Abstract
The rapid growth of population and industrialization have intensified the problem of water pollution globally. To meet the challenge of industrialization, the use of synthetic dyes in the textile industry, dyeing and printing industry, tannery and paint industry, paper and pulp industry, cosmetic and food industry, dye manufacturing industry, and pharmaceutical industry has increased exponentially. Among these industries, the textile industry is prominent for the water pollution due to the hefty consumption of water and discharge of coloring materials in the effluent. The discharge of this effluent into the aquatic reservoir affects its biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total dissolved solids (TDS), total suspended solids (TSS), and pH. The release of the effluents without any remedial treatment will generate a gigantic peril to the aquatic ecosystem and human health. The ecological-friendly treatment of the dye-containing wastewater to minimize the detrimental effect on human health and the environment is the need of the hour. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the catastrophic effects of textile dyes on human health and the environment. This review provides a comprehensive insight into the dyes and chemicals used in the textile industry, focusing on the typical treatment processes for their removal from industrial wastewaters, including chemical, biological, physical, and hybrid techniques.

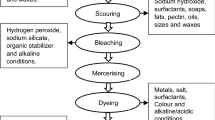
Copyright 2020, Elsevier

Copyright 2020, Elsevier; and the experimental setup for wastewater treatment produced in acrylic fiber manufacturing industry by ozonation process (B). Reproduced with permission (Zheng et al. 2015). Copyright 2015, Elsevier

Copyright 2020, Elsevier and schematic view of pressure-driven membrane processes (crossflow mode) for treating wastewater (B). Reproduced with permission (Behroozi and Ataabadi 2021). Copyright 2021, Elsevier

Copyright 2020, Elsevier


Copyright 2022, Elsevier and process flow chart of advanced pre-treatment of biogas slurry (B). Reproduced with permission (Alengebawy et al. 2021). Copyright 20,201 Elsevier
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data presented herein are constant with the published literature.
References
Aassila H, Aboussabiq FE, Dari K et al (2018) Biodecolorization of methyl orange by bacteria isolated from textile industrial wastes : optimization of cultural and nutritional parameters. J Mater Environ Sci 9:1787–2779
Achilli A, Marchand EA, Childress AE (2011) A performance evaluation of three membrane bioreactor systems: aerobic, anaerobic, and attached-growth. Water Sci Technol 63:2999–3005. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2011.559
Adams CD, Gorg S (2002) Effect of pH and Gas-Phase Ozone Concentration on the Decolorization of Common Textile Dyes. J Environ Eng 128:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2002)128:3(293)
Agbe H, Raza N, Dodoo-Arhin D et al (2018) H2O2 rejuvenation-mediated synthesis of stable mixed-morphology Ag3PO4 photocatalysts. Heliyon 4:e00599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00599
Ahamad A, Raju NJ, Madhav S, Khan AH (2020) Trace elements contamination in groundwater and associated human health risk in the industrial region of southern Sonbhadra, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ Geochemistry Heal 4210(42):3373–3391. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10653-020-00582-7
Ahmad A, Mohd-Setapar SH, Chuong CS et al (2015a) Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv 5:30801–30818. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA16959J
Ahmad A, Hamidah Mohd-Setapar S, Sing Chuong C et al (2015b) Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv 5:30801–30818. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA16959J
Akpor OB, Muchie M (2010) Remediation of heavy metals in drinking water and wastewater treatment systems: Processes and applications. Int J Phys Sci 5:1807–1817. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJPS.9000482
Al-Amrani WA, Hanafiah MAKM, Mohammed A-HA (2022) A comprehensive review of anionic azo dyes adsorption on surface-functionalised silicas. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Alengebawy A, Jin K, Ran Y et al (2021) Advanced pre-treatment of stripped biogas slurry by polyaluminum chloride coagulation and biochar adsorption coupled with ceramic membrane filtration. Chemosphere 267:129197. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2020.129197
Alexandratos SD (2008) Ion-Exchange Resins: A Retrospective from Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:388–398. https://doi.org/10.1021/IE801242V
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J Chem 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Alpat SK, Özbayrak Ö, Alpat Ş, Akçay H (2008) The adsorption kinetics and removal of cationic dye, Toluidine Blue O, from aqueous solution with Turkish zeolite. J Hazard Mater 151:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2007.05.071
Al-Sabti K (2000) Chlorotriazine Reactive Azo Red 120 Textile Dye Induces Micronuclei in Fish. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1006/EESA.2000.1931
Alves de Lima RO, Bazo AP, Salvadori DMF et al (2007) Mutagenic and carcinogenic potential of a textile azo dye processing plant effluent that impacts a drinking water source. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 626:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2006.08.002
Amini M, Arami M, Mahmoodi NM, Akbari A (2011) Dye removal from colored textile wastewater using acrylic grafted nanomembrane. Desalination 267:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2010.09.014
An Y, Jiang L, Cao J et al (2007) Sudan I induces genotoxic effects and oxidative DNA damage in HepG2 cells. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 627:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2006.11.004
Anjaneyulu Y, Sreedhara Chary N, Samuel Suman Raj D (2005) Decolourization of Industrial Effluents – Available Methods and Emerging Technologies – A Review. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol 44(4):245–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11157-005-1246-Z
Apostol LC, Pereira L, Pereira R et al (2012) Biological decolorization of xanthene dyes by anaerobic granular biomass. Biodegradation 23:725–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9548-7
Aqeel K, Mubarak HA, Amoako-Attah J, et al (2020) Electrochemical removal of brilliant green dye from wastewater. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 888. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/888/1/012036
Argurio P, Fontananova E, Molinari R, Drioli E (2018) Photocatalytic membranes in photocatalytic membrane reactors. Processes 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6090162
Asano T, Levine AD (1996) Wastewater reclamation, recycling and reuse: Past, present, and future. Water Sci Technol 33:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1223(96)00401-5
Asghar A, Raman AAA, Daud WMAW (2015) Advanced oxidation processes for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for textile wastewater treatment: a review. J Clean Prod 87:826–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2014.09.010
Avvannavar SM, Mani M, Kumar N (2008) An integrated assessment of the suitability of domestic solar still as a viable safe water technology for India. Environ Eng Manag J 7(6):667–685
Ayadi I, Monteiro SM, Regaya I et al (2015) Biochemical and histological changes in the liver and gills of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus exposed to Red 195 dye. RSC Adv 5:87168–87178. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA13127H
Ayele A, Getachew D, Kamaraj M, Suresh A (2021) Phycoremediation of Synthetic Dyes: An Effective and Eco-Friendly Algal Technology for the Dye Abatement. J Chem 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9923643
Azbar N, Yonar T, Kestioglu K (2004) Comparison of various advanced oxidation processes and chemical treatment methods for COD and color removal from a polyester and acetate fiber dyeing effluent. Chemosphere 55:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.046
Babu BR, Parande AK, Raghu S, Kumar TP (2007) An overview wastes produced during cotton textile processing and effluent treatment methods. J Cotton Sci 1:110–122
Bae JS, Freeman HS (2007) Aquatic toxicity evaluation of new direct dyes to the Daphnia magna. Dye Pigment 73:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DYEPIG.2005.10.015
Banat IM, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) Microbial decolorization of textile-dyecontaining effluents: A review. Bioresour Technol 58:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00113-7
Bayraktaroğlu M, Husein İ, Aktaş Uygun D, Uygun M (2020) Lectin-Modified Cryogels for Laccase Immobilization: a Decolorization Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 2312(231):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11270-020-4395-3
Bazin I, Ibn Hadj Hassine A, Haj Hamouda Y et al (2012) Estrogenic and anti-estrogenic activity of 23 commercial textile dyes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 85:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2012.08.003
Bazrafshan E, Zakeri HR, Vieira MGA, et al (2022) Slaughterhouse Wastewater Treatment by Integrated Chemical Coagulation and Electro-Fenton Processes. Sustainability 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811407
Behroozi AH, Ataabadi MR (2021) Improvement in microfiltration process of oily wastewater: A comprehensive review over two decades. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104981. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2020.104981
