Abstract
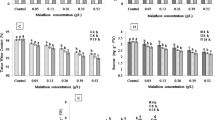
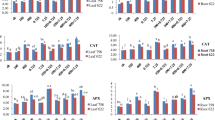
The current study investigated the putative role of salicylic acid (SA) in modulating Pb2+-induced DNA and oxidative damage in Allium cepa roots. Pb2+ exposure enhanced free radical generation and reduced DNA integrity and antioxidant machinery after 24 h; however, SA pre-treatment (for 24 h) ameliorated Pb2+ toxicity. Pb2+ exposure led to an increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) accumulation and enhanced superoxide radical and hydroxyl radical levels. SA improved the efficiency of enzymatic antioxidants (ascorbate and guaiacol peroxidases [APX, GPX], superoxide dismutases [SOD], and catalases [CAT]) at 50-μM Pb2+ concentration. However, SA pre-treatment could not improve the efficiency of CAT and APX at 500 μM of Pb2+ treatment. Elevated levels of ascorbate and glutathione were observed in A. cepa roots pre-treated with SA and exposed to 50 μM Pb2+ treatment, except for oxidized glutathione. Nuclear membrane integrity test demonstrated the ameliorating effect of SA by reducing the number of dark blue–stained nuclei as compared to Pb2+ alone treatments. SA was successful in reducing DNA damage in cell exposed to higher concentration of Pb2+ (500 μM) as observed through comet assay. The study concludes that SA played a major role in enhancing defense mechanism and protecting against DNA damage by acclimatizing the plant to Pb2+-induced toxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Khan S (2020) Heavy metal phytotoxicity: DNA Damage. In: Faisal M, Saquib Q, Alatar AA, Al-Khedhairy AA (eds) Cellular and molecular phytotoxicity of heavy metals. Springer, Cham, Switzerland, pp 157–177
Agnihotri A, Gupta P, Dwivedi A, Seth CS (2018) Counteractive mechanism(s) of salicylic acid in response to lead toxicity in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. cv. Varuna. Planta 248:49–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2867-0
Ahmad B, Jalee H, Sadiq Y, Khan MMA, Shabbir A (2018) Response of exogenous salicylic acid on cadmium induced photosynthetic damage, antioxidant metabolism and essential oil production in peppermint. Plant Growth Regul 86:273–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-018-0427-z
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang M-Q (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9030042
Amjadi Z, Namdjoyan S, Soorki AA (2021) Exogenous melatonin and salicylic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seedlings. Ecotoxicology 30:387–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02364-y
ATSDR (2019) Priority list of hazardous substances. Agency for Toxic Substances and Diseases. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/SPL/index.html
Belkadhi A, De Haro A, Obregon S, Chaïbi W, Djebali W (2015) Positive effects of salicylic acid pretreatment on the composition of flax plastidial membrane lipids under cadmium stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1457–1467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3475-6
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chandel S, Kaur S, Issa M, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2019) Appraisal of immediate and late effects of mobile phone radiations at 2100 MHz on mitotic activity and DNA integrity in root meristems of Allium cepa. Protoplasma 256:1399–1407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-019-01386-y
Duez P, Dehon G, Kumps A, Dubois J (2003) Statistics of the comet assay: a key to discriminate between genotoxic effects. Mutagenesis 18:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/18.2.159
Duman F, Akosy A, Ozturk F, Erciyes AC (2010) Exogenous salicylate application affects the lead and copper accumulation characteristics of Lemna gibba L. Z Naturforsch C 65:675–680. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2010-11-1207
El Dakak RA, Hassan IA (2020) The alleviative effects of salicylic acid on physiological indices and defense mechanisms of maize (Zea mays L. Giza 2) stressed with cadmium. Environ Process 7:873–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00448-1
Emamverdian A, Ding Y, Mokhberdoran F (2020) The role of salicylic acid and gibberellin signaling in plant responses to abiotic stress with an emphasis on heavy metals. Plant Signal Behav 15:1777372. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2020.1777372
Faraz A, Faizan M, Sami F, Siddiqui H, Hayat S (2019) Supplementation of salicylic acid and citric acid for alleviation of cadmium toxicity to Brassica juncea. J Plant Growth Regul 39:641–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-10007-0
Gichner T, Žnidar I, Száková J (2008) Evaluation of DNA damage and mutagenicity induced by lead in tobacco plants. Mutat Res 652:186–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.02.009
Hajaji AN, Gouia H (2019) ROS scavenging and NH4+ nitrogen fertilizer roles in alleviation of Cd-induced oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Russ J Plant Physiol 66:495–502. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443719030063
Halim NIA, Phang IC (2017) Salicylic acid mitigates Pb stress in Nicotiana tabacum. Sci Heritage J 1:16–19. https://doi.org/10.26480/gws.01.2017.16.19
