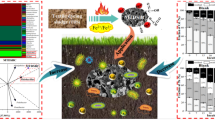
Abstract
The preparation of magnetic biochar from sewage sludge and rice straw for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation has greater application prospects, but its remediation mechanism was rarely considered by combining soil physicochemical properties with microbial community. In this study, the effects of magnetic sewage sludge biochar (SSB) and rice straw biochar (RSB) on Cd and Pb immobilization in paddy soil were compared and analyzed by 60-day soil incubation experiments. The results illustrated that DTPA-Cd and DTPA-Pb were reduced by 51.53% (43.07%) and 53.57% (50.47%), while the percentage of residual fraction of the BCR procedure was enhanced by 31.27% (30.78%) of Cd and 27.25% (23.22%) of Pb in the SSB (RSB) treatment, respectively. Fe was detected on both SSB and RSB surfaces, but SSB had rougher and a larger specific surface area compared to RSB. The addition of SSB and RSB in paddy soil increased soil pH and TOC content, and affected the diversity and species of soil microbial community. Compared with the CK group, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota, and Lysobacter decreased, and the relative abundance of Actinobacteriota, Pontibacter, and Alkaliphilus increased with SSB and RSB treatments, all of which reflected the bioavailability of Cd and Pb reduction.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Awasthi MK, Liu T, Chen H, Verma S, Duan Y, Awasthi SK, Wang Q, Ren X, Zhao J, Zhang Z (2019) The behavior of antibiotic resistance genes and their associations with bacterial community during poultry manure composting. Bioresour Technol 280:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.030
Bates ST, Berg-Lyons D, Caporaso JG, Walters WA, Fierer N (2011) Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.171
Bogusz A, Oleszczuk P (2020) Effect of biochar addition to sewage sludge on cadmium, copper and lead speciation in sewage sludge-amended soil. Chemosphere 239:124719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124719
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014) Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils–to mobilize or to immobilize? J Hazard Mater 266:141–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.018
Chen W, Wang F, Li Z, Li Q (2020) A comprehensive evaluation of the treatment of lead in MSWI fly ash by the combined cement solidification and phosphate stabilization process. Waste Manage 114:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.06.041
Chen Z, Wang Y, Xia D, Jiang X, Fu D, Shen L, Wang H, Li QB (2016) Enhanced bioreduction of iron and arsenic in sediment by biochar amendment influencing microbial community composition and dissolved organic matter content and composition. J Hazard Mater 311:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.069
Chong W, Shao J, Yun F, Gdz B, Zhong X (2005) Lead contamination in tea garden soils and factors affecting its bioavailability. Chemosphere 59(8):1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.058
Dan Y, Ji M, Tao S, Luo G, Shen Z, Zhang Y, Sang W (2021) Impact of rice straw biochar addition on the sorption and leaching of phenylurea herbicides in saturated sand column. Sci Total Environ 769:144536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144536
Frišták V, Micháleková-Richveisová B, Víglašová E, Ďuriška L, Galamboš M, Moreno-Jimenéz E, Pipíška M, Soja G (2017) Sorption separation of Eu and As from single-component systems by Fe-modified biochar: kinetic and equilibrium study. J Iran Chem Soc 14(3):521–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-1000-1
Guo Q, Li N, Xie S (2019) Heavy metal spill influences bacterial communities in freshwater sediments. Arch Microbiol 201(6):847–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01650-y
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B, Usman M, Gurajala HK, Rashid MS, He Z, Yang X (2020) Efficiency of lime, biochar, Fe containing biochar and composite amendments for Cd and Pb immobilization in a co-contaminated alluvial soil. Environ Pollut 257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113609
Hamid Y, Tang L, Yaseen M, Hussain B, Zehra A, Aziz MZ, He ZL, Yang X (2019) Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium and lead immobilization in contaminated soil under rice-wheat cropping system. Chemosphere 214:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.113
Jiang TY, Jiang J, Xu RK, Li Z (2012) Adsorption of Pb(II) on variable charge soils amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Chemosphere 89(3):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.04.028
Jla B, Yda B, Yan SC, Lu F, Min Z, Hha B, C D (2020) A novel method for solidification/stabilization of Cd(II), Hg(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) by activated electrolytic manganese slag. Journal of hazardous materials 409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124933
Kumpiene J, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2008) Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments–a review. Waste Manage 28(1):215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.12.012
Lan J, Zhang S, Dong Y, Li J, Li S, Feng L, Hou H (2021) Stabilization and passivation of multiple heavy metals in soil facilitating by pinecone-based biochar: mechanisms and microbial community evolution. J Hazard Mater 420:126588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126588
Li L, Jia Z, Hang M, Bao W, Li Y (2019) The effect of two different biochars on remediation of Cd-contaminated soil and Cd uptake by Lolium perenne. Environ Geochem Health (3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00257-y
Li S, Zhao B, Jin M, Hu L, He Z (2020) A comprehensive survey on the horizontal and vertical distribution of heavy metals and microorganisms in soils of a Pb/Zn smelter. J Hazard Mater 400:123255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123255