Benkhaya S, M’rabet S, El Harfi A (2020) A review on classifications, recent synthesis and applications of textile dyes. Inorg Chem Commun 115:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2020.107891
Berkessa YW, Yan B, Li T et al (2020) Treatment of anthraquinone dye textile wastewater using anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor: Performance and microbial dynamics. Chemosphere 238:124539. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2019.124539
Bhatia D, Sharma NR, Singh J, Kanwar RS (2017) Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: A review. 47:1836–1876. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1393263
Bilgiç H, Gökçay CF, Hasirci N (1997) Color removal by white-rot fungi. Stud Environ Sci 66:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-1116(97)80045-3
Birhanli E, Yesilada O (2006) Increased production of laccase by pellets of Funalia trogii ATCC 200800 and Trametes versicolor ATCC 200801 in repeated-batch mode. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:1286–1293. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENZMICTEC.2006.03.015
Blánquez P, Casas N, Font X et al (2004) Mechanism of textile metal dye biotransformation by Trametes versicolor. Water Res 38:2166–2172. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2004.01.019
Blümel S, Stolz A (2003) Cloning and characterization of the gene coding for the aerobic azoreductase from Pigmentiphaga kullae K24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 622(62):186–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00253-003-1316-5
Blümel S, Knackmuss H-J, Stolz A (2002) Molecular Cloning and Characterization of the Gene Coding for the Aerobic Azoreductase from Xenophilus azovorans KF46F. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3948–3955. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.8.3948-3955.2002
Boye B, Dieng MM, Brillas E (2002) Degradation of herbicide 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid by advanced electrochemical oxidation methods. Environ Sci Technol 36:3030–3035. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0103391
Bulla LMC, Polonio JC, de Portela-Castro ALB et al (2017) Activity of the endophytic fungi Phlebia sp. and Paecilomyces formosus in decolourisation and the reduction of reactive dyes’ cytotoxicity in fish erythrocytes. Environ Monit Assess1892 189:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-017-5790-0
Burdett BC (1982) The Colour Index: The Past, Present and Future of Colorant Classification. J Soc Dye Colour 98:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1478-4408.1982.TB03625.X
Buthelezi SP, Olaniran AO, Pillay B (2012) Textile Dye Removal from Wastewater Effluents Using Bioflocculants Produced by Indigenous Bacterial Isolates. Molecules 17:14260–14274. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES171214260
Cammarota MC Jr, Sant’Anna GLS (2008) Decolorization of kraft bleach plant E1 stage effluent in a fungal bioreactor. Environ Technol 13:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593339209385129
Carmen Z, Daniel S (2012) Textile organic dyes – characteristics, polluting effects and separation/elimination procedures from industrial effluents – a critical overview. In: Puzyn T, Mostrag-Szlichtyng A (eds) Organic Pollutants Ten Years After the Stockholm Convention - Environmental and Analytical Update. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/32373
Catherine Tee PN, Janice Wong YT, Sherry JP, Bols NC (2011) Effect of acid blue 80, an anthracenedione dye, on rainbow trout liver, gill and gut cells in vitro. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1874–1878. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2011.07.026
Cerniglia CE, Zhuo Z, Manning BW et al (1986) Mutagenic activation of the benzidine-based dye Direct Black 38 by human intestinal microflora. Mutat Res Lett 175:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-7992(86)90138-7
Chairungsri W, Subkomkaew A, Kijjanapanich P, Chimupala Y (2022) Direct dye wastewater photocatalysis using immobilized titanium dioxide on fixed substrate. Chemosphere 286:131762. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.131762
Chang I-S, Le Clech P, Jefferson B, Judd S (2002) Membrane Fouling in Membrane Bioreactors for Wastewater Treatment. J Environ Eng 128:1018–1029. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9372(2002)128:11(1018)
Chanyaland S, Kumar P (2017) Decolorization of textile dye by laccase from newl isolated endophytic fungus Daldinia sp. KAVAKA 48 (1):33–41. http://www.fungiindia.co.in/images/kavaka/48/6.pdf
Charumathi D, Das N (2012) Packed bed column studies for the removal of synthetic dyes from textile wastewater using immobilised dead C. tropicalis. Desalination 285:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2011.09.023
Chen KC, Wu JY, Liou DJ, Hwang SCJ (2003) Decolorization of the textile dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. J Biotechnol 101:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00303-6
Chen HL, Burns LD (2016) Environmental Analysis of Textile Products: 24:248–261. https://doi.org/10.1177/0887302X06293065
Chequer FMD, Angeli JPF, Ferraz ERA et al (2009) The azo dyes Disperse Red 1 and Disperse Orange 1 increase the micronuclei frequencies in human lymphocytes and in HepG2 cells. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 676:83–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2009.04.004
Chivukula M, Renganathan V (1995) Phenolic Azo Dye Oxidation by Laccase from Pyricularia oryzae. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4374–4377. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.61.12.4374-4377.1995
Chou PH, Matsui S, Misaki K, Matsuda T (2006) Isolation and Identification of Xenobiotic Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligands in Dyeing Wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 41:652–657. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES061500G
Chowdhary P, Bharagava RN, Mishra S, Khan N (2020) Role of Industries in Water Scarcity and Its Adverse Effects on Environment and Human Health. Environ Concerns Sustain Dev 235–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-5889-0_12
Chung KT, Chen SC, Claxton LD (2006) Review of the Salmonella typhimurium mutagenicity of benzidine, benzidine analogues, and benzidine-based dyes. Mutat Res Mutat Res 612:58–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRREV.2005.08.001
Colin Garner R, Nutman CA (1977) Testing of some azo dyes and their reduction products for mutagenicity using Salmonella typhimurium TA 1538. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen 44:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/0027-5107(77)90110-5
Cosenza A, Chaiprapat SS, Mannina G (2020) Biofouling management in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Curr Dev Biotechnol Bioeng Adv Membr Sep Process Sustain Water Wastewater Manag - Anaerob Membr Bioreact Process Technol 79–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819852-0.00004-X
Costa AFS, Albuquerque CDC, Salgueiro AA, Sarubbo LA (2018) Color removal from industrial dyeing and laundry effluent by microbial consortium and coagulant agents. Process Saf Environ Prot 118:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSEP.2018.03.001
Daneshvar N, Ashassi-Sorkhabi H, Tizpar A (2003) Decolorization of orange II by electrocoagulation method. Sep Purif Technol 31:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5866(02)00178-8
Daneshvar N, Khataee AR, Rasoulifard MH, Pourhassan M (2007) Biodegradation of dye solution containing Malachite Green: Optimization of effective parameters using Taguchi method. J Hazard Mater 143:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2006.09.016
Danish Khan M, Abdulateif H, Ismail IM, et al (2015) Bioelectricity generation and bioremediation of an azo-dye in a microbial fuel cell coupled activated sludge process. PLoS One 10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138448
Dastjerdi R, Montazer M (2010) A review on the application of inorganic nano-structured materials in the modification of textiles: Focus on anti-microbial properties. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 79:5–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.03.029
De Aragão UG, Freeman H, Warren SH et al (2005a) Mutagenicity evaluation of the commercial product CI Disperse Blue 291 using different protocols of the Salmonella assay. Food Chem Toxicol 43:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCT.2004.08.011
De Aragão UG, Freeman HS, Warren SH et al (2005b) The contribution of azo dyes to the mutagenic activity of the Cristais River. Chemosphere 60:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2004.11.100
Deng D, Lamssali M, Aryal N et al (2020) Textiles wastewater treatment technology: A review. Water Environ Res 92:1805–1810. https://doi.org/10.1002/WER.1437
Dey S, Islam A (2015) A review on textile wastewater characterization in Bangladesh. Resour Environ 5:15–44. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.re.20150501.03
Dhamotharan R, Murugesan S, Sridharan MC, Yoganandam M (2009) Biological decolorization and removal of metal from dye industry effluent by microalgae. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 6:111–120
Dhananjeyan MR, Mielczarski E, Thampi KR et al (2001) Photodynamics and surface characterization of TiO2 and Fe2O3 photocatalysts immobilized on modified polyethylene films. J Phys Chem B 105:12046–12055. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp011339q