Hediji H, Kharbech O, Massoud MB, Boukari N, Debez A, Chaibi W, Chaoui A, Djebali W (2021) Salicylic acid mitigates cadmium toxicity in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings by modulating cellular redox status. Environ Exp Bot 186:104432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104432
Hu ZB, Cools T, De Veylder L (2016) Mechanisms used by plants to cope with DNA damage. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:439–462. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-111902
Huang D, Sun Y, Ma Z, Ke M, Cui Y, Chen Z, Chen C, Ji C, Tran TM, Yang L, Lam SM (2019) Salicylic acid-mediated plasmodesmal closure via Remorin-dependent lipid organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116:21274–21284. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1911892116
Hussain SJ, Khan NA, Anjum NA, Masood A, Khan MIR (2020) Mechanistic elucidation of salicylic acid and sulphur-induced defence systems, nitrogen metabolism, photosynthetic, and growth potential of mungbean (Vigna radiata) under salt stress. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10159-4
Islam F, Yasmeen T, Arif MS, Riaz M, Shahzad SM, Imran Q, Ali I (2016) Combined ability of chromium (Cr) tolerant plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) and salicylic acid (SA) in attenuation of chromium stress in maize plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 108:456–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.08.014
Kaur G, Kaur S, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK, Rishi V (2015) Biochemical adaptations in Zea mays roots to short-term Pb2+ exposure: ROS generation and metabolism. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1564-y
Khan MIR, Fatma M, Per TS, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:462. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00462
Kohli SK, Bali S, Tejpal R, Bhalla V, Verma V, Bhardwaj R, Alqarawi AA, Abd-Allah EF, Ahmad P (2019) In-situ localization and biochemical analysis of bio-molecules reveals Pb-stress amelioration in Brassica juncea L. by co-application of 24-epibrassinolide and salicylic acid. Sci Rep 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39712-2
Kumar A, Prasad MNV, Achary VMM, Panda BB (2013) Elucidation of lead-induced oxidative stress in Talinum triangulare roots by analysis of antioxidant responses and DNA damage at cellular level. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:4551–4561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1354-6
Kumar A, Kumar A, Cabral-Pinto MMS, Chaturvedi AK, Shabnam AA, Subrahmanyam G, Mondal R, Gupta DK, Malyan SK, Kumar S, Khan A, Yadav KK (2020) Lead toxicity: health hazards, influence on food chain, and sustainable remediation approaches. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(7):2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072179
Kumari A, Pandey-Rai S (2018) Enhanced arsenic tolerance and secondary metabolism by modulation of gene expression and proteome profile in Artemisia annua L. after application of exogenous salicylic acid. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:590–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.10.010
Li C, Zhou K, Qin W, Tian C, Qi M, Yan X, Han W (2019) A review on heavy metals contamination in soil: effects, sources, and remediation techniques. Soil Sediment Contam 28:380-394. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2019.1592108
Liu S, Dong Y, Xu L, Kong J (2014) Effects of foliar applications of nitric oxide and salicylic acid on salt-induced changes in photosynthesis and antioxidative metabolism of cotton seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 73:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9868-6
López-Orenes A, Martínez-Pérez A, Calderón AA, Ferrer MA (2014) Pb-induced responses in Zygophyllum fabago plants are organ-dependent and modulated by salicylic acid. Plant Physiol Biochem 84:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.09.003
Mohamed HI, El-Shazly HH, Badr A (2020) Role of salicylic acid in biotic and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. In: Lone R, Shuab R, Kamili A (eds) Plant Phenolics in Sustainable Agriculture. Springer, Singapore, pp 533–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4890-1_23
Mostofa MG, Fujita M (2013) Salicylic acid alleviates copper toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by up-regulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicology 22:959–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1073-x
Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Alam MM, Fujita M (2015) Roles of exogenous glutathione in antioxidant defense system and methylglyoxal detoxification during salt stress in mung bean. Biol Plant 59:745–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-015-0542-x
Namdjoyan S, Kermanian H, Soorki AA, Tabatabaei SM, Elyasi N (2017) Interactive effects of salicylic acid and nitric oxide in alleviating zinc toxicity of Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Ecotoxicology 26:752–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1806-3
Nikolova I, Georgieva M, Stoilov L, Katerova Z, Todorova D (2013) Optimization of neutral comet assay for studying DNA double-strand breaks in pea and wheat. J Biosci Biotechnol 2:151–157
