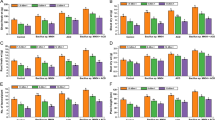
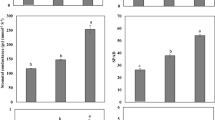
Abstract
Soil contamination with readily soluble salts and heavy metals is a major challenge concerning sustainable crop production. The use of organic wastes in agriculture not only helps in waste reduction but also acts as a soil conditioner and bio-stimulant for enhancing crop growth. In this regard, a pot experiment was conducted to investigate the effect of raw and processed animal manure (AM) on the growth, yield, and physicochemical parameters of Brassica napus L. developed under salinity and Ni stress. The experiment comprised two salinity levels (1.05 and 8 dS m−1), two Ni levels (0 and 50 mg kg−1), and two types of AMs (raw and processed at a rate of 2% w/w). A control treatment without AM incorporation was also included. In results, the application of AM markedly increased the growth and yield of B. napus under Ni and salinity stress; at the same time, it improved the physiological and chemical parameters of the said crop. Similarly, incorporation of processed AM significantly improved nutrient uptake and decreased Na/K ratios in the shoot and grain under the different stress conditions, as compared to the control. Likewise, Ni uptake in the grain, shoot, and root samples was also significantly reduced under the AM treatment. Also, the application of AM significantly reduced the daily intake of metal (DIM) index and the health risk index (HRI) values under the different stress conditions, as compared to the control. In conclusion, the application of processed AM constitutes an effective agricultural strategy to alleviate the adverse effects of Ni and salinity stress on growth, physiology, and yield of B. napus, thus resulting in enhanced productivity, as well as reduced risks associated with human health.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abrar MM, Saqib M, Abbas G, Atiq-ur-Rahman M, Mustafa A, Shah SAA, Mehmood K, Maitlo AA, Sun N, Xu M (2020) Evaluating the contribution of growth, physiological, and ionic components towards salinity and drought stress tolerance in Jatropha curcas. Plants 9(11):1574
Ahmad M, Naseer I, Hussain A, Zahid Mumtaz M, Mustafa A, Hilger TH, Ahmad Zahir Z, Minggang X (2019) Appraising endophyte–plant symbiosis for improved growth, nodulation, nitrogen fixation, and abiotic stress tolerance: an experimental investigation with chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Agron 9(10):621
Amin H, Arain BA, Jahangir TM, Abbasi MS, Amin F (2018) Accumulation and distribution of lead (Pb) in plant tissues of guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) and sesame (Sesamum indicum L.): profitable phytoremediation with biofuel crops. Geo Ecol Landsc 2:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2018.1452464
Arif MS, Yasmeen T, Shahzad SM, Riaz M, Rizwan M, Iqbal S, Asif M, Soliman MH, Ali S (2019) Lead toxicity induced phytotoxic effects on mung bean can be relegated by lead tolerant Bacillus subtilis (PbRB3). Chemosphere 234:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.024
Bashir MA, Naveed M, Ahmad Z, Gao B, Mustafa A, Núñez-Delgado A (2020) Combined application of biochar and sulfur regulated growth, physiological, antioxidant responses and Cr removal capacity of maize (Zea mays L.) in tannery polluted soils. J Environ Manag 259:110051
Caporale AG, Pigna M, Sommella A, Dynes JJ, Cozzolino V, Violante A (2013) Influence of compost on the mobility of arsenic in soil and its uptake by bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) irrigated with arsenite-contaminated water. J Environ Manag 128:837–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.06.041
Debiase G, Montemurro F, Fiore A, Rotolo C, Farrag K, Miccolis A, Brunetti G (2016) Organic amendment and minimum tillage in winter wheat grown in Mediterranean conditions: effects on yield performance, soil fertility and environmental impact. Eur J Agron 75:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.12.009
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00025-9
Ditta A, Khalid A (2016) Bio-organo-phos: A sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. In: Larramendy M, Soloneski S (eds) Organic fertilizers-from basic concepts to applied outcomes. InTech Croatia, pp 109–136. https://doi.org/10.5772/62473