Ding F, Li N, Han B et al (2009) The binding of C.I. Acid Red 2 to human serum albumin: Determination of binding mechanism and binding site using fluorescence spectroscopy. Dye Pigment 83:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DYEPIG.2009.05.003
Ding F, Zhang L, Diao JX et al (2012) Human serum albumin stability and toxicity of anthraquinone dye alizarin complexone: An albumin–dye model. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2012.01.009
Ding J, Wu H, Wu P (2020) Preparation of highly permeable loose nanofiltration membranes using sulfonated polyethylenimine for effective dye/salt fractionation. Chem Eng J 396:125199. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2020.125199
Dixit S, Yadav A, Dwivedi PD, Das M (2015) Toxic hazards of leather industry and technologies to combat threat: A review. J Clean Prod 87:39–49
Dolez PI, Benaddi H (2018) Toxicity testing of textiles. Adv Charact Test Text 151–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100453-1.00008-8
Dos Santos AB, Cervantes FJ, Van Lier JB (2003) Azo dye reduction by thermophilic anaerobic granular sludge, and the impact of the redox mediator anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) on the reductive biochemical transformation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2004 641(64):62–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00253-003-1428-Y
Drouiche N, Aoudj S, Hecini M et al (2009) Study on the treatment of photovoltaic wastewater using electrocoagulation: Fluoride removal with aluminium electrodes—Characteristics of products. J Hazard Mater 169:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2009.03.073
Elisangela F, Andrea Z, Fabio DG et al (2009) Biodegradation of textile azo dyes by a facultative Staphylococcus arlettae strain VN-11 using a sequential microaerophilic/aerobic process. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 63:280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2008.10.003
El-Sheekh MM, Gharieb MM, Abou-El-Souod GW (2009) Biodegradation of dyes by some green algae and cyanobacteria. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 63:699–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2009.04.010
Faraco V, Pezzella C, Miele A et al (2008) Bio-remediation of colored industrial wastewaters by the white-rot fungi Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pleurotus ostreatus and their enzymes. Biodegrad 202(20):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10532-008-9214-2
Ferraz ERA, Grando MD, Oliveira DP (2011a) The azo dye Disperse Orange 1 induces DNA damage and cytotoxic effects but does not cause ecotoxic effects in Daphnia similis and Vibrio fischeri. J Hazard Mater 192:628–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2011.05.063
Ferraz ERA, Umbuzeiro GA, de-Almeida G et al (2011) Differential toxicity of Disperse Red 1 and Disperse Red 13 in the Ames test, HepG2 cytotoxicity assay, and Daphnia acute toxicity test. Environ Toxicol 26:489–497. https://doi.org/10.1002/TOX.20576
Foroutan R, Mohammadi R, Farjadfard S et al (2019) Eggshell nano-particle potential for methyl violet and mercury ion removal: Surface study and field application. Adv Powder Technol 30:2188–2199. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APT.2019.06.034
Fu Y, Viraraghavan T (2002) Removal of Congo Red from an aqueous solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Adv Environ Res 7:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(01)00123-X
Gahlout M, Gupte S, Gupte A (2012) Optimization of culture condition for enhanced decolorization and degradation of azo dye reactive violet 1 with concomitant production of ligninolytic enzymes by Ganoderma cupreum AG-1. 3 Biotech 32(3):143–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-012-0079-Z
Gallagher KA, Healy MG, Allen SJ (1997) Biosorption of synthetic dye and metal ions from aqueous effluents using fungal biomass. Stud Environ Sci 66:27–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-1116(97)80033-7
Gerundo N, Alderman DJ, Clifton-Hadley RS, Feist SW (1991) Pathological effects of repeated doses of malachite green: a preliminary study. J Fish Dis 14:521–532. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1365-2761.1991.TB00607.X
Ghaffari SB, Sarrafzadeh MH, Fakhroueian Z et al (2017) Functionalization of ZnO nanoparticles by 3-mercaptopropionic acid for aqueous curcumin delivery: Synthesis, characterization, and anticancer assessment. Mater Sci Eng C 79:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.065
Giardina P, Faraco V, Pezzella C et al (2009) Laccases: a never-ending story. Cell Mol Life Sci 673(67):369–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00018-009-0169-1
Gogate PR, Pandit AB (2004) A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment I: oxidation technologies at ambient conditions. Adv Environ Res 8:501–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(03)00032-7
Gomaa OM, Linz JE, Reddy CA (2008) Decolorization of Victoria blue by the white rot fungus, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2410(24):2349–2356. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11274-008-9750-2
Gopi K, Jayaprakashvel M (2017) Dye degrading potential of laccase and tannase from endophytic fungi. Res J Pharm Technol 10:4108–4110. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2017.00746.6
Gopinath A, Pisharody L, Popat A, Nidheesh PV (2022) Supported catalysts for heterogeneous electro-Fenton processes: Recent trends and future directions. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 26:100981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2022.100981
Gunawan FM, Mangindaan D, Khoiruddin K, Wenten IG (2019) Nanofiltration membrane cross-linked by m-phenylenediamine for dye removal from textile wastewater. Polym Adv Technol 30:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1002/PAT.4473
Güngördü A, Birhanli A, Ozmen M (2012) Biochemical response to exposure to six textile dyes in early developmental stages of Xenopus laevis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 201(20):452–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-012-1063-1
Gupta VK, Suhas (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal – A review. J Environ Manage 90:2313–2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2008.11.017
Güyer GT, Nadeem K, Dizge N (2016) Recycling of pad-batch washing textile wastewater through advanced oxidation processes and its reusability assessment for Turkish textile industry. J Clean Prod 139:488–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2016.08.009
Hai FI, Yamamoto K, Fukushi K (2007) Hybrid treatment systems for dye wastewater. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 37:315–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380601174723
Hai FI, Yamamoto K, Nakajima F, Fukushi K (2009) Factors governing performance of continuous fungal reactor during non-sterile operation – The case of a membrane bioreactor treating textile wastewater. Chemosphere 74:810–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2008.10.025
HajKacem S, Galai S, Hernández Fernandez FJ et al (2019) Bioreactor Membranes for Laccase Immobilization Optimized by Ionic Liquids and Cross-Linking Agents. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 1901(190):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12010-019-03085-Z
Hamdy A, Mostafa MK, Nasr M (2018) Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for methylene blue removal from aqueous solutions and textile wastewater treatment, with cost estimation. Water Sci Technol 78:367–378. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2018.306
Hamedi H, Ehteshami M, Mirbagheri SA et al (2019) Current Status and Future Prospects of Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) and Fouling Phenomena: A Systematic Review. Can J Chem Eng 97:32–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/CJCE.23345
Harb M, Hong PY (2017) Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Effluent Reuse: A Review of Microbial Safety Concerns. Ferment 3(3):1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/FERMENTATION3030039
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2017a) Testing the advanced oxidation processes on the degradation of Direct Blue 86 dye in wastewater. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2016.09.006
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2017b) Advanced oxidation processes of Mordant Violet 40 dye in freshwater and seawater. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2016.09.004
Hassaan MA, Nemr AE, Madkour FF (2015) Ultraviolet assisted ozone degradation process of Acid Red 17 dye. In: Fifth International Conference on Aquatic Resources (Challenges, Development and Sustainability) -ICAR-15", 29-30 November 2015, Alexandria, Egypt
Hassaan MA, Nemr AE, Madkour FF (2016a) Color removal and detoxification of Chrysophenine G (Direct Yellow 12) using Ultraviolet assisted ozone degradation for Possible Water Reuse. In: International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment, 1-3 November 2016, Alexandria, Egypt
Hassaan MA, Nemr AE, Madkour FF(2016b) Examination of advanced oxidation processes on decolorization of Direct Blue 86 dye in two different wastewater. In: International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment, 1-3 November 2016, Alexandria, Egypt
Hassaan MA, Nemr AE, Madkour FF (2016c) Removal of Mordant Violet 40 Dye from wastewater using UV/O 3 Advanced Oxidation Processes. In: International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment, 1-3 November 2016, Alexandria, Egypt.
