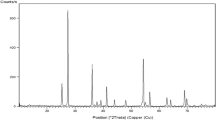
Abstract
Titanium dioxide (nano-TiO2) is used abundantly in various industrial products and novel medical therapies. In addition, the impact of climate change on the health and safety will undoubtedly increase in the future. However, the effects of exposure to these nanoparticles and heat stress on hippocampal DNA damage and apoptosis remain unclear. This study was conducted to evaluate the DNA damage and apoptosis in the hippocampal tissue and the physiological responses in mice induced by intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) and heat stress for 14 consecutive days. The results showed that heat stress and TiO2-NPs were induced in the mouse hippocampus that led to hippocampal reactive oxygen species generation, oxidative damage of DNA, and apoptosis in a partly dose-dependent manner, especially at very hot temperature. High doses of nanosized TiO2 and severe heat stress significantly damaged the function of the hippocampus, as shown in the comet assay and apoptosis tests. The results of this study may provide data for appropriate measures to control and assess the risk of nano-TiO2 and thermal stress hazards to human health, especially workers. Safety guidelines and policies should be considered when handling nanomaterials in a hot environment.





Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The data that support this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Adusumilli NC, Mordorski B, Nosanchuk J, Friedman JM, Friedman AJ (2021) Curcumin nanoparticles as a photoprotective adjuvant. Exp Dermatol 30(5):705–709
Aghmasheh S, Ostad SN, Abedi A (2020) Pharmacological properties of pt (ii) and pt (iv) complexes with 2, 2′-dipyridylamine; the comparative in vitro thereof. Cell Biochem Biophys 78(4):521–529
Aliebrahimi S, Kouhsari SM, Arab SS, Shadboorestan A, Ostad SN (2018) Phytochemicals, withaferin a and carnosol, overcome pancreatic cancer stem cells as c-met inhibitors. Biomed Pharmacother 106:1527–1536
Attia H, Nounou H, Shalaby M (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induced oxidative DNA damage, inflammation and apoptosis in rat’s brain after oral exposure. Toxics 6(2):29
Council NR (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals: Eighth edition. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press
Cui Y, Gong X, Duan Y, Li N, Hu R, Liu H, Hong M, Zhou M, Wang L, Wang H (2010) Hepatocyte apoptosis and its molecular mechanisms in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 183(1-3):874–880
Dawood M, Koshio S, Zaineldin A, Van Doan H, Ahmed H, Elsabagh M, Abdel-Daim M (2019) An evaluation of dietary selenium nanoparticles for red sea bream (Pagrus major) aquaculture: growth, tissue bioaccumulation, and antioxidative responses. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(30):30876–30884
Das S, Das J, Samadder A, Boujedaini N, Khuda-Bukhsh AR (2012) Apigenin-induced apoptosis in a375 and a549 cells through selective action and dysfunction of mitochondria. Exp Biol Med 237(12):1433–1448
DeBow S, Colbourne F (2003) Brain temperature measurement and regulation in awake and freely moving rodents. Methods 30(2):167–171
Dehghan H, Habibi E, Habibi P, Maracy MR (2013) Validation of a questionnaire for heat strain evaluation in women workers. Int J Prev Med 4(6):631
El-Said KS, Ali EM, Kanehira K, Taniguchi A (2014) Molecular mechanism of DNA damage induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in toll-like receptor 3 or 4 expressing human hepatocarcinoma cell lines. J Nanobiotechnology 12:48
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicologic pathology 35(4):495–516
Gao G, Ze Y, Li B, Zhao X, Zhang T, Sheng L, Hu R, Gui S, Sang X, Sun Q (2012) Ovarian dysfunction and gene-expressed characteristics of female mice caused by long-term exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 243:19–27
Ghanbarian M, Nicknam MH, Mesdaghinia A, Yunesian M, Hassanvand MS, Soleimanifar N, Rezaei S, Atafar Z, Ghanbarian M, Faraji M (2019) Investigation and comparison of in vitro genotoxic potency of pm 10 collected in rural and urban sites at tehran in different metrological conditions and different seasons. Biol Trace Elem Res 189(1):301–310
Glei M, Schneider T, Schlörmann W (2016) Comet assay: an essential tool in toxicological research. Arch Toxicol 90(10):2315–2336
