Change 127:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.09.022
Avom D, Nkengfack H, Fotio HK, Totouom A (2020) ICT and environmental quality in sub-Saharan Africa: effects and transmission channels. Technol Forecast Soc Change 155:120028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120028
Baltagi BH, Feng Q, Kao C (2012) A Lagrange Multiplier test for cross-sectional dependence in a fixed effects panel data model. J Econom 170:164–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2012.04.004
Batool Z, Raza SMF, Ali S, Abidin SZU (2022) ICT, renewable energy, financial development, and CO2 emissions in developing countries of East and South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18664-7
Batool Z, Raza SMF, Ali S, Abidin SZU (2022) ICT, renewable energy, financial development, and CO2 emissions in developing countries of East and South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:35025–35035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18664-7
Belkhir L, Elmeligi A (2018) Assessing ICT global emissions footprint: trends to 2040 & recommendations. J Clean Prod 177:448–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.239
Ben Mbarek M, Ben Ali N, Feki R (2014) Causality relationship between CO2 emissions, GDP and energy intensity in Tunisia. Environ Dev Sustain 16:1253–1262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9525-x
Bhujabal P, Sethi N, Padhan PC (2021) ICT, foreign direct investment and environmental pollution in major Asia Pacific countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:42649–42669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13619-w
Bieser JCT, Hilty LM (2018) Assessing indirect environmental effects of information and communication technology (ICT): a systematic literature review. Sustain 10:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082662
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange Multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47:239–253. https://doi.org/10.2307/2297111
Bui DT (2020) Transmission channels between financial development and CO2 emissions: a global perspective. Heliyon 6:e05509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05509
Chen X, Gong X, Li D, Zhang J (2019) Can information and communication technology reduce CO2 emission? A quantile regression analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:32977–32992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06380-8
Chien F, Anwar A, Hsu CC et al (2021) The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol Soc 65:101587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101587
Dabbous A (2018) The impact of information and communication technology and financial development on energy consumption: a dynamic heterogeneous panel analysis for MENA countries. Int J Energy Econ Policy 8:70–76
Danish (2019) Effects of information and communication technology and real income on CO2 emissions: the experience of countries along Belt and Road. Telemat Informatics 45:101300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2019.101300
Danish KN, Baloch MA et al (2018) The effect of ICT on CO2 emissions in emerging economies: does the level of income matters? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:22850–22860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2379-2
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49:431–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.02.011
Dong X, Jiang Q, Wang J (2021) Assessing embodied carbon emission and its intensities in the ICT industry: the global case. Front Energy Res 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2021.685021
Driscoll JC, Kraay AC (1998) Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev Econ Stat 80:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1162/003465398557825
Dumitrescu E, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels ☆. Econ Model 29:1450–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2012.02.014
Esquivias MA, Sugiharti L, Rohmawati H, et al (2022) Nexus between Technological innovation, renewable energy, and human capital on the environmental sustainability in emerging Asian economies: a panel quantile regression approach. Energies 15:. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072451
Essandoh OK, Islam M, Kakinaka M (2020) Linking international trade and foreign direct investment to CO2 emissions: any differences between developed and developing countries? Sci Total Environ 712:136437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136437
Fagas G, Gallagher JP, Gammaitoni L, Paul DJ (2017) Energy challenges for ICT. ICT- energy concepts for energy efficiency and sustainability. https://doi.org/10.5772/66678
Farooqi ZU, Makhdum MSA, Yaseen MR (2020) Impact of information and communication technology (ICT) investment on different components of human development in developing countries. Int Rev Manag Bus Res 9:108–129. https://doi.org/10.30543/9-4(2020)-11
Freitag C, Berners-Lee M, Widdicks K et al (2021) The real climate and transformative impact of ICT: a critique of estimates, trends, and regulations. Patterns 2:100340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2021.100340
Haldar A, Sethi N (2022) Environmental effects of information and communication technology – exploring the roles of renewable energy, innovation, trade and financial development. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 153:111754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111754
Haseeb A, Xia E, Saud S et al (2019) Does information and communication technologies improve environmental quality in the era of globalization? An empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:8594–8608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04296-x
Heberle J, Sattarhoff C (2017) A fast algorithm for the computation of HAC covariance matrix estimators. Econometrics 5:. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics5010009
Hussen A (2004) Principles of environmental economics: an integrated economic and ecological approach, 2nd edn. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203507421
Ibrahim KM, Waziri SI (2020) Improving ICT and renewable energy for environmental sustainability in sub-Saharan Africa. J Res Emerg Mark 2:82–90. https://doi.org/10.30585/jrems.v2i3.471
IEA (2017) Digitalization & energy. IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/digitalisation-and-energy
IEA (2019) Energy efficiency 2019. IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/energy-efficiency-2019
IEA (2020) Energy technology perspectives 2020. OECD Publishing, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/d07136f0-en