Hoffmann MR, Martin ST, Choi W, Bahnemann DW (1995) Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis. Chem Rev 95:69–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00033a004
Holkar CR, Jadhav AJ, Pinjari DV et al (2016) A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J Environ Manage 182:351–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2016.07.090
Hossain L, Sarker SK, Khan MS (2018) Evaluation of present and future wastewater impacts of textile dyeing industries in Bangladesh. Environ Dev 26:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2018.03.005
Hu AY, Stuckey DC (2006) Treatment of Dilute Wastewaters Using a Novel Submerged Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor. J Environ Eng 132:190–198. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2006)132:2(190)
Husain Q (2008) Potential Applications of the Oxidoreductive Enzymes in the Decolorization and Detoxification of Textile and Other Synthetic Dyes from Polluted Water: A Review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 26:201–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550600969936
IAEA (2008) Radiation treatment of polluted water and wastewater. Publised by International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria. https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/te_1598_web.pdf
IARC (1972) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. In : Some inorganic substances, Chlorinated Hydrocarbons, Aromatic Amines, N-Nitroso compounds, and natural products, vol. 1, pp 184
IARC (1982) IARC Monographs on the evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. In: Some Industrial Chemicals and Dyestuffs, vol. 29, pp 416
IARC (2014) IARC Monographs on the evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (No.106: Trichloroethylene, Tetrachloroethylene, and Some Other Chlorinated Agents)
Imran Q, Hanif MA, Riaz MS et al (2012) Coagulation/flocculation of tannery wastewater using immobilized chemical coagulants. J Appl Res Technol 10:79–86
Islam MM, Mahmud K, Faruk O, Billah S (2011) Assessment of environmetal impacts for textile dyeing industries in Bangladesh. Proc Int Conf Green Technol Environ Conserv GTEC-2011 173–181. https://doi.org/10.1109/GTEC.2011.6167665
Islam T, Halim MA (2021) Washing Defects and Remedial actions of Denim Garments and Statistical Review of Denim Sectors in Emerging Economy. J Manag Sci Eng Res 4:30–40. https://doi.org/10.30564/jmser.v4i1.2941
Islam SU, Mohammad F (2015) Natural colorants in the presence of anchors so-called mordants as promising coloring and antimicrobial agents for textile materials. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:2361–2375. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSSUSCHEMENG.5B00537
Jadhav JP, Parshetti GK, Kalme SD, Govindwar SP (2007) Decolourization of azo dye methyl red by Saccharomyces cerevisiae MTCC 463. Chemosphere 68:394–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2006.12.087
Jäger I, Hafner C, Schneider K (2004) Mutagenicity of different textile dye products in Salmonella typhimurium and mouse lymphoma cells. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 561:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2004.03.005
Jamee R, Siddique R (2019) Biodegradation of synthetic dyes of textile effluent by microorganisms: an environmentally and economically sustainable approach. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 9:114–118. https://doi.org/10.1556/1886.2019.00018
Jankowska K, Zdarta J, Grzywaczyk A et al (2020) Electrospun poly(methyl methacrylate)/polyaniline fibres as a support for laccase immobilisation and use in dye decolourisation. Environ Res 184:109332. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2020.109332
Jegatheesan V, Pramanik BK, Chen J et al (2016) Treatment of textile wastewater with membrane bioreactor: A critical review. Bioresour Technol 204:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2016.01.006
Jiang L, Choo KH (2016) Photocatalytic mineralization of secondary effluent organic matter with mitigating fouling propensity in a submerged membrane photoreactor. Chem Eng J 288:798–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2015.12.060
Jiang Y, Qin S, Xu Y (2022) Impact of green credit policy on sustainability performance of high-pollution enterprises. Environ Sci Pollut Res 79199–79213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21315-6
Jun LY, Yon LS, Mubarak NM et al (2019) An overview of immobilized enzyme technologies for dye and phenolic removal from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102961. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2019.102961
Kant R (2011) Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Nat Sci 2012:22–26. https://doi.org/10.4236/NS.2012.41004
Kant R (2012) Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Nat Sci 04:22–26. https://doi.org/10.4236/ns.2012.41004
Karabelas AJ, Plakas K V., Sarasidis VC (2018) How Far Are We From Large-Scale PMR Applications? Curr Trends Futur Dev Membr Photocatalytic Membr Photocatalytic Membr React 233–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813549-5.00009-8
Karim MM, Das AK, Lee SH (2006) Treatment of colored effluent of the textile industry in Bangladesh using zinc chloride treated indigenous activated carbons. Anal Chim Acta 576:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2006.01.079
Karisma D, Febrianto G, Mangindaan D (2018) Removal of dyes from textile wastewater by using nanofiltration polyetherimide membrane. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 109. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/109/1/012012
Karthik V, Kumar PS, Harsha Vardhan K, et al (2020) Adsorptive behaviour of surface tailored fungal biomass for the elimination of toxic dye from wastewater. 1 16. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1787400
Kashefi S, Borghei SM, Mahmoodi NM (2019) Covalently immobilized laccase onto graphene oxide nanosheets: Preparation, characterization, and biodegradation of azo dyes in colored wastewater. J Mol Liq 276:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2018.11.156
Kasinath A, Novotný Č, Svobodová K et al (2003) Decolorization of synthetic dyes by Irpex lacteus in liquid cultures and packed-bed bioreactor. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00279-X
Kaushik P, Rawat N, Mathur M et al (2012) Arsenic Hyper-tolerance in Four Microbacterium Species Isolated from Soil Contaminated with Textile Effluent. Toxicol Int 19:188. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-6580.97221
Khalid A, Arshad M, Crowley DE (2009) Biodegradation potential of pure and mixed bacterial cultures for removal of 4-nitroaniline from textile dye wastewater. Water Res 43:1110–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2008.11.045
Khan AA, Husain Q (2007) Decolorization and removal of textile and non-textile dyes from polluted wastewater and dyeing effluent by using potato (Solanum tuberosum) soluble and immobilized polyphenol oxidase. Bioresour Technol 98:1012–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2006.04.008
Khan MI, Khan SA, Yusuf M et al (2010) Eco-friendly shades on wool using mixed mordants with Acacia catechu (Cutch). Colourage 57:81–88
Khan R, Bhawana P, Fulekar MH (2012) Microbial decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes: a review. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technology 121(12):75–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11157-012-9287-6
Khataee AR, Vatanpour V, Amani Ghadim AR (2009) Decolorization of C.I. Acid Blue 9 solution by UV/Nano-TiO2, Fenton, Fenton-like, electro-Fenton and electrocoagulation processes: A comparative study. J Hazard Mater 161:1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.075
Khatri M, Ahmed F, Shaikh I et al (2017) Dyeing and characterization of regenerated cellulose nanofibers with vat dyes. Carbohydr Polym 174:443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2017.06.125
Khattab TA, Abdelrahman MS, Rehan M (2019) Textile dyeing industry: environmental impacts and remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 274(27):3803–3818. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-019-07137-Z
Khlifi R, Belbahri L, Woodward S et al (2010) Decolourization and detoxification of textile industry wastewater by the laccase-mediator system. J Hazard Mater 175:802–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.079
Khorvash S, Behnam S (2019) Removal of methylene blue dye by immobilized mixture of brown alga Dictyota cervicornis and activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat 162:383–390. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24334
Khouni I, Louhichi G, Ghrabi A (2020) Assessing the performances of an aerobic membrane bioreactor for textile wastewater treatment: Influence of dye mass loading rate and biomass concentration. Process Saf Environ Prot 135:364–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSEP.2020.01.011
Kim TH, Lee Y, Yang J et al (2004) Decolorization of dye solutions by a membrane bioreactor (MBR) using white-rot fungi. Desalination 168:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2004.07.011
Kim TH, Park C, Kim S (2005) Water recycling from desalination and purification process of reactive dye manufacturing industry by combined membrane filtration. J Clean Prod 13:779–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2004.02.044
Kirby N, Marchant R, McMullan G (2000) Decolourisation of synthetic textile dyes by Phlebia tremellosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 188:93–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1574-6968.2000.TB09174.X