Golbabaei F, Heydari A, Moradi G, Dehghan H, Moradi A, Habibi P (2020) The effect of cooling vests on physiological and perceptual responses: a systematic review. Int J Occup Saf Ergon, 1-33
Grande F, Tucci P (2016) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a risk for human health? Mini Rev Med Chem 16(9):762–769
Gui S, Zhang Z, Zheng L, Cui Y, Liu X, Li N, Sang X, Sun Q, Gao G, Cheng Z (2011) Molecular mechanism of kidney injury of mice caused by exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 195:365–370
Habibi P, Momeni R, Dehghan H (2015) Relationship of environmental, physiological, and perceptual heat stress indices in iranian men. Int J Prev Med 6
Habibi P, Moradi G, Moradi A, Golbabaei F (2021a) A review on advanced functional photonic fabric for enhanced thermoregulating performance. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag, 100504
Habibi P, Moradi G, Moradi A, Heydari A (2021b) The impacts of climate change on occupational heat strain in outdoor workers: a systematic review. Urban Clim 36:100770
Harikai N, Tomogane K, Miyamoto M, Shimada K, Onodera S, Tashiro S-i (2003) Dynamic responses to acute heat stress between 34 c and 38.5 c, and characteristics of heat stress response in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 26(5):701–708
Hu R, Gong X, Duan Y, Li N, Che Y, Cui Y, Zhou M, Liu C, Wang H, Hong F (2010) Neurotoxicological effects and the impairment of spatial recognition memory in mice caused by exposure to tio2 nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31(31):8043–8050
Hu R, Zheng L, Zhang T, Gao G, Cui Y, Cheng Z, Cheng J, Hong M, Tang M, Hong F (2011) Molecular mechanism of hippocampal apoptosis of mice following exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 191(1-3):32–40
Jia X, Wang S, Zhou L, Sun L (2017) The potential liver, brain, and embryo toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on mice. Nanoscale Res Lett 12(1):1–14
Kantidze O, Velichko A, Luzhin A, Razin S (2016) Heat stress-induced DNA damage. Acta Naturae 8(2 (29))
Kjellstrom T, Lemke B, Venugopal V. (2013). Occupational health and safety impacts of climate conditions Climate vulnerability: understanding and addressing threats to essential resources (Vol. 1, pp. 145-156): Elsevier Inc.
Li N, Duan Y, Hong M, Zheng L, Fei M, Zhao X, Wang J, Cui Y, Liu H, Cai J (2010) Spleen injury and apoptotic pathway in mice caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticules. Toxicol Lett 195(2-3):161–168
Liu S, Xu L, Zhang T, Ren G, Yang Z (2010) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by nanosized titanium dioxide in pc12 cells. Toxicology 267(1-3):172–177
Ma L, Liu J, Li N, Wang J, Duan Y, Yan J, Liu H, Wang H, Hong F (2010) Oxidative stress in the brain of mice caused by translocated nanoparticulate tio2 delivered to the abdominal cavity. Biomaterials 31(1):99–105
Maroni P, Bendinelli P, Tiberio L, Rovetta F, Piccoletti R, Schiaffonati L (2003) In vivo heat-shock response in the brain: signalling pathway and transcription factor activation. Mol Brain Res 119(1):90–99
Meena R, Rani M, Pal R, Rajamani P (2012) Nano-tio2-induced apoptosis by oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage and activation of p53 in human embryonic kidney cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167(4):791–808
Mohammed E, Safwat G (2013) Assessment of the ameliorative role of selenium nanoparticles on the oxidative stress of acetaminophen in some tissues of male albino rats. Beni-Seuf Univ J Appl 2(2):80–85
Mohammed E, Safwat G (2020) Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract mitigates titanium dioxide nanoparticle (TiO2-NPs)–induced hepatotoxicity through TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 196(2):579–589
Mohammed E, Hashem K, Abdelazem A, Foda F (2020) Prospective protective effect of ellagic acid as a SIRT1 activator in iron oxide nanoparticle-induced renal damage in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 198(1):177–188
Norton A, Leaman J (2004) The day after tomorrow: public opinion on climate change. MORI Social Research Institute, London
Osano E, Kishi J, Takahashi Y (2003) Phagocytosis of titanium particles and necrosis in tnf-α-resistant mouse sarcoma l929 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 17(1):41–47
