Abstract
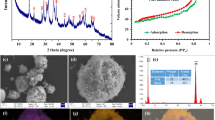
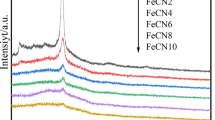
Reactive species serve as a key to remediate the contamination of refractory organic contaminants in advanced oxidation processes. In this study, a novel heterogeneous catalyst, CoMgFe-LDH layered doubled hydroxide (CoMgFe-LDH), was prepared for an efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) to oxidize Rhodamine B (RhB). The characterization results showed that CoMgFe-LDH had a good crystallographic structure. Correspondingly, the CoMgFe-LDH/PMS process exhibited good capacity to remove RhB, which was equivalent to degradation performance as homogeneous Co(II)/PMS process. The RhB oxidation in the CoMgFe-LDH/PMS process was well described with pseudo-first-order kinetic model. Additionally, the oxidation process presented an excellent stability, and only 0.9% leaching rate was detected after six sequential reaction cycles at pH 5.0. The effects of initial pH, CoMgFe-LDH dosage, PMS concentration, RhB concentration, and inorganic anions on the RhB degradation were discussed in detail. Quenching experiments showed that sulfate radicals (SO4•−) acted as the dominant reactive species. Further, the removal of RhB from simulated wastewater was explored. The removal efficiency of RhB (90 μM) could reach 94.3% with 0.8 g/L of catalyst and 1.2 mM of PMS addition at pH 5.0, which indicated the CoMgFe-LDH/PMS process was also effective in degrading RhB in wastewater.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are fully available without restriction.
References
Ahmadi M, Ghanbari F (2019) Organic dye degradation through peroxymonosulfate catalyzed by reusable graphite felt/ferriferrous oxide: mechanism and identification of intermediates. Mater Res Bull 111:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.10.027
Al-Buriahi AK, Al-Gheethi AA, Kumar PS, Mohamed RMSR, Yusof H, Alshalif AF, Khalifa NA (2022) Elimination of rhodamine B from textile wastewater using nanoparticle photocatalysts: a review for sustainable approaches. Chemosphere 287:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132162
Al-Gheethi AA, Azhar QM, Kumar PS, Yusuf AA, Al-Buriahi AK, Mohamed R (2022) Sustainable approaches for removing Rhodamine B dye using agricultural waste adsorbents: a review. Chemosphere 287:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132080
Aljerf L (2018) High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: kinetics and equilibrium study. J Environ Manage 225:120–132
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD (2004) Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ Sci Technol 38(13):3705–3712. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035121o
Ball DL, Edwards JO (1956) The kinetics and mechanism of the decomposition of Caro’s acid. J Am Chem Soc 78:1125–1129. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01587a011
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An Updated Review. Appl Catal B 166:603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Cao JY, Lai LD, Lai B, Yao G, Chen X, Song LP (2019) Degradation of tetracycline by peroxymonosulfate activated with zero-valent iron: performance, intermediates, toxicity and mechanism. Chem Eng J 364:45–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.113
Cao J, Sun S, Li X, Yang Z, Xiong W, Wu Y (2020) Efficient charge transfer in aluminum-cobalt layered double hydroxide derived from Co-ZIF for enhanced catalytic degradation of tetracycline through peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem Eng J 382:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122802
Chen Y, Yan JC, Ouyang D, Lu H, Chen MF (2017) Heterogeneously catalyzed persulfate by CuMgFe layered double oxide for the degradation of phenol. Appl Catal A 528:10–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2017.03.020
Chen HJ, Chen Z, Zhao GX, Zhang ZB, Xu C, Liu YH, Chen J, Zhuang L, Haya T, Wang XK (2018) Enhanced adsorption of U(VI) and 241Am (III) from wastewater using Ca/Al layered double hydroxide@carbon nanotube composites. J Hazard Mater 347:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.12.062
Deng J, Shao YH, Gao NY, Tan CQ, Zhou SQ, Hu XH (2013) CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst of oxone for the degradation of diclofenac in water. J Hazard Mater 262:836–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.09.049
Fan Y, Ji Y, Zheng G, Lu J, Kong D, Yin X, Zhou Q (2017) Degradation of atrazine in heterogeneous Co3O4 activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation process: kinetics, mechanisms, and reaction pathways. Chem Eng J 330:831–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.020