Kishor R, Purchase D, Saratale GD et al (2021) Ecotoxicological and health concerns of persistent coloring pollutants of textile industry wastewater and treatment approaches for environmental safety. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105012. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2020.105012
Kobya M, Can OT, Bayramoglu M (2003) Treatment of textile wastewaters by electrocoagulation using iron and aluminum electrodes. J Hazard Mater 100:163–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00102-X
Krishnappa B, Saravu S, Shivanna JM, et al (2022) Fast and effective removal of textile dyes from the wastewater using reusable porous nano-carbons: a study on adsorptive parameters and isotherms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 79067–79081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21251-5
Křížová H (2016) Natural dyes : their past, present, future and sustainability. Recent Dev Fibrous Mater Sci 461:59–71
Kurade MB, Waghmode TR, Kagalkar AN, Govindwar SP (2012) Decolorization of textile industry effluent containing disperse dye Scarlet RR by a newly developed bacterial-yeast consortium BL-GG. Chem Eng J 184:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2011.12.058
Kurade MB, Waghmode TR, Patil SM et al (2017) Monitoring the gradual biodegradation of dyes in a simulated textile effluent and development of a novel triple layered fixed bed reactor using a bacterium-yeast consortium. Chem Eng J 307:1026–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2016.09.028
Kurt E, Koseoglu-Imer DY, Dizge N et al (2012) Pilot-scale evaluation of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for process reuse of segregated textile dyewash wastewater. Desalination 302:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2012.05.019
Lade HS, Waghmode TR, Kadam AA, Govindwar SP (2012) Enhanced biodegradation and detoxification of disperse azo dye Rubine GFL and textile industry effluent by defined fungal-bacterial consortium. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 72:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2012.06.001
Lahkimi A, Oturan MA, Oturan N, Chaouch M (2007) Removal of textile dyes from water by the electro-Fenton process. Environ Chem Lett 5:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-006-0058-x
Lankinen VP, Inkeröinen MM, Pellinen J, Hatakka AI (1991) The Onset of Lignin-Modifying Enzymes, Decrease of AOX and Color Removal by White-Rot Fungi Grown on Bleach Plant Effluents. Water Sci Technol 24:189–198. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.1991.0475
Lebleu N, Roques C, Aimar P, Causserand C (2010) Effects of membrane alterations on bacterial retention. J Memb Sci 348:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEMSCI.2009.10.045
Lee BH, Kim HJ, Yu WR (2009) Fabrication of long and discontinuous natural fiber reinforced polypropylene biocomposites and their mechanical properties. Fibers Polym 101(10):83–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12221-009-0083-Z
Lee CS, Robinson J, Chong MF (2014) A review on application of flocculants in wastewater treatment. Process Saf Environ Prot 92:489–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSEP.2014.04.010
Lee KE, Morad N, Teng TT, Poh BT (2012) Development, characterization and the application of hybrid materials in coagulation/flocculation of wastewater: A review. Chem Eng J 203:370–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.109
Lellis B, Fávaro-Polonio CZ, Pamphile JA, Polonio JC (2019) Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol Res Innov 3:275–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORI.2019.09.001
Li H, Zhang R, Tang L et al (2015) Manganese peroxidase production from cassava residue by Phanerochaete chrysosporium in solid state fermentation and its decolorization of indigo carmine. Chinese J Chem Eng 23:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.11.001
Li Y, Cui W, Liu L et al (2016) Removal of Cr(VI) by 3D TiO2-graphene hydrogel via adsorption enriched with photocatalytic reduction. Appl Catal B Environ 199:412–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.053
Liang J, Ning X, Kong M et al (2017) Elimination and ecotoxicity evaluation of phthalic acid esters from textile-dyeing wastewater. Environ Pollut 231:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.006
Lin J, Tang CY, Ye W et al (2015) Unraveling flux behavior of superhydrophilic loose nanofiltration membranes during textile wastewater treatment. J Memb Sci 493:690–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEMSCI.2015.07.018
Lin J, Lai Q, Liu Y et al (2017) Laccase – methacrylyol functionalized magnetic particles: Highly immobilized, reusable, and efficacious for methyl red decolourization. Int J Biol Macromol 102:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2017.03.169
Lu R, Ma L, He F et al (2016) White-rot fungus Ganoderma sp.En3 had a strong ability to decolorize and tolerate the anthraquinone, indigo and triphenylmethane dye with high concentrations. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39:381–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1521-5
Lucas MS, Amaral C, Sampaio A et al (2006) Biodegradation of the diazo dye Reactive Black 5 by a wild isolate of Candida oleophila. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENZMICTEC.2005.09.004
Luo M, Li M, Jiang S et al (2020) Supported growth of inorganic-organic nanoflowers on 3D hierarchically porous nanofibrous membrane for enhanced enzymatic water treatment. J Hazard Mater 381:120947. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2019.120947
Madhav S, Ahamad A, Singh P, Mishra PK (2018) A review of textile industry: Wet processing, environmental impacts, and effluent treatment methods. Environ Qual Manag 27:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/TQEM.21538
Madhav S, Ahamad A, Singh AK, et al (2020) Water Pollutants: Sources and Impact on the Environment and Human Health. 43–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0671-0_4
Mahurpawar M (2015b) Effects of heavy metals on human health. Int J Res -GRANTHAALAYAH 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.29121/granthaalayah.v3.i9SE.2015.3282
Malik A, Akhtar R, Grohmann E (2014) Environmental deterioration and human health: Natural and anthropogenic determinants. Environ Deterior Hum Heal Nat Anthropog Determ 1–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7890-0
Mani S, Chowdhary P, Bharagava RN (2019a) Textile Wastewater Dyes: Toxicity Profile and Treatment Approaches. Emerg Eco-Friendly Approaches Waste Manag 219–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8669-4_11
Mansour HB, Barillier D, Corroler D et al (2009a) In vitro study of DNA damage induced by acid orange 52 and its biodegradation derivatives. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:489–495. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-333.1
Mansour HB, Mosrati R, Limem I et al (2009b) Genotoxic and antibutyrylcholinesterasic activities of acid violet 7 and its biodegradation products. Drug Chem Toxicol 32:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480540902862277
Mansour HB, Ayed-Ajmi Y, Mosrati R et al (2010) Acid violet 7 and its biodegradation products induce chromosome aberrations, lipid peroxidation, and cholinesterase inhibition in mouse bone marrow. Environ Sci Pollut Res 177(17):1371–1378. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-010-0323-1
Markarian J (2008) Product differentiation pushes advances in colour and special effects forward. Plast Addit Compd 10:16–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1464-391X(08)70054-0
Marzall-Pereira M, Savi DC, Bruscato EC et al (2019) Neopestalotiopsis species presenting wide dye destaining activity: report of a mycelium-associated laccase. Microbiol Res 228:126299. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICRES.2019.126299
Masood N, Farooqi A, Zafar MI (2019) Health risk assessment of arsenic and other potentially toxic elements in drinking water from an industrial zone of Gujrat, Pakistan: a case study. Environ Monit Assess 1912 191:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-019-7223-8
Mayyahi AA, Al-Asadi HAA (2018) Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for wastewater treatment and reuse: A brief review. Asian J Appl Sci Technol 2:18–30. http://ajast.net/data/uploads/6002.pdf
Meal PF, Cocker J, Wilson HK, Gilmour JM (1981) Search for benzidine and its metabolites in urine of workers weighing benzidine-derived dyes. Occup Environ Med 38:191–193. https://doi.org/10.1136/OEM.38.2.191
Mehrnia MR, Azami H, Sarrafzadeh MH (2013) Fouling mitigation in membrane bioreactors using multivalent cations. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 109:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFB.2013.03.009
Mignani M, Nosenzo G, Gualdi A (1999) Innovative ultrafiltration for wastewater reuse. Desalination 124(1–3):287–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(99)00114-9
Mirjalili M, Karimi L (2013) Antibacterial dyeing of polyamide using turmeric as a natural dye. Autex Res J 13:51–56. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10304-012-0023-7
Mishra S, Bharagava RN, More N, et al (2019) Heavy Metal Contamination: An Alarming Threat to Environment and Human Health. Environ Biotechnol Sustain Futur 103–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7284-0_5