Lin H, Liu C, Li B, Dong Y (2021) Trifolium repens L. regulated phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by promoting soil enzyme activities and beneficial rhizosphere associated microorganisms. J Hazard Mater 402:123829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123829
Lin Y, Ye Y, Hu Y, Shi H (2019) The variation in microbial community structure under different heavy metal contamination levels in paddy soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.057
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42(3):421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x
Liu H, Zhou Y, Qin S, Kumar Awasth S, Liu T, Liu H, Zhang Z, Kumar Awasthi M (2021) Distribution of heavy metal resistant bacterial community succession in cow manure biochar amended sheep manure compost. Bioresour Technol 335:125282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125282
Lu HP, Li ZA, Gascó G, Méndez A, Shen Y, Paz-Ferreiro J (2018) Use of magnetic biochars for the immobilization of heavy metals in a multi-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 622–623:892–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.056
Lu K, Yang X, Gielen G, Bolan N, Wang H (2017) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil. J Environ Manage 186(Pt 2):285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.05.068
Lucchini P, Quilliam RS, DeLuca TH, Vamerali T, Jones DL (2014) Does biochar application alter heavy metal dynamics in agricultural soil? Agric Ecosys Environ 184:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2013.11.018
Lyu H, Tang J, Cui M, Gao B, Shen B (2020) Biochar/iron (BC/Fe) composites for soil and groundwater remediation: synthesis, applications, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 246:125609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125609
Mendez A, Paz-Ferreiro J, Araujo F, Gasco G (2014) Biochar from pyrolysis of deinking paper sludge and its use in the treatment of a nickel polluted soil. J Anal Appl Pyrol 107(may):46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2014.02.001
Mounia B, Merzoug B, Chaouki B, Djaouza AA (2013) Physico-chemical characterization of limestones and sandstones in a complex geological context, examplenorth-east constantine: preliminary results. Int J Eng Technol, 114-118.https://doi.org/10.7763/IJET.2013.V5.523
O’Dell R, Silk W, Green P, Claassen V (2007) Compost amendment of Cu-Zn minespoil reduces toxic bioavailable heavy metal concentrations and promotes establishment and biomass production of Bromus carinatus (Hook and Arn.). Environ Pollut 148(1):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.10.037
Pan H, Yang X, Chen H, Sarkar B, Bolan N, Shaheen SM, Wu F, Che L, Ma Y, Rinklebe J, Wang H (2021) Pristine and iron-engineered animal- and plant-derived biochars enhanced bacterial abundance and immobilized arsenic and lead in a contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 763:144218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144218
Puga AP, Abreu CA, Melo L, Paz-Ferreiro J, Beesley L (2015) Cadmium, lead, and zinc mobility and plant uptake in a mine soil amended with sugarcane straw biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4977-6
Qu J, Yuan Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Tao Y, Jiang Z, Yu H, Dong M, Zhang Y (2022) Stabilization of lead and cadmium in soil by sulfur-iron functionalized biochar: performance, mechanisms and microbial community evolution. J Hazard Mater 425:127876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127876
Rajapaksha AU, Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Zhang M, Vithanage M, Mandal S, Gao B, Bolan NS, Ok YS (2016) Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: potential and implication of biochar modification. Chemosphere 148(Apr) 276–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.01.043
Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P(1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monitor Jem 1. https://doi.org/10.1039/A807854H
Sizmur T, Fresno T, Akgul G, Frost H, Moreno-Jimenez E (2017) Biochar modification to enhance sorption of inorganics from water. Bioresour Technol 246:34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.082
Sqt A, Lu WA, Yll B, Jm A (2020) Degradation of organic pollutants by ferrate/biochar: enhanced formation of strong intermediate oxidative iron species. Water Res 183.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116054
Sutherland RA, Tack F (2000) Metal phase associations in soils from an urban watershed, Honolulu Hawaii. Sci Total Environ 256(2–3):103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00458-7
Tan Z, Wang Y, Zhang L, Huang Q (2017) Study of the mechanism of remediation of Cd-contaminated soil by novel biochars. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(32):24844–24855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0109-9
Tomczyk B, Siatecka A, Bogusz A, Oleszczuk P (2021) Ecotoxicological assessment of sewage sludge-derived biochars-amended soil. Environ Pollut, 116484.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116484
Tomczyk B, Siatecka A, Gao Y, Yong SO, Oleszczuk P (2020) The convertion of sewage sludge to biochar as a sustainable tool of PAHs exposure reduction during agricultural utilization of sewage sludges. J Hazard Mater 392:122416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122416
Trakal L, BingöL D, PohořEly M, HrušKa M, Komárek M (2014) Geochemical and spectroscopic investigations of Cd and Pb sorption mechanisms on contrasting biochars: engineering implications. Bioresource Technol 171:442–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.108