Feizi R, Ahmad M, Jorfi S, Ghanbari F (2019) Sunset yellow degradation by ultrasound/peroxymonosulfate/CuFe2O4: influential factors and degradation processes. Korean J Chem Eng 36(6):886–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-019-0268-0
Gao YS, Zhang Z, Wu JW, Yi XF, Zheng A, Umar A, O’Hare D, Wang Q (2013) Comprehensive investigation of CO2 adsorption on Mg–Al–CO3 LDH-derived mixed metal oxides. J Mater Chem A 1:12782–12790. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA13039H
Ghanbari F, Moradi M (2017) Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants Review. Chem Eng J 310:41–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.064
Gong C, Chen F, Yang Q, Lou K, Yao FB, Wang S, Wang XL (2017) Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by Fe-Co layered doubled hydroxide for efficient catalytic degradation of Rhoadmine B. Chem Eng J 321:222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.117
Guo R, Zhu YL, Cheng XW, Li JJ (2020) Efficient degradation of lomefloxacin by Co-Cu-LDH activating peroxymonosulfate process: optimization, dynamics, degradation pathway and mechanism. J Heat Mater 399:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122966
Hong YC, Zhou HY, Xiong ZK, Liu Y, Yao G, Lai B (2020) Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by CoMgFe-LDO for degradation of carbamazepine: efficiency, mechanism and degradation pathways. Chem Eng J 391:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123604
Hu PD, Long MC (2016) Cobalt-catalyzed sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation: a review on heterogeneous catalysts and applications. Appl Catal B 181:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.024
Huang Y, Sheng B, Wang Z, Liu Q, Yuan R, Xiao D, Liu J (2018) Deciphering the degradation/chlorination mechanisms of maleic acid in the Fe (II)/peroxymonosulfate process: an often overlooked effect of chloride. Water Res 145:453–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.08.055
Huang D, Zhang G, Yi J, Cheng M, Lai C, Xu P (2021) Progress and challenges of metal-organic frameworks-based materials for SR-AOPs applications in water treatment. Chemosphere 263:1–25
Jaafarzadeh N, Ghanbari F, Ahmadi M (2017) Efficient degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by peroxymonosulfate/magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles/ozone: a novel combination of advanced oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 320:436–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.036
Jawad A, Lang J, Liao Z, Khan A, Ifthikar J, Lv Z, Long S, Chen Z (2018) Activation of persulfate by CuOx@Co-LDH: a novel heterogeneous system for contaminant degradation with broad pH window and controlled leaching. Chem Eng J 335:548–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.097
Ji Y, Dong C, Kong D, Lu J, Zhou Q (2015) Heat-activated persulfate oxidation of atrazine: implications for remediation of groundwater contaminated by herbicides. Chem Eng J 263:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.097
Jinisha R, Gandhimathi R, Ramesh ST, Nidheesh PV, Velmathi S (2018) Removal of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution by electro-Fenton process using iron-doped mesoporous silica as a heterogeneous catalyst. Chemosphere 200: 446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.11
Kohantorabi M, Moussavi G, Giannakis S (2021) A review of the innovations in metal-and carbon-based catalysts explored for heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation, with focus on radical vs. non-radical degradation pathways of organic contaminants. Chem Eng J 411:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127957
Li W, Wu P, Zhu Y, Huang Z, Lu Y, Li Y, Dang Z, Zhu N (2015a) Catalytic degradation of bisphenol A by CoMnAl mixed metal oxides catalyzed peroxymonosulfate: performance and mechanism. Chem Eng J 279:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.001
Li W, Wu PX, Yang SS, Zhu YJ, Kang CX, Tran LT, Zeng BL (2015b) 3D hierarchical honeycomb structured MWCNTs coupled with CoMnAl–LDO: fabrication and application for ultrafast catalytic degradation of bisphenol A. Rsc Adv 12:8859–8867. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA15339A
Li XN, Liu JY, Rykov AI, Han HX, Jin CZ, Liu X, Wang JH (2015c) Excellent photo-Fenton catalysts of Fe-Co Prussian blue analogues and their reaction mechanism study. Appl Catal b: Environ 179:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.033
Li XQ, Zhang QH, Ma K, Li HM, Guo Z (2015d) Identification and determination of 34 water- soluble synthetic dyes in foodstuff by high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection-ion trap time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 182:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.019