Molinari R, Pirillo F, Falco M et al (2004) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes by using a membrane reactor. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 43:1103–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2004.01.008
Morsy SAGZ, Ahmad Tajudin A, Ali MSM, Shariff FM (2020) Current Development in Decolorization of Synthetic Dyes by Immobilized Laccases. Front Microbiol 11:2350. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2020.572309/BIBTEX
Mozia S (2010) Photocatalytic membrane reactors (PMRs) in water and wastewater treatment. A Review. Sep Purif Technol 73:71–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2010.03.021
Muralimohan N, Palanisamy T, Vimaladevi MN (2014) Experimental Study on Removal Efficiency of Blended Coagulants in Textile Wastewater Treatment. Int J Res Eng Technol 2:2321–8843
Myers CR, Myers JM (1992) Localization of cytochromes to the outer membrane of anaerobically grown Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Bacteriol 174:3429–3438. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.174.11.3429-3438.1992
Naseri A, Samadi M, Mahmoodi NM et al (2017) Tuning Composition of Electrospun ZnO/CuO Nanofibers: Toward Controllable and Efficient Solar Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants. J Phys Chem C 121:3327–3338. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b10414
Naveed S, Bhatti I, Ali K (2006) Membrane Technology and Its Suitability for Treatment of Textile Waste Water in Pakistan. J Res Sci 17:155–164
Nestmann ER, Douglas GR, Matula TI, Grant CE, Kowbel DJ (1979) Mutagenic activity of rhodamine dyes and their impurities as detected by mutation induction in Salmonella and DNA damage in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res 39(11):4412–4417
Ngieng NS, Zulkharnain A, Roslan HA, Husaini A (2013) Decolourisation of Synthetic Dyes by Endophytic Fungal Flora Isolated from Senduduk Plant ( Melastoma malabathricum ). ISRN Biotechnol 2013:1–7. https://doi.org/10.5402/2013/260730
Nidheesh PV, Ganiyu SO, Martínez-Huitle CA et al (2022) Recent advances in electro-Fenton process and its emerging applications. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 0:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2022.2093074
Noreen M, Shahid M, Iqbal M et al (2017) Measurement of cytotoxicity and heavy metal load in drains water receiving textile effluents and drinking water in vicinity of drains. Measurement 109:88–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2017.05.030
Novotný Č, Dias N, Kapanen A et al (2006) Comparative use of bacterial, algal and protozoan tests to study toxicity of azo- and anthraquinone dyes. Chemosphere 63:1436–1442. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2005.10.002
O’Shea KE, Dionysiou DD (2012) Advanced oxidation processes for water treatment. J Phys Chem Lett 3:2112–2113
Ogugbue C, Oranusi N (2006) Toxicity of azo dyes to the freshwater shrimp (Desmocaris trispinosa). Int J Nat Appl Sci 1:37–44
Oliveira GAR, Ferraz ERA, Chequer FMD et al (2010) Chlorination treatment of aqueous samples reduces, but does not eliminate, the mutagenic effect of the azo dyes Disperse Red 1, Disperse Red 13 and Disperse Orange 1. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 703:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2010.09.001
Ong CS, Lau WJ, Goh PS et al (2015) The impacts of various operating conditions on submerged membrane photocatalytic reactors (SMPR) for organic pollutant separation and degradation: a review. RSC Adv 5:97335–97348. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA17357D
Oturan MA (2000) Ecologically effective water treatment technique using electrochemically generated hydroxyl radicals for in situ destruction of organic pollutants: Application to herbicide 2,4-D. J Appl Electrochem 30:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003994428571
Oturan MA, Aaron JJ (2014) Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: principles and applications. A review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44(23):2577–2641. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.829765
Özcan AS, Erdem B, Özcan A (2004) Adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto Na–bentonite and DTMA–bentonite. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2004.07.035
Pandey S, Ramontja J (2016) Natural Bentonite Clay and Its Composites for Dye Removal: Current State and Future Potential. Am J Chem Appl 3:8–19
Panigrahi T, Santhoskumar AU (2020) Adsorption process for reducing heavy metals in Textile Industrial Effluent with low cost adsorbents. Prog Chem Biochem Res 3:135–139. https://doi.org/10.33945/SAMI/PCBR.2020.2.7
Papagianni M (2004) Fungal morphology and metabolite production in submerged mycelial processes. Biotechnol Adv 22:189–259
Patel SKS, Otari SV, Li J et al (2018) Synthesis of cross-linked protein-metal hybrid nanoflowers and its application in repeated batch decolorization of synthetic dyes. J Hazard Mater 347:442–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2018.01.003
Paździor K, Bilińska L, Ledakowicz S (2019) A review of the existing and emerging technologies in the combination of AOPs and biological processes in industrial textile wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 376:120597. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2018.12.057
Pearce CI, Lloyd JR, Guthrie JT (2003a) The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: A review. Dye Pigment 58:179–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(03)00064-0
Pearce CI, Christie R, Boothman C et al (2006) Reactive azo dye reduction by Shewanella strain J18 143. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:692–703. https://doi.org/10.1002/BIT.21021
Peralta-Zamora P, Pereira CM, Tiburtius ERL et al (2003) Decolorization of reactive dyes by immobilized laccase. Appl Catal B Environ 42:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(02)00220-5
Phugare SS, Kalyani DC, Patil AV, Jadhav JP (2011) Textile dye degradation by bacterial consortium and subsequent toxicological analysis of dye and dye metabolites using cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress studies. J Hazard Mater 186:713–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2010.11.049
Popli S, Patel UD (2014) Destruction of azo dyes by anaerobic–aerobic sequential biological treatment: a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 121(12):405–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13762-014-0499-X
Puvaneswari N, Muthukrishnan J, Gunasekaran P (2006) Toxicity assessment and microbial degradation of azo dyes. Indian J Exp Biol 44:618–626
Raghu S, Ahmed Basha C (2007) Chemical or electrochemical techniques, followed by ion exchange, for recycle of textile dye wastewater. J Hazard Mater 149:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2007.03.087
Raj R, Tripathi A, Das S, Ghangrekar MM (2021) Removal of caffeine from wastewater using electrochemical advanced oxidation process: A mini review. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 4:100129. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSCEE.2021.100129
Ramalho PA, Scholze H, Cardoso MH et al (2002) Improved conditions for the aerobic reductive decolourisation of azo dyes by Candida zeylanoides. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:848–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00189-8
Raman CD, Kanmani S (2016) Textile dye degradation using nano zero valent iron: A review. J Environ Manage 177:341–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2016.04.034
Ramavandi B, Farjadfard S (2014) Removal of chemical oxygen demand from textile wastewater using a natural coagulant. Korean J Chem Eng 31:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0197-2
Rashidi HR, Sulaiman NMN, Hashim NA et al (2014) Synthetic reactive dye wastewater treatment by using nano-membrane filtration. New Pub Balaban 55:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.912964
Rather LJ, Shahid-Ul-Islam SM et al (2016) Ecological dyeing of Woolen yarn with Adhatoda vasica natural dye in the presence of biomordants as an alternative copartner to metal mordants. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3041–3049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.06.019
Ren L, Yu S, Li J, Li L (2019) Pilot study on the effects of operating parameters on membrane fouling during ultrafiltration of alkali/surfactant/polymer flooding wastewater: optimization and modeling. RSC Adv 9:11111–11122. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA10167A
Rezvani F, Sarrafzadeh MH (2020) Autotrophic granulation of hydrogen consumer denitrifiers and microalgae for nitrate removal from drinking water resources at different hydraulic retention times. J Environ Manage 268:110674. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2020.110674
Robens JF, Dill GS, Ward JM et al (1980) Thirteen-week subchronic toxicity studies of Direct Blue 6, Direct Black 38, and Direct Brown 95 dyes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 54:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008X(80)90170-2
Robinson T, Nigam PS (2008) Remediation of textile dye waste water using a white-rot fungus Bjerkandera adusta through solid-state fermentation (SSF). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 151:618–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12010-008-8272-6
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol 77:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00080-8
Robinson T, Chandran B, Nigam P (2002a) Removal of dyes from a synthetic textile dye effluent by biosorption on apple pomace and wheat straw. Water Res 36:2824–2830. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00521-8
