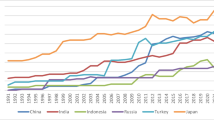
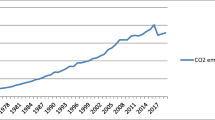
Abstract
The “environment” has become one of the important and debatable topics of the world and policymakers identifying the new predictors of CO2 emissions. Therefore, some economies have been promoting fiscal decentralization to encourage environmental quality by granting more financial autonomy to provincial and sub-national governments. Therefore, this study evaluates the dynamic effect of fiscal decentralization on CO2 in selected nine Asian economies using a fresh dynamic panel ARDL model from 1984 to 2017. The empirical findings show that fiscal decentralization has asymmetric effects on CO2 emissions because a positive change in revenue and expenditure decentralization reduced CO2 emissions in Asia. Moreover, a negative change in expenditure decentralization has also enhanced CO2 emissions in the long run. Thus, clean environmental policies and recommendations can be revised and proposed based on nonlinear findings in the modern era.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets/ materials used and/or analyzed for present manuscript are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Ali S (2019a) Investigating the non-linear relationship between urbanization and CO 2 emissions: An empirical analysis. Air Qual Atmos Health 12(8):945–953
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali, N (2019b) Does globalization increase the ecological footprint? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(18):18565–18582
Anser MK, Khan MA, Awan U, Batool R, Zaman K, Imran M, Sasmoko, Indrianti Y, Khan A, Bakar ZA (2020) The role of technological innovation in a dynamic model of the environmental supply chain curve: evidence from a panel of 102 countries. Processes 8(9):1033
Awan U (2020) Steering for sustainable development goals: a typology of sustainable innovation. In: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals
Awan U, Kraslawski A, Huiskonen J (2019) Progress from blue to the green world: multilevel governance for pollution prevention planning and sustainability. In: Handbook of environmental materials management
Awan U, Arnold MG, Gölgeci I (2021a) Enhancing green product and process innovation: towards an integrative framework of knowledge acquisition and environmental investment. Bus Strateg Environ 30(2):1283–1295
Awan U, Bhutta MKS, Huiskonen J, Kraslawski A (2021b) Deployment of sustainable development framework in export manufacturing firms for the common good. In: Integrating Social Responsibility and Sustainable Development: Addressing Challenges and Creating Opportunities, p 133
Bardhan P (1997) Corruption and development: a review of issues. J Econ Lit 35(3):1320–1346
Batterbury SP, Fernando JL (2006) Rescaling governance and the impacts of political and environmental decentralization: an introduction. World Dev 34(11):1851–1863
Blomquist W, Dinar A, Kemper KE (2010) A framework for institutional analysis of decentralization reforms in natural resource management. Soc Nat Resour 23(7):620–635
Chang CP, Hao Y (2017) Environmental performance, corruption and economic growth: global evidence using a new data set. Appl Econ 49(5):498–514
Chen X, Chang CP (2020) Fiscal decentralization, environmental regulation, and pollution: a spatial investigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–23
Cheng Y, Awan U, Ahmad S, Tan Z (2021) How do technological innovation and fiscal decentralization affect the environment? A story of the fourth industrial revolution and sustainable growth. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 162:120398
Dean JM, Lovely ME, Wang H (2005) Are foreign investors attracted to weak environmental regulations? Evaluating the evidence from China. The World Bank
Du J, Sun Y (2021) The nonlinear impact of fiscal decentralization on carbon emissions: from the perspective of biased technological progress. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–10
Fell H, Kaffine DT (2014) Can decentralized planning really achieve first-best in the presence of environmental spillovers? J Environ Econ Manag 68(1):46–53
Goel RK, Mazhar U, Nelson MA, Ram R (2017) Different forms of decentralization and their impact on government performance: Micro-level evidence from 113 countries. Econ Model 62:171–183
Gray WB, Shadbegian RJ (2004) “Optimal” pollution abatement—whose benefits matter, and how much? J Environ Econ Manag 47(3):510–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2003.01.001
Hafeez M, Chunhui Y, Strohmaier D, Ahmed M, Jie L (2018) Does finance affect environmental degradation: evidence from One Belt and One Road Initiative region? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(10):9579–9592
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Yuan Q, Zhuo Z, Stromaier D (2019) A global prospective of environmental degradations: economy and finance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(25):25898–25915
Halkos GE, Paizanos EΑ (2013) The effect of government expenditure on the environment: an empirical investigation. Ecol Econ 91:48–56
He Q (2015) Fiscal decentralization and environmental pollution: evidence from Chinese panel data. China Econ Rev 36:86–100
Helland E, Whitford AB (2003) Pollution incidence and political jurisdiction: evidence from the TRI. J Environ Econ Manag 46(3):403–424