Uchimiya M, Klasson KT, Wartelle LH, Lima IM (2011) Influence of soil properties on heavy metal sequestration by biochar amendment: 1. copper sorption isotherms and the release of cations. Chemosphere 82(10):1431–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.050
Wang C, Chen D, Shen J, Yuan Q, Fan F, Wei W, Li Y, Wu J (2021a) Biochar alters soil microbial communities and potential functions 3–4 years after amendment in a double rice cropping system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 311.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107291
Wang F (2014) Use of phytoremediation and biochar to remediate heavy metal polluted soils: a review. Solid Earth 1(5):2155–2179. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-5-65-2014
Wang L, Chen H, Wu J, Huang L, Brookes PC, Mazza Rodrigues JL, Xu J, Liu X (2021b) Effects of magnetic biochar-microbe composite on Cd remediation and microbial responses in paddy soil. J Hazard Mater 414:125494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125494
Wang S, Gao B, Zimmerman AR, Li Y, Ma L, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015) Removal of arsenic by magnetic biochar prepared from pinewood and natural hematite. Bioresour Technol 175:391–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.104
Wang Z, Shen R, Ji S, Xie L, Zhang H (2021c) Effects of biochar derived from sewage sludge and sewage sludge/cotton stalks on the immobilization and phytoavailability of Pb, Cu, and Zn in sandy loam soil. J Hazard Mater 419:126468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126468
Wu B, Luo H, Wang X, Liu H, Peng H, Sheng M, F. Xu F, Xu H (2022) Effects of environmental factors on soil bacterial community structure and diversity in different contaminated districts of Southwest China mine tailings. Sci Total Environ 802.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149899
Wu J, Li Z, Huang D, Liu X, Xu J (2020) A novel calcium-based magnetic biochar is effective in stabilization of arsenic and cadmium co-contamination in aerobic soils. J Hazard Mater 387:122010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.122010
Xia Y, Tang Y, Shih K, Li B (2020) Enhanced phosphorus availability and heavy metal removal by chlorination during sewage sludge pyrolysis. J Hazard Mater 382(Jan15):121110.121111-121110.121118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121110
Xu Y, Seshadri B, Sarkar B, Wang H, Rumpel C, Sparks D, Farrell M, Hall T, Yang X, Bolan N (2018) Biochar modulates heavy metal toxicity and improves microbial carbon use efficiency in soil. Sci Total Environ 621:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.214
Yang G, Hu Y, Wang J (2019) Biohydrogen production from co-fermentation of fallen leaves and sewage sludge. Biores Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121342
Yang F, Xu Z, Huang Y, Tsang DCW, Ok YS, Zhao L, Qiu H, Xu X, Cao X (2021) Stabilization of dissolvable biochar by soil minerals: release reduction and organo-mineral complexes formation. J Hazard Mater 412:125213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125213
Yang Q, Mašek O, Zhao L, Nan H, Yu S, Yin J, Li Z, Cao X (2021a) Country-level potential of carbon sequestration and environmental benefits by utilizing crop residues for biochar implementation.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.116275
Yang X, Pan H, Shaheen SM, Wang H, Rinklebe J (2021b) Immobilization of cadmium and lead using phosphorus-rich animal-derived and iron-modified plant-derived biochars under dynamic redox conditions in a paddy soil. Environ Int 156:106628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106628
Ye Q, Roh Y, Carroll SL, Blair B, Zhou JZ, Zhang CL, Fields MW (2004) Alkaline anaerobic respiration: isolation and characterization of a novel alkaliphilic and metal-reducing bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(9):5595–5602. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.9.5595-5602.2004
Zeng XY, Li SW, Leng Y, Kang XH (2020) Structural and functional responses of bacterial and fungal communities to multiple heavy metal exposure in arid loess. Sci Total Environ 723:138081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138081
Zhang A, Cui L, Pan G, Li L, Hussain Q, Zhang X, Zheng J, Crowley D (2010) Effect of biochar amendment on yield and methane and nitrous oxide emissions from a rice paddy from Tai Lake plain China. Agric Ecosys Environ 139(4):469–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2010.09.003
Zhang M, Song G, Gelardi DL, Huang L, Yong SO (2020) Evaluating biochar and its modifications for the removal of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate in water. Water Res 186:116303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116303
Zhu J, Zhang J, Li Q, Han T, Xie J, Hu Y, Chai L (2013) Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial community composition in sediment contaminated with multiple heavy metals from the Xiangjiang River in China. Mar Pollut Bull 70(1–2):134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.02.023
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Fund for State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse Foundation (no. PCRRF19001) and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (no. 22ZR1401700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yinzhu Diao: conceptualization, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft. Lei Zhou: writing—reviewing and editing. Mengyuan Ji: software. Xiaoxia Wang: validation, supervision. Yitong Dan: Investigation. Wenjing Sang: funding acquisition, resources, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diao, Y., Zhou, L., Ji, M. et al. Immobilization of Cd and Pb in soil facilitated by magnetic biochar: metal speciation and microbial community evolution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 71871–71881 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20750-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20750-9