Robinson T, Chandran B, Nigam P (2002b) Studies on desorption of individual textile dyes and a synthetic dye effluent from dye-adsorbed agricultural residues using solvents. Bioresour Technol 84:299–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00039-1
Rosa JM, Garcia VSG, Boiani NF et al (2019) Toxicity and environmental impacts approached in the dyeing of polyamide, polyester and cotton knits. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102973. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2019.102973
Rosa JM, Tambourgi EB, Vanalle RM et al (2020) Application of continuous H2O2/UV advanced oxidative process as an option to reduce the consumption of inputs, costs and environmental impacts of textile effluents. J Clean Prod 246:119012. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.119012
Routoula E, Patwardhan SV (2020a) Degradation of Anthraquinone Dyes from Effluents: A Review Focusing on Enzymatic Dye Degradation with Industrial Potential. Environ Sci Technol 54:647–664. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.9B03737
Rovira J, Domingo JL (2019) Human health risks due to exposure to inorganic and organic chemicals from textiles: A review. Environ Res 168:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2018.09.027
Roy Choudhury AK (2014) Environmental Impacts of the Textile Industry and Its Assessment Through Life Cycle Assessment 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-287-110-7_1
Russ R, Rau J, Stolz A (2000) The Function of Cytoplasmic Flavin Reductases in the Reduction of Azo Dyes by Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1429–1434. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.4.1429-1434.2000
Sadr Ghayeni SB, Beatson PJ, Schneider RP, Fane AG (1998) Water reclamation from municipal wastewater using combined microfiltration-reverse osmosis (ME-RO): Preliminary performance data and microbiological aspects of system operation. Desalination 116:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(98)00058-7
Salami F, Habibi Z, Yousefi M, Mohammadi M (2018) Covalent immobilization of laccase by one pot three component reaction and its application in the decolorization of textile dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 120:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2018.08.077
Samsami S, Mohamadi M, Sarrafzadeh MH et al (2020) Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: Overview and perspectives. Process Saf Environ Prot 143:138–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.05.034
Sandoval MA, Espinoza LC, Coreño O, et al (2022) A comparative study of anodic oxidation and electrocoagulation for treating cattle slaughterhouse wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108306
Sanghi R, Bhattacharya B, Singh V (2007) Seed gum polysaccharides and their grafted co-polymers for the effective coagulation of textile dye solutions. React Funct Polym 67:495–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2007.02.012
Sarker MR, Chowdhury M, Deb A (2019) Reduction of Color Intensity from Textile Dye Wastewater Using Microorganisms: A Review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 8:3407–3415. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2019.802.397
Scalbi S, Tarantini M, Mattioli D (2005) Efficient use of water in the textile finishing industry. https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12079/1118
Schneider K, Hafner C, Jäger I (2004) Mutagenicity of textile dye products. J Appl Toxicol 24:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/JAT.953
Sekomo CB, Rousseau DPL, Saleh SA, Lens PNL (2012) Heavy metal removal in duckweed and algae ponds as a polishing step for textile wastewater treatment. Ecol Eng 44:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLENG.2012.03.003
Selcuk H (2005) Decolorization and detoxification of textile wastewater by ozonation and coagulation processes. Dye Pigment 64:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.03.020
Sharif A (2020) Microbial degradation of textile industry effluents: A review. Pure Appl Biol 9. https://doi.org/10.19045/BSPAB.2020.90251
Sharma MK, Sobti RC (2000) Rec effect of certain textile dyes in Bacillus subtilis. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 465:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5718(99)00201-6
Siddiqui MF, Singh L, Zularisam AW, Sakinah M (2013) Biofouling mitigation using Piper betle extract in ultrafiltration MBR. New Pub Balaban 51:6940–6951. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.793477
Siddiqui MF, Singh L, Wahid ZA (2017) Treatment of Dye Wastewater for Water Reuse Using Membrane Bioreactor and Biofouling Control. Waste Biomass Manag - A Holist Approach 121–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49595-8_6
Silva LGM, Moreira FC, Souza AAU et al (2018) Chemical and electrochemical advanced oxidation processes as a polishing step for textile wastewater treatment: A study regarding the discharge into the environment and the reuse in the textile industry. J Clean Prod 198:430–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.07.001
Singh Arora D, Kumar Sharma R (2009) Ligninolytic Fungal Laccases and Their Biotechnological Applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol1606 160:1760–1788. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12010-009-8676-Y
Singh M, Singh DK (2013) Biodegradation of Endosulfan in Broth Medium and in Soil Microcosm by Klebsiella sp. M3. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 922(92):237–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00128-013-1168-3
Singh PK, Singh RL (2017) Bio-removal of Azo Dyes: A Review. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 5:108–126. https://doi.org/10.3126/IJASBT.V5I2.16881
Solutions M (2021) MS@Internal/Submerged MBR (iMBR). In: Website. https://www.membrane-solutions.com/iMBR.htm. Accessed 27 Nov 2021
Srinivasan S, Sadasivam SK, Gunalan S et al (2019) Application of docking and active site analysis for enzyme linked biodegradation of textile dyes. Environ Pollut 248:599–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2019.02.080
Stahlmann R, Wegner M, Riecke K et al (2006) Sensitising potential of four textile dyes and some of their metabolites in a modified local lymph node assay. Toxicology 219:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOX.2005.11.005
Stiborová M, Martínek V, Rýdlová H et al (2002) Sudan I is a potential carcinogen for humans: Evidence for its metabolic activation and detoxication by human recombinant cytochrome P450 1A1 and liver microsomes. Cancer Res 62:5678–5684
Sun H, Yang H, Huang W, Zhang S (2015) Immobilization of laccase in a sponge-like hydrogel for enhanced durability in enzymatic degradation of dye pollutants. J Colloid Interface Sci 450:353–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2015.03.037
Sun J, Guo N, Niu LL et al (2017) Production of Laccase by a New Myrothecium verrucaria MD-R-16 Isolated from Pigeon Pea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] and its Application on Dye Decolorization. Mol 22:673. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES22040673
Surpăţeanu M, Zaharia C (2004) Advanced oxidation processes for decolorization of aqueous solution containing acid red G azo dye. Cent Eur J Chem 24(2):573–588. https://doi.org/10.2478/BF02482722
Sutedja A, Josephine CA, Mangindaan D (2018) Polysulfone thin film composite nanofiltration membranes for removal of textile dyes wastewater. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 109. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/109/1/012042
Suteu D, Zaharia C, Muresan A et al (2009) Using of industrial waste materials for textile wastewater treatment. Environ Eng Manag J 8:1097–1102. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2009.160
Suteu D, Zaharia C, Malutan T (2012) Biosorbents based on lignin used in biosorption processes from wastewater treatment: A review. Lignin Prop Appl Biotechnol Bioenergy 279–306
Suzuki Y, Yoda T, Ruhul A, Sugiura W (2001) Molecular Cloning and Characterization of the Gene Coding for Azoreductase from Bacillus sp. OY1-2 Isolated from Soil *. J Biol Chem 276:9059–9065. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.M008083200
Tamaro M, Monti Bragadin C, Banfi E (1975) Mutagenic activity of anthraquinone derivatives used as dyes in a textile factory. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan 54:105–107
Tatarko M, Bumpus JA (1998) Biodegradation of Congo Red by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Water Res 32:1713–1717. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00378-3
Togo C, Mutambanengwe C, Whiteley C (2010) Decolourisation and degradation of textile dyes using a sulphate reducing bacteria (SRB) – biodigester microflora co-culture. African J Biotechnol 7:114–121. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajb.v7i2.58337
Tsuboy MS, Angeli JPF, Mantovani MS et al (2007) Genotoxic, mutagenic and cytotoxic effects of the commercial dye CI Disperse Blue 291 in the human hepatic cell line HepG2. Toxicol Vitr 21:1650–1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIV.2007.06.020
Tuncay D, Yagar H (2020) Decolorization of Reactive Blue-19 textile dye by Boletus edulis laccase immobilized onto rice husks. Int J Environ Sci Technol 176(17):3177–3188. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13762-020-02641-Z