Ditta A, Arshad M, Zahir ZA, Jamil A (2015) Comparative efficacy of rock phosphate enriched organic fertilizer vs. mineral phosphatic fertilizer for nodulation, growth and yield of lentil. Int J Agric Biol 17:589–595. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/17.3.14.954
Ditta A, Imtiaz M, Mehmood S, Rizwan MS, Mubeen F, Aziz O, Qian Z, Ijaz R, Tu S (2018a) Rock phosphate enriched organic fertilizer with phosphate solubilizing microorganisms improves nodulation, growth and yield of legumes. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 49:2715–2725. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2018.1538374
Ditta A, Muhammad J, Imtiaz M, Mehmood S, Qian Z, Tu S (2018b) Application of rock phosphate enriched composts increases nodulation, growth and yield of chickpea. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 7:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-017-0187-1
Dolliver H, Gupta S (2008) Antibiotic losses in leaching and surface runoff from manure-amended agricultural land. J Environ Qual 37:1227–1237. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2007.0392
EPA-IRIS. Nickel, soluble salts; CASRN Various. Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) Chemical Assessment Summary, File First On-Line 09/30/1987. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0271_summary.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2021)
Estefan G, Sommer R, Ryan J (2013) Soil and plant analysis: laboratory manual. In: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA), Beirut, Lebanon
Farooq N, Kanwal S, Ditta A, Hussain A, Naveed M, Jamshaid MU, Iqbal M (2018) Comparative efficacy of KCl blended composts vs. sole application of KCl or K2SO4 in improving K nutrition, photosynthetic capacity and growth of maize. Soil Environ 37:68–74. https://doi.org/10.25252/SE/17/51273
Fitz WJ, Wenzel WW (2002) Arsenic transformations in the soil-rhizosphere-plant system: fundamentals and potential application to phytoremediation. J Biotechol 99:259–278
Fourati E, Wali M, Vogel-Mikuš K, Abdelly C, Ghnaya T (2016) Nickel tolerance, accumulation and subcellular distribution in the halophytes Sesuvium portulacastrum and Cakile maritima. Plant Physiol Biochem 108:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.07.024
Garau G, Porceddu A, Sanna M, Silvetti M, Castaldi P (2019) Municipal solid wastes as a resource for environmental recovery: impact of water treatment residuals and compost on the microbial and biochemical features of As and trace metal-polluted soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.007
Genchi G, Carocci A, Lauria G, Sinicropi MS, Catalano A (2020) Nickel: human health and environmental toxicology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030679
Ghallab A, Usman ARA (2007) Effect of sodium chloride-induced salinity on phyto-availability and speciation of Cd in soil solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 185:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9424-y
Ghirardini A, Grillini V, Verlicchi P (2020) A review of the occurrence of selected micropollutants and microorganisms in different raw and treated manure–environmental risk due to antibiotics after application to soil. Sci Total Environ 707:136118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136118
Godfray HCJ, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Pretty J, Robinson S, Thomas SM, Toulmin C (2010) Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Sci 327:812–818. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1185383
Guellim A, Catterou M, Chabrerie O, Tetu T, Hirel B, Dubois F, Ahmed HB, Kichey T (2019) Identification of phenotypic and physiological markers of salt stress tolerance in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) through integrated analyses. Agron 9:844. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120844
Hamid S, Ahmad I, Akhtar MJ, Iqbal MN, Shakir M, Tahir M, Rasool A, Sattar A, Khalid M, Ditta A, Zhu B (2021) Bacillus subtilis Y16 and biogas slurry enhanced potassium to sodium ratio and physiology of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) to mitigate salt stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13419-2
Hernández T, Chocano C, Moreno JL, García C (2016) Use of compost as an alternative to conventional inorganic fertilizers in intensive lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) crops—effects on soil and plant. Soil Tillage Res 160:14–22