Holmstrom B, Milgrom P (1991) Multitask principal-agent analyses: incentive contracts, asset ownership, and job design. J Law Econ Org 7:24–52
Ji X, Umar M, Ali S, Ali W, Tang K, Khan Z (2020) Does fiscal decentralization and eco-innovation promote sustainable environment? A case study of selected fiscally decentralized countries. Sustain Dev
Khan Z, Ali S, Dong K, Li RYM (2021) How does fiscal decentralization affect CO2 emissions? The roles of institutions and human capital. Energy Econ 94:105060
Köllner T, Schelske O, Seidl I (2002) Integrating biodiversity into intergovernmental fiscal transfers based on cantonal benchmarking: a Swiss case study. Basic Appl Ecol 3(4):381–391
Konisky DM (2007) Regulatory Competition and Environmental Enforcement: Is There a Race to the Bottom? Am J Polit Sci 51(4):853–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5907.2007.00285.x
Levinson A (2003) Environmental regulatory competition: a status report and some new evidence. Natl Tax J 56(1 I):91–106. https://doi.org/10.17310/ntj.2003.1.06
Li B, Hao Y, Chang CP (2018) Does an anticorruption campaign deteriorate environmental quality? Evidence from China. Energy Environ 29(1):67–94
Li X, Yu Z, Salman A, Ali Q, Hafeez M, Aslam MS (2021a) The role of financial development indicators in sustainable development environmental degradation nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1-12
Li X, Younas MZ, Andlib Z, Ullah S, Sohail S, Hafeez M (2020b) Examining the asymmetric effects of Pakistan’s fiscal decentralization on economic growth and environmental quality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(5):5666–5681
List JA, Gerking S (2000) Regulatory federalism and environmental protection in the United States. J Reg Sci 40(3):453–471
Liu Y, Zhu J, Li EY, Meng Z, Song Y (2020) Environmental regulation, green technological innovation, and eco-efficiency: The case of Yangtze river economic belt in China. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 155:119993
Mahmood MT, Shahab S, Hafeez M (2020) Energy capacity, industrial production, and the environment: an empirical analysis from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:4830–4839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07161-z
Millimet DL (2003) Assessing the empirical impact of environmental federalism. J Reg Sci 43(4):711–733
Mu R (2018) Coupling of problems, political attention, policies and institutional conditions: explaining the performance of environmental targets in the national five-year plans in China. Sustainability 10(5):1477
Oates WE (1993) Fiscal decentralization and economic development. Natl Tax J 46(2):237–243
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Pickman HA (1998) The effect of environmental regulation on environmental innovation. Bus Strateg Environ 7(4):223–233
Rassier DG, Earnhart D (2011) Short-run and long-run implications of environmental regulation on financial performance. Contemp Econ Policy 29(3):357–373
Shin Y, Yu B, Greenwood-Nimmo M (2014) Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. In: Festschrift in honor of Peter Schmidt. Springer, New York, pp 281–314
Sigman H (2014) Decentralization and environmental quality: an international analysis of water pollution levels and variation. Land Econ 90(1):114–130
Smulders S, Tsur Y, Zemel A (2012) Announcing climate policy: can a green paradox arise without scarcity? J Environ Econ Manag 64(3):364–376
Song M, Du J, Tan KH (2018) Impact of fiscal decentralization on green total factor productivity. Int J Prod Econ 205:359–367
Su CW, Umar M, Khan Z (2021) Does fiscal decentralization and eco-innovation promote renewable energy consumption? Analyzing the role of political risk. Sci Total Environ 751:142220
Sun G, Yuan C, Hafeez M, Raza S, Jie L, Liu X (2020) Does regional energy consumption disparities assist to control environmental degradation in OBOR: an entropy approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(7):7105–7119
Tian GP, Wang YH (2018) Spatial spillover effects between fiscal decentralization, local governments competition and carbon emissions. China Popul Resour Environ 28(10):36–44
Ullah S, Majeed MT, Chishti MZ (2020) Examining the asymmetric effects of fiscal policy instruments on environmental quality in Asian economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(30):38287–38299
Zhang K, Zhang ZY, Liang QM (2017) An empirical analysis of the green paradox in China: from the perspective of fiscal decentralization. Energy Policy 103:203–211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Phan The Cong has provided the idea. Phan The Cong, Vipin Jain , Eko Priyo Purnomo, Muhammad Monirul Islam, and John William Grimaldo Guerrero have done the data acquisitions and analysis and written the whole draft. Nafeesa Mughal and Sana Ullah read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
I am free to contact any of the people involved in the research to seek further clarification and information.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
The Phan, C., Jain, V., Purnomo, E.P. et al. Controlling environmental pollution: dynamic role of fiscal decentralization in CO2 emission in Asian economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 65150–65159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15256-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15256-9