Li Z, Chen M, Zhang QW, Qu J, Ai ZQ, Li YJ (2017) Mechanochemical synthesis of ultrafine ZnS/Zn-Al layered double hydroxide heterojunction and their photocatalytic activities in dye degradation. Appl Clay Sci 144:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.05.015
Li J, Yan J, Yao G, Zhang Y, Li X, Lai B (2019) Improving the degradation of atrazine in the three-dimensional (3D) electrochemical process using CuFe2O4 as both particle electrode and catalyst for persulfate activation. Chem Eng J 361:1317–1332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.144
Li T, Du XG, Deng JQ, Qi K, Zhang JD, Gao LL, Yue XP (2021) Efficient degradation of Rhodamine B by magnetically recoverable Fe3O4-modified ternary CoFeCu-layered double hydroxides via activating peroxymonosulfate. J Environ Sci 108:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.02.020
Liu BY, Wang Y, Hao X, Wang J, Yang ZL, Yang Q (2022) Green synthesis of stable structure spindle FeCo-LDH through Fe-MOF template for efficient degradation of 2,4-D. J Water Process Eng 46:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102602
Lou XY, Guo YG, Xiao DX, Wang ZH, Lu SY, Liu JS (2013) Rapid dye degradation with reactive oxidants generated by chloride-induced peroxymonosulfate activation. Environ Sci Pollut R 20(9):6317–6323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1678-x
Lou YY, Liu C, Zhao MQ (2022) CoFe-LDO nanoparticles as a novel catalyst of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for histidine removal. Environ Sci Pollut R 29:16517–16528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16853-4
Lu RJ, Xu X, Chang YZ, Zhu Y, Xu SL, Zhang FZ (2012) Improvement of photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles on selectively reconstructed layered double hydroxide. Appl Catal B 111–112:389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.10.022
Lu H, Sui M, Yuan B, Wang J, Lv Y (2019) Efficient degradation of nitrobenzene by Cu-Co-Fe-LDH catalyzed peroxymonosulfate to produce hydroxyl radicals. Chem Eng J 357:140–149
Natarajan TS, Thomas M, Natarajan K, Bajaj HC, Tayade RJ (2011) Study on UV-LED/TiO2 process for degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Chem Eng J 169(1–3):126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.02.066
Othman I, Zain JH, Haija MA, Banat F (2020) Catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate using CeVO4 for phenol degradation: an insight into the reaction pathway. Appl Catal B 266:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118601
Pang Y, Kong L, Chen D, Yuvaraja G, Mehmood S (2020) Facilely synthesized cobalt doped hydroxyapatite as hydroxyl promoted peroxymonosulfate activator for degradation of Rhodamine B. J Hazard Mater 384:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121447
Parida KM, Mohapatra L (2012) Carbonate intercalated Zn/Fe layered double hydroxide: a novel photocatalyst for the enhanced photo degradation of azo dyes. Chem Eng J 179:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.10.070
Poskrebyshev GA, Neta P, Huie RE (2001) Equilibrium constant of the reaction ·OH+ HNO3⇆ H2O+ NO3. in aqueous solution. J Geophys Res: Atmos 106:4995–5004. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900702
Salehi G, Abazari R, Mahjoub AR (2018) Visible-light-induced graphitic-C3N4@nickel-aluminum layered double hydroxide nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity for removal of dyes in water. Inorg Chem 57:8681–8691. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01636
Shao P, Tian J, Yang F, Duan X, Gao S, Shi W, Wang S (2018) Identification and regulation of active sites on nanodiamonds: establishing a highly efficient catalytic system for oxidation of organic contaminants. Adv Funct Mater 28(13):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201705295
Sideris PJ, Nielsen UG, Gan Z, Grey CP (2008) Mg/Al ordering in layered double hydroxides revealed by multinuclear NMR spectroscopy. Science 321:113–117. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1157581
Wang J, Wang S (2018) Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem Eng J 334:1502–1517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.059
Wang YX, Sun HQ, MingAng H, Tadé MO, Wang SB (2015) 3D-hierarchically structured MnO2 for catalytic oxidation of phenol solutions by activation of peroxymonosulfate: Structure dependence and mechanism. Appl Catal b: Environ 164:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.09.004
Wang C, Cao Y, Wang H (2019) Copper-based catalyst from waste printed circuit boards for effective Fenton-like discoloration of Rhodamine B at neutral pH. Chemosphere 230:278–285
Yan JC, Chen Y, Qian LB, Gao WG, Ouyang D, Chen MF (2017) Heterogeneously catalyzed persulfate with a CuMgFe layered double hydroxide for the degradation of ethylbenzene. J Hazard Mater 338:372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.007