Osman IF, Najafzadeh M, Sharma V, Shukla RK, Jacob BK, Dhawan A, Anderson D (2018) Tio2 nps induce DNA damage in lymphocytes from healthy individuals and patients with respiratory diseases-an ex vivo/in vitro study. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18(1):544–555
Petković J, Zegura B, Stevanović M, Drnovšek N, Uskoković D, Novak S, Filipič M (2011) DNA damage and alterations in expression of DNA damage responsive genes induced by tio2 nanoparticles in human hepatoma hepg2 cells. Nanotoxicology 5(3):341–353
Qian C, Wang J-Q, Song C-L, Wang L-L, Ji L-N, Chao H (2013) The induction of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in cancer cells by ruthenium (ii) asymmetric complexes. Metallomics 5(7):844–854
Ryu AR, Bang IC, Lee SA, Lee MY (2016) The protective role of phytochemicals on tio2 nanoparticles-induced DNA damage in lymphocytes. J Environ Biol 37(5):913–917
Shakeel M, Jabeen F, Shabbir S, Asghar MS, Khan MS, Chaudhry AS (2016) Toxicity of nano-titanium dioxide (tio 2-np) through various routes of exposure: a review. Biol Trace Elem Res 172(1):1–36
Sharma HS, Sharma A (2007) Nanoparticles aggravate heat stress induced cognitive deficits, blood–brain barrier disruption, edema formation and brain pathology. Prog Brain Res 162:245–273
Shin J, Lee E, Seo S, Kim H, Kang J, Park E (2010) Nanosized titanium dioxide enhanced inflammatory responses in the septic brain of mouse. Neuroscience 165(2):445–454
Shrivastava R, Raza S, Yadav A, Kushwaha P, Flora SJ (2014) Effects of sub-acute exposure to tio2, zno and al2o3 nanoparticles on oxidative stress and histological changes in mouse liver and brain. Drug Chem Toxicol 37(3):336–347
Varlamova E, Turovsky E, Blinova E (2021) Therapeutic potential and main methods of obtaining selenium nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 22(19):10808
Wang JJ, Sanderson BJ, Wang H (2007) Cyto-and genotoxicity of ultrafine tio2 particles in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 628(2):99–106
Wang Y, Cui H, Zhou J, Li F, Wang J, Chen M, Liu Q (2015) Cytotoxicity, DNA damage, and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human non-small cell lung cancer a549 cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(7):5519–5530
Wu J, Liu W, Xue C, Zhou S, Lan F, Bi L, Xu H, Yang X, Zeng F-D (2009) Toxicity and penetration of tio2 nanoparticles in hairless mice and porcine skin after subchronic dermal exposure. Toxicol Lett 191(1):1–8
Yeung A, Tzvetkov N, El-Tawil O, Bungǎu S, Abdel-Daim M, Atanasov A (2019) Antioxidants: scientific literature landscape analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019
Ze Y, Hu R, Wang X, Sang X, Ze X, Li B, Su J, Wang Y, Guan N, Zhao X (2014a) Neurotoxicity and gene-expressed profile in brain-injured mice caused by exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 102(2):470–478
Ze Y, Sheng L, Zhao X, Hong J, Ze X, Yu X, Pan X, Lin A, Zhao Y, Zhang C (2014b) Tio2 nanoparticles induced hippocampal neuroinflammation in mice. PloS one 9(3):e92230
Acknowledgements
This research was part of a Ph.D. thesis supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services (grant number 9611138001 and 99-2-99-49075). The authors are grateful to the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, for the technical support and collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.Gh.Kh. and M.R.M. conceived of the presented idea. P.H. helped in the coordination of the study and material preparation. A.R.F. performed statistical analysis and interpretation and drafted the manuscript. S.N.O. and F.G. supervised the first draft and commented on previous version of the manuscript. V.M. discussed the results and encouraged investigating a specific aspect of this work. SH.A. helped in the data collection and designed the analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The thesis was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (IR.TUMS.SPH.REC.1399.044).
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participant
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habibi, P., Ostad, S.N., Monazzam, M.R. et al. Thermal stress and TiO2 nanoparticle–induced oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in mouse hippocampus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 90128–90139 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21796-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21796-5