Hofmann N, Beaulieu MS (2001) A geographical profile of manure production in Canada, 2001. Statistics Canada, Ottawa, p 24
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P (2012) What a waste: a global review of solid waste management. In: Urban Development Series. World Bank, Washington, DC
Huang H, Rizwan M, Li M, Song F, Zhou S, He X, Ding R, Dai Z, Yuan Y, Cao M, Xiong S, Tu S (2019) Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic silicon fertilizers on antioxidant response, Cd/Pb accumulation and health risk assessment in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ Pollut 255:113146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113146
Hussain S, Khaliq A, Tanveer M, Matloob A, Hussain HA (2018) Aspirin priming circumvents the salinity-induced effects on wheat emergence and seedling growth by regulating starch metabolism and antioxidant enzyme activities. Acta Physiol Plant 40:68
Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Ditta A, Tahir MU, Ahmad M, Mumtaz MZ, Hayat K, Hussain S (2020) Production and implication of bio-activated organic fertilizer enriched with zinc-solubilizing bacteria to boost up maize (Zea mays L.) production and biofortification under two cropping seasons. Agron 10:39. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010039
Jafarinia M, Shariati M (2012) Effects of salt stress on photosystem II of canola plant (Brassica napus, L.) probing by chlorophyll a fluorescence measurement. Iran J Sci Technol 36:73–76. https://doi.org/10.22099/IJSTS.2012.2058
Jan FA, Ishaq M, Khan S, Ihsanullah I, Ahmad I, Shakiryllah M (2010) A comparative study of human health risks via consumption of food crops grown on wastewater irrigated soil (Peshawar) and relatively clean water irrigated soil (lower Dir). J Hazard Mater 179:612–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.047
Kamran M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Zong Y, Abbasi GH, Rafiq MT, Shaaban M, Mustafa A, Bashir S, Rafay M, Mehmood S (2019) Biochar alleviates Cd phytotoxicity by minimizing bioavailability and oxidative stress in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) cultivated in Cd-polluted soil. J Environ Manag 250:109500
Kamran M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Huang L, Riaz M, Bashir S, Mustafa A, Abbasi GH, Xue B, Ali U (2020) Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J Plant Growth Regul 39(1):266–281
Kotula L, Clode PL, Jimenez JDLC, Colmer TD (2019) Salinity tolerance in chickpea is associated with the ability to ‘exclude’ Na from leaf mesophyll cells. J Exp Bot 70:4991–5002. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz241
Lakhdar A, Falleh H, Ouni Y, Oueslati S, Debez A, Ksouri R, Abdelly C (2011) Municipal solid waste compost application improves productivity, polyphenol content, and antioxidant capacity of Mesembryanthemum edule. J Hazard Mater 191:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.092
Latif A, Bilal M, Asghar W, Azeem M, Ahmad MI, Abbas A, Ahmad MZ, Shahzad T (2018) Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables and assessment of their potential health risk. J Environ Anal Chem 5:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2380-2391.1000234
Lee CG, Lee S, Park JA, Park C, Lee SJ, Kim SB, An B, Yun ST, Lee SH, Choi JW (2017) Removal of copper, nickel and chromium mixtures from metal plating wastewater by adsorption with modified carbon foam. Chemosphere 166:203–211
Lim SL, Lee LH, Wu TY (2016) Sustainability of using composting and vermicomposting technologies for organic solid waste biotransformation: recent overview, greenhouse gases emissions and economic analysis. J Clean Prod 111:262–278
Li-Ping L, Xiao-Hua L, Hong-Bo S, Zhao-Pu L, Ya T, Quan-Suo Z, Jun-Qin Z (2015) Ameliorants improve saline–alkaline soils on a large scale in northern Jiangsu Province. China Ecol Eng 81:328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.04.032
Liu YZ, Imtiaz M, Ditta A, Rizwan MS, Ashraf M, Mehmood S, Aziz O, Mubeen F, Ali M, Elahi NN, Ijaz R, Lelel S, Shuang C, Tu S (2020) Response of growth, antioxidant enzymes and root exudates production towards As stress in Pteris vittata and Astragalus sinicus colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:2340–2352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06785-5
Mayak S, Tirosh T, Glick BR (2004) Plant growth-promoting bacteria that confer resistance in tomato to salt stress. Plant Sci 166:525–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2003.10.025