Sharma M, Mahajan P, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2019) 24-Epibrassinolide pre-treatment reduces alkaline-induced oxidative stress in red rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23192–23197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05474-7
Shi GR, Cai QS, Liu QQ, Wu L (2009) Salicylic acid-mediated alleviation of cadmium toxicity in hemp plants in relation to cadmium uptake, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzymes. Acta Physiol Plant 31:969–977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0312-5
Sihag S, Brar B, Joshi UN (2019) Salicylic acid induces amelioration of chromium toxicity and affects antioxidant enzyme activity in Sorghum bicolor L. Int J Phytoremediation 21:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1524827
Silva S, Silva P, Oliveira H, Gaivão I, Matos M, Pinto-Carnide O, Santos C (2017) Pb low doses induced genotoxicity in Lactuca sativa plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 112:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.12.026
Singh HP, Kaur S, Batish DR, Sharma VP, Sharma N, Kohli RK (2009) Nitric oxide alleviates arsenic toxicity by reducing oxidative damage in the roots of Oryza sativa (rice). Nitric Oxide 20:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2009.02.004
Singh VP, Kumar J, Singh M, Singh S, Prasad SM, Dwivedi R, Singh MPVVB (2016) Role of salicylic acid-seed priming in the regulation of chromium (VI) and UV-B toxicity in maize seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 78:79–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0076-4
Surapu V, Ediga A, Meriga B (2014) Salicylic acid alleviates aluminum toxicity in tomato seedlings (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) through activation of antioxidant defense system and proline biosynthesis. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 5:777–789. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2014.59091
Sychta K, Słomka A, Kuta E (2021) Insights into plant programmed cell death induced by heavy metals—discovering a terra incognita. Cells 10:65. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010065
Vareda JP, Valente AJM, Durães L (2019) Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: a review. J Environ Manag 246:101–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.126
Wang S, Wei M, Cheng H, Wu B, Du D, Wang C (2020) Indigenous plant species and invasive alien species tend to diverge functionally under heavy metal pollution and drought stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 205:111160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111160
Wang F, Tan H, Huang L, Cai C, Ding Y, Bao H, Chen Z, Zhu C (2021) Application of exogenous salicylic acid reduces Cd toxicity and Cd accumulation in rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207:111198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111198
Wani AB, Chadar H, Wani AH, Singh S, Upadhyay N (2017) Salicylic acid to decrease plant stress. Environ Chem Lett 15:101–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-016-0584-0
Xia H, Ni Z, Hu R, Lin L, Deng H, Wang J, Tang Y, Sun G, Wang X, Li H, Liao M (2020) Melatonin alleviates drought stress by a non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidative system in kiwifruit seedlings. Int J Mol Sci 21:852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030852
Zaid A, Mohammad F, Wani SH, Siddique KMH (2019) Salicylic acid enhances nickel stress tolerance by up-regulating antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems in mustard plants. Ecotoxic Environ Safe 180:575–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.042
Zhang X, Zhang H, Zhang H, Tang M (2020) Exogenous melatonin application enhances Rhizophagus irregularis symbiosis and induces the antioxidant response of Medicago truncatula under lead stress. Front Microbiol 11:516. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00516
Zulfiqar U, Farooq M, Hussain S, Maqsood M, Hussain M, Ishfaq M, Ahmad M, Anjum MZ (2019) Lead toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation. J Environ Manag 250:109557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109557
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
The funds for undertaking this research were provided by University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HPS and DRB conceived the idea and designed this study. GK collected the data. GK, PS, and SR did the analysis and wrote the draft. PS and SR edited the earlier versions of the manuscript. HPS, DRB, and RKK edited the final versions of manuscript. All the authors contributed to the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philipp Gariguess
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Gurpreet Kaur, Padma Sharma and Sonia Rathee are equal Principal/first authors.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, G., Sharma, P., Rathee, S. et al. Salicylic acid pre-treatment modulates Pb2+-induced DNA damage vis-à-vis oxidative stress in Allium cepa roots. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 51989–52000 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14151-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14151-7