Yan JF, Li J, Peng JL, Zhang H, Zhang YH, Lai B (2019) Efficient degradation of sulfamethoxazole by the CuO@Al2O3 (EPC) coupled PMS system: optimization, degradation pathways and toxicity evaluation. Chem Eng J 359:1097–1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.074
Yang H, Zhuang S, Hu Q, Hu L, Yang L, Au C, Yi B (2018) Competitive reactions of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals with sulfonamides in Fe2+/S2O82− system: reaction kinetics, degradation mechanism and acute toxicity. Chem Eng J 339:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.106
Yang WN, Li J, Wang MY, Sun XF, Liu Y, Yang J (2020) A colorimetric strategy for ascorbic acid sensing based on the peroxidase-like activity of core-shell Fe3O4/CoFe-LDH hybrid. Colloids Surf B 188:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110742
Zeng H, Deng L, Yang K, Huang B, Zhang H, Shi Z, Zhang W (2021) Degradation of sulfamethoxazole using peroxymonosulfate activated by self-sacrificed synthesized CoAl-LDH@CoFe-PBA nanosheet: Reactive oxygen species generation routes at acidic and alkaline pH. Sep Purif Technol 268:1–13
Zeng HX, Zhang WQ, Deng L, Luo JM, Zhou SQ, Liu X, Pei Y, Shi Z, Crittenden J (2018) Degradation of dyes by peroxymonosulfate activated by ternary CoFeNi-layered double hydroxide: catalytic performance, mechanism and kinetic modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci, 515:92–100
Zhang LH, Li F, Evans DG, Duan X (2010) Evolution of structure and performance of Cu-based layered double hydroxides. J Mater Sci 45:3741–3751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4423-6
Zhang W, Su Y, Zhang X, Yang Y, Guo X (2016) Facile synthesis of porous NiCo2O4 nanoflakes as magnetic recoverable catalysts towards the efficient degradation of RhB. RSC 6(69):64626–64633. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA12706A
Zhang HJ, Liu XT, Ma J, Lin CY, Qi CD, Li XW, Zhou Z, Guo XF (2018) Activation of peroxymonosulfate using drinking water treatment residuals for the degradation of atrazine. J Hazard 344:1220–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.038
Zhang Q, He D, Li X, Feng W, Lyu C, Zhang Y (2020) Mechanism and performance of singlet oxygen dominated peroxymonosulfate activation on CoOOH nanoparticles for 2, 4-dichlorophenol degradation in water. J Hazard Mater 384:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121350
Zhang X, Guo Y, Shi S, Liu E, Li T, Wei S, Zhao Z (2021) Efficient and stable iron-copper montmorillonite heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for removing Rhodamine B. Chem Phys Lett 776:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138673
Zhang L, Yang X, Zhou R, Lin S, Zhou L (2022) High-efficiency carbamazepine degradation using a Ni/Co-LDH as the peroxymonosulfate activator: performance, mechanism and degradation pathway. Appl Surf Sci 574:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151580
Zhao JW, Chen J, Xu SM, Shao MF, Zhang Q, Wei F, Ma J, Wei M, Evans DG, Duan X (2014) Hierarchical NiMn layered double hydroxide/carbon nanotubes architecture with superb energy density for flexible supercapacitors. Adv Funct Mater 24:2938–2946. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201303638
Zheng H, Zhou Y, Wang D, Zhu M, Sun X, Jiang S, Zhang L (2022) Surface-functionalized PVDF membranes by facile synthetic Cu-MOF-74 for enhanced contaminant degradation and antifouling performance. Colloids Surf A 651:1–12
Zhou HY, Peng JL, Li JY, You JJ, Lai LD, Liu R (2021) Metal-free black-red phosphorus as an efficient heterogeneous reductant to boost Fe3+/Fe2+ cycle for peroxymonosulfate activation. Water Res 188:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116529
Zou YD, Wang XX, Ai YJ, Liu YH, Li JX, Ji YF, Wang XK (2016) Coagulation behavior of graphene oxide on nanocrystallined Mg/AI layered double hydroxides: batch experimental and theoretical calculation study. Environ Sci Technol 50:3658–3667. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00255
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21307057), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (LBH-Z13062), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3072020CF0209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by YH Liu, DL Chen, and WT Guan. The manuscript was written by YH Liu and CL Wang. GF Liu supervised this research and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Liu, Y., Chen, D. et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co-Mg-Fe layered doubled hydroxide for efficient degradation of Rhodamine B. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 37634–37645 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24983-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24983-6