Mclean JE, Bledsoe BE (1992) Behavior of metals in soils. EPA Ground Water Issue EPA 540-S-92-018:25. Environ Protect Agency, Washington, DC, USA
Mehmood S, Saeed DA, Rizwan M, Khan MN, Aziz O, Bashir S, Ibrahim M, Ditta A, Akmal M, Mumtaz MA, Ahmed E, Irshad S, Imtiaz M, Tu S, Shaheen A (2018a) Impact of different amendments on biochemical responses of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) plants grown in lead-cadmium contaminated soil. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.09.019
Mehmood S, Rizwan M, Bashir S, Ditta A, Aziz O, Yong LZ, Dai Z, Akmal M, Ahmed W, Adeel M, Imtiaz M, Tu S (2018b) Comparative effects of biochar, slag and ferrous–Mn ore on lead and cadmium immobilization in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2222-3
Moodie CD, Smith HW, McCreery RA 1959. Laboratory manual of soil fertility, 13, pp. 31-39
Muhammad N, Nafees M, Khan MH, Ge L, Lisak G (2020) Effect of biochars on bioaccumulation and human health risks of potentially toxic elements in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivated on industrially contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 260:113887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113887
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Mustafa A, Minggang X, Shah SAA, Abrar MM, Nan S, Baoren W, Zejiang C, Saeed Q, Naveed M, Mehmood K, Núñez-Delgado A (2020) Soil aggregation and soil aggregate stability regulate organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a red soil of southern China. J Environ Manag 270:110894
Mustafa A, Hu X, Abrar MM, Shah SAA, Nan S, Saeed Q, Kamran M, Naveed M, Conde-Cid M, Hongjun G, Ping Z (2021) Long-term fertilization enhanced carbon mineralization and maize biomass through physical protection of organic carbon in fractions under continuous maize cropping. Appl Soil Ecol 165:103971
Naeem MA, Shabbir A, Amjad M, Abbas G, Imran M, Murtaza B, Tahir M, Ahmad A (2020) Acid treated biochar enhances cadmium tolerance by restricting its uptake and improving physio-chemical attributes in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110218
Naliwajski MR, Skłodowska M (2018) The relationship between carbon and nitrogen metabolism in cucumber leaves acclimated to salt stress. Peer J 6:e6043. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6043
Naveed M, Sajid H, Mustafa A, Niamat B, Ahmad Z, Yaseen M, Kamran M, Rafique M, Ahmar S, Chen JT (2020a) Alleviation of salinity-induced oxidative stress, improvement in growth, physiology and mineral nutrition of canola (Brassica napus L.) through calcium-fortified composted animal manure. Sustainability 12(3):846
Naveed M, Mustafa A, Azhar SQTA, Kamran M, Zahir ZA, Núñez-Delgado A (2020b) Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN and tree twigs derived biochar together retrieved Pb-induced growth, physiological and biochemical disturbances by minimizing its uptake and translocation in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). J Environ Manag 257:109974
Naveed M, Bukhari SS, Mustafa A, Ditta A, Alamri S, El-Esawi MA, Rafique M, Ashraf S, Siddiqui MH (2020c) Mitigation of nickel toxicity and growth promotion in sesame through the application of a bacterial endophyte and zeolite in nickel contaminated soil. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(23):8859
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In: Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods, pp. 961-1010. SSSA Book Ser. 5.3. Madison, WI: ASA and SSSA. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.3.c34
Niamat B, Naveed M, Ahmad Z, Yaseen M, Ditta A, Mustafa A, Rafique M, Bibi R, Minggang X (2019) Calcium-enriched animal manure alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress on growth, physiology and nutrients homeostasis of Zea mays L. Plants 8:480. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8110480
Nie J, Pan Y, Shi J, Guo Y, Yan Z, Duan X, Xu M (2015) A comparative study on the uptake and toxicity of nickel added in the form of different salts to maize seedlings. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:15075–15087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121214972
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorous. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal, Madison, pp 403–430