Uday USP, Bandyopadhyay TK, Bhunia B (2016) Bioremediation and Detoxification Technology for Treatment of Dye(s) from Textile Effluent. Text Wastewater Treat. https://doi.org/10.5772/62309
Ulson de Souza SMAG, Forgiarini E, Ulson de Souza AA (2007) Toxicity of textile dyes and their degradation by the enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP). J Hazard Mater 147:1073–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2007.06.003
Ulu A, Birhanli E, Boran F et al (2020) Laccase-conjugated thiolated chitosan-Fe3O4 hybrid composite for biocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 150:871–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2020.02.006
Velusamy S, Roy A, Sundaram S, Kumar Mallick T (2021) A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal Through Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Chem Rec 21:1570–1610. https://doi.org/10.1002/TCR.202000153
Venturini S, Tamaro M (1979) Mutagenicity of anthraquinone and azo dyes in Ames’ Salmonella typhimurium test. Mutat Res Toxicol 68:307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(79)90163-0
Verma Y (2008) Acute toxicity assessment of textile dyes and textile and dye industrial effluents using Daphnia magna bioassay. Toxicol Ind Health 24:491–500. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233708095769
Verma SK, Kumar A, Lal M, Debnath M (2015) Biodegradation of Synthetic Dye by Endophytic Fungal Isolate in Calotropis procera Root. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 3:373–380. https://doi.org/10.3126/IJASBT.V3I3.13136
Waghmode TR, Kurade MB, Kabra AN, Govindwar SP (2012) Degradation of Remazol Red dye by Galactomyces geotrichum MTCC 1360 leading to increased iron uptake in Sorghum vulgare and Phaseolus mungo from soil. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 171(17):117–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12257-011-0307-0
Wang C, Yediler A, Lienert D et al (2002) Toxicity evaluation of reactive dyestuffs, auxiliaries and selected effluents in textile finishing industry to luminescent bacteria Vibrio fischeri. Chemosphere 46:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00086-8
Wang WY, Irawan A, Ku Y (2008a) Photocatalytic degradation of Acid Red 4 using a titanium dioxide membrane supported on a porous ceramic tube. Water Res 42:4725–4732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.08.021
Wang Y-J, Duan Y-F, Yang L-G et al (2008b) Comparison of mercury removal characteristic between fabric filter and electrostatic precipitators of coal-fired power plants. J Fuel Chem Technol 36:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(08)60009-2
Wang Z, Ma J, Tang CY et al (2014) Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J Memb Sci 468:276–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEMSCI.2014.05.060
Wang Q, Wang T, Lv Z et al (2020) TiO2 Sol-Gel Coated PAN/O-MMT Multi-Functional Composite Nanofibrous Membrane Used as the Support for Laccase Immobilization: Synergistic Effect between the Membrane Support and Enzyme for Dye Degradation. Polym 12:139. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM12010139
Wawrzkiewicz M (2013) Removal of C.I. Basic Blue 3 dye by sorption onto cation exchange resin, functionalized and non-functionalized polymeric sorbents from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Chem Eng J 217:414–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2012.11.119
Yacout DMM, Hassouna MS (2016) Identifying potential environmental impacts of waste handling strategies in textile industry. Environ Monit Assess1888 188:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-016-5443-8
Yadav AK, Jain CK, Malik DS (2014) Toxic characterization of textile dyes and effluents in relation to human health hazards. J Sustain Environ Res 3:95–102
Yang Y, Yu W, He S et al (2019) Rapid adsorption of cationic dye-methylene blue on the modified montmorillonite/graphene oxide composites. Appl Clay Sci 168:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLAY.2018.11.013
Young L, Yu J (1997) Ligninase-catalysed decolorization of synthetic dyes. Water Res 31:1187–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00380-6
Youssef Z, Colombeau L, Yesmurzayeva N et al (2018) Dye-sensitized nanoparticles for heterogeneous photocatalysis: Cases studies with TiO2, ZnO, fullerene and graphene for water purification. Dye Pigment 159:49–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DYEPIG.2018.06.002
Yurtsever A, Sahinkaya E, Aktaş Ö et al (2015) Performances of anaerobic and aerobic membrane bioreactors for the treatment of synthetic textile wastewater. Bioresour Technol 192:564–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2015.06.024
Zaharia C, Diaconescu R, Surpateanu M (2006) Optimization study of a wastewater chemical treatment with ponilit GT-2 anionic polyelectrolyte. Environ Eng Manag J 5:1273–1290. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2006.107
Zaharia C, Diaconescu R, Surpăţeanu M (2007) Study of flocculation with PONILIT GT-2 anionic polyelectrolyte applied into a chemical wastewater treatment. Cent Eur J Chem 5:239–256. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-006-0057-6
Zeiger E, Anderson B, Haworth S et al (1992) Salmonella mutagenicity tests: V. Results from the testing of 311 chemicals. Environ Mol Mutagen 19:2–141. https://doi.org/10.1002/EM.2850190603
Zeiner M, Rezić I, Steffan I (2007) Analytical Methods for the Determination of Heavy Metals in the Textile Industry. Kem u Ind Časopis Kemičara i Kem Inženjera Hrvat 56:587–595
Zeiner M, Reziæ I, Steffanm I (2016) Analytical methods for the determination of heavy metals in the tetile industry analytical methods for the determination of heavy metals in the textile industry. Kem Ind 56(11):587–595
Zhang X, Liu Y, Yan K, Wu H (2007) Decolorization of anthraquinone-type dye by bilirubin oxidase-producing nonligninolytic fungus Myrothecium sp. IMER1. J Biosci Bioeng 104:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1263/JBB.104.104
Zhang W, Yang Q, Luo Q et al (2020) Laccase-Carbon nanotube nanocomposites for enhancing dyes removal. J Clean Prod 242:118425. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.118425
Zhang Y, Zhao K, Zhang Z et al (2021) Polypropylene non-woven supported calcium alginate hydrogel filtration membrane for efficient separation of dye/salt at low salt concentration. Desalination 500:114845. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2020.114845
Zheng T, Wang Q, Zhang T et al (2015) Microbubble enhanced ozonation process for advanced treatment of wastewater produced in acrylic fiber manufacturing industry. J Hazard Mater 287:412–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2015.01.069
Zheng F, Cui BK, Wu XJ et al (2016) Immobilization of laccase onto chitosan beads to enhance its capability to degrade synthetic dyes. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 110:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2016.03.004
Zheng X, Shen Z-P, Shi L et al (2017a) Photocatalytic Membrane Reactors (PMRs) in Water Treatment: Configurations and Influencing Factors. Catal 7:224. https://doi.org/10.3390/CATAL7080224
Zheng X, Shen ZP, Shi L, et al (2017b) Photocatalytic membrane reactors (PMRs) in water treatment: Configurations and influencing factors. Catalysts 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080224
Zhou C, Wen XH (2009) [Degradation of acid blue 45 in a white-rot fungi reactor operated under non-sterile conditions]. Huan Jing ke Xue= Huanjing Kexue 30:1797–1801
Zhu Z, Chen Z, Luo X et al (2020) Biomimetic dynamic membrane (BDM): Fabrication method and roles of carriers and laccase. Chemosphere 240:124882. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2019.124882
Zille A (2005) Laccase reactions for textile applications. PhD thesis, Universidade do Minho, Portugal. http://repositorium.uminho.pt/bitstream/1822/4899/1/ZillePhD.pdf
Zimmermann T, Kulla HG, Leisinger T (1982) Properties of Purified Orange II Azoreductase, the Enzyme Initiating Azo Dye Degradation by Pseudomonas KF46. Eur J Biochem 129:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1432-1033.1982.TB07040.X
Zimmermann T, Gasser F, Kulla HG, Leisinger T (1984) Comparison of two bacterial azoreductases acquired during adaptation to growth on azo dyes. Arch Microbiol1381 138:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425404
Zohoorian H, Ahmadzadeh H, Molazadeh M, et al (2020) Microalgal bioremediation of heavy metals and dyes. Handb Algal Sci Technol Med 659–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818305-2.00041-3
Zuorro A, Lavecchia R, Monaco MM et al (2019) Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive. Catalysts 9:645–661
Acknowledgements
Technical supports from the “ZR Research Institute for Advanced Materials”, Sherpur-2100, Bangladesh, are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tarekul Islam and Md. Reazuddin Repon have contributed to the conceptualization, methodology, data collection, and original draft preparation. Tarikul Islam, Zahid Sarwar and Mohammed M. Rahman have contributed to editing, reviewing, and approval of contents. Md. Reazuddin Repon has supervised all stages of preparing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published final version of this review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, T., Repon, M., Islam, T. et al. Impact of textile dyes on health and ecosystem: a review of structure, causes, and potential solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 9207–9242 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24398-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24398-3