Joyce PJ, Finnveden G, Håkansson C, Wood R (2019) A multi-impact analysis of changing ICT consumption patterns for Sweden and the EU: indirect rebound effects and evidence of decoupling. J Clean Prod 211:1154–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.207
Khan FN, Sana A, Arif U (2020) Information and communication technology (ICT) and environmental sustainability: a panel data analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:36718–36731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09704-1
Liu X, Latif Z, Danish et al (2021) The corruption-emissions nexus: do information and communication technologies make a difference? Util Policy 72:101244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2021.101244
Lorente DB, Álvarez-Herranz A (2016) Economic growth and energy regulation in the environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16478–16494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6773-3
Malmodin J, Lundén D (2018) The energy and carbon footprint of the global ICT and E & M sectors 2010-2015. Sustain 10:. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093027
Mani M, Wheeler D (1998) In search of pollution havens? Dirty industry in the world economy, 1960 to 1995. J Environ Dev 7:215–247. https://doi.org/10.1177/107049659800700302
Moore GE (1998) Cramming more components onto integrated circuits. Proc IEEE 86:82–85. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.1998.658762
Moyer JD, Hughes BB (2012) ICTs: do they contribute to increased carbon emissions? Technol Forecast Soc Change 79:919–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2011.12.005
Murshed M (2020) Does ICT-trade openness ensure energy and environmental sustainability? Empirical evidence from selected South Asian economies. https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/97944/1/MPRA_paper_97944.pdf
Nchofoung TN, Asongu SA (2022) ICT for sustainable development: global comparative evidence of globalisation thresholds. Telecomm Policy 46:102296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2021.102296
Park Y, Meng F, Baloch MA (2018) The effect of ICT, financial development, growth, and trade openness on CO(2) emissions: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:30708–30719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3108-6
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross-sectional dependence in panels. Empir Econ 60:13–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-020-01875-7
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econom 22:265–312
Poudel BN, Paudel KP, Bhattarai K (2009) Searching for an environmental Kuznets curve in carbon dioxide pollutant in Latin American countries. J Agric Appl Econ 41:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1074070800002522
Pradhan RP, Arvin M, Nair M et al (2017) ICT-finance-growth nexus: empirical evidence from the Next-11 countries. Cuad Econ 40:115–134
Raheem ID, Tiwari AK, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2020) The role of ICT and financial development in CO2 emissions and economic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1912–1922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06590-0
Saidi K, Rahman MM (2021) The link between environmental quality, economic growth, and energy use: new evidence from five OPEC countries. Environ Syst Decis 41:3–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-020-09762-3
Salahuddin M, Gow J (2016) The effects of Internet usage, financial development and trade openness on economic growth in South Africa: a time series analysis. Telemat Informatics 33:1141–1154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2015.11.006
Salahuddin M, Alam K, Ozturk I, Sohag K (2018) The effects of electricity consumption, economic growth, financial development and foreign direct investment on CO2 emissions in Kuwait. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:2002–2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.009
Sharma GD, Rahman MM, Jain M, Chopra R (2021) Nexus between energy consumption, information and communications technology, and economic growth: an enquiry into emerging Asian countries. J Public Aff 21:. https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2172
Shobande OA, Asongu SA (2022) The critical role of education and ICT in Promoting environmental sustainability in Eastern and Southern Africa: a panel VAR approach. Technol Forecast Soc Change 176:121480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121480
Usman M, Hammar N (2021) Dynamic relationship between technological innovations, financial development, renewable energy, and ecological footprint: fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:15519–15536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11640-z
Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020) Assessment of the role of renewable energy consumption and trade policy on environmental degradation using innovation accounting: evidence from the US. Renew Energy 150:266–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.151
Vélez-Henao JA, Font Vivanco D, Hernández-Riveros JA (2019) Technological change and the rebound effect in the STIRPAT model: a critical view. Energy Policy 129:1372–1381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.03.044
Verma A, Giri AK (2020) ICT diffusion, financial development, and economic growth: panel evidence from SAARC countries. J Public Aff 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2557
Weili L, KhanKhan HI, Han L (2022) The impact of information and communication technology, financial development, and energy consumption on carbon dioxide emission: evidence from the Belt and Road countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:27703–27718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18448-5
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69:709–748
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, analysis, and writing – original draft were performed by Anushka Verma. Literature analysis was performed by Arjoo Kumari. The final draft of the manuscript was reviewed and edited by A.K. Giri. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
As the corresponding author, I confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved for submission by all the named authors.
Consent for publication
We give our consent for the article to be published in ESPR. We declare that this manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication to a preprint server prior to submission on ESPR.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, A., Kumari, A. & Giri, A.K. Environmental effects of ICT diffusion, energy consumption, financial development, and globalization: panel evidence from SAARC economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 38349–38362 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25049-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25049-3