Ramzani PMA, Shan L, Anjum S, Khan W-U-D, Ronggui H, Iqbal M, Virk ZA, Kausar S (2017) Improved quinoa growth, physiological response, and seed nutritional quality in three soils having different stresses by the application of acidified biochar and compost. Plant Physiol Biochem 116:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.05.003
Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Zhu J, Yousaf B, Hussain M, Ali L, Ditta A, Ihsan MZ, Huang G, Ashraf M, Hu H (2021) Immobilization of Pb and Cu by organic and inorganic amendments in contaminated soil. Geoderma 385:114803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114803
Ryan J, Estefan G, Rashid A (2001) Soil and plant analysis: laboratory manual. ICARDA, Aleppo
Sabir M, Ali A, Zia-Ur-Rehman M, Hakeem KR (2015) Contrasting effects of farmyard manure (FYM) and compost for remediation of metal contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediat 17:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2014.898019
Sabir A, Naveed M, Bashir MA, Hussain A, Mustafa A, Zahir ZA, Kamran M, Ditta A, Núñez-Delgado A, Saeed Q, Qadeer A (2020) Cadmium mediated phytotoxic impacts in Brassica napus: managing growth, physiological and oxidative disturbances through combined use of biochar and Enterobacter sp. MN17. J Environ Manag 265:110522
Saeed Z, Naveed M, Imran M, Bashir M, Sattar A, Mustafa A, Xu A, M. (2019) Combined use of Enterobacter sp. MN17 and zeolite reverts the adverse effects of cadmium on growth, physiology and antioxidant activity of Brassica napus. PLoS One 14:e0213016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213016
Saleem MH, Kamran M, Zhou Y, Parveen A, Rehman M, Ahmar S, Malik Z, Mustafa A, Anjum RMA, Wang B, Liu L (2020) Appraising growth, oxidative stress and copper phytoextraction potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) grown in soil differentially spiked with copper. J Environ Manag 257:109994
Shahbaz AK, Lewińska K, Iqbal J, Ali Q M-u-R, Iqbal M, Abbas F, Tauqeer HM, Ramzani PMA (2018) Improvement in productivity, nutritional quality, and antioxidative defense mechanisms of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) in nickel contaminated soil amended with different biochar and zeolite ratios. J Environ Manag 218:256–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.046
Shahzad H, Ullah S, Iqbal M, Bilal HM, Shah GM, Ahmad S, Zakir A, Ditta A, Farooqi MA, Ahmad I (2019) Effects of salinity sources and levels on growth, physiology and nutrient contents of maize crop. Ital J Agron 14:199–207. https://doi.org/10.4081/ija.2019.1326
Sohail MI, Arif M, Rauf A, Rizwan M, Ali S, Saqib M, Zia-ur-Rehman M (2019) Organic manures for cadmium tolerance and remediation. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Prasad MNV, Nahar K (eds) Cadmium tolerance in plants: agronomic, molecular, signaling, and omic approaches. Elsevier Inc, pp 19–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815794-7.00002-3
Soltanpour PN (1985) Use of ammonium bicarbonate DTPA soil test to evaluate elemental availability and toxicity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 16:323–338. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103628509367607
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dickey DA (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 3rd edn. Mc-Graw-Hill Co, New York, USA
Torres GN, Camargos SL, Weber OLDS, Maas KDB, Scaramuzza WL, Pereira M (2016) Growth and micronutrient concentration in maize plants under nickel and lime applications. Revista Caatinga 29:796–804. https://doi.org/10.1590/1983-21252016v29n403rc
Tsolakidou MD, Stringlis IA, Fanega-Sleziak N, Papageorgiou S, Tsalakou A, Pantelides IS (2019) Rhizosphere-enriched microbes as a pool to design synthetic communities for reproducible beneficial outputs. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 95(10):138
Ullah N, Ditta A, Khalid A, Mehmood S, Rizwan MS, Mubeen F, Imtiaz M (2020) Integrated effect of algal biochar and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on physiology and growth of maize under deficit irrigations. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00112-0
USEPA. 1989. Risk assessment guidance for superfund. Vol I: Human health evaluation manual (Part A). EPA/540/1-89/002
Wang X, Wang G, Guo T, Xing Y, Mo F, Wang H, Fan J, Zhang F (2020) Effects of plastic mulch and nitrogen fertilizer on the soil microbial community, enzymatic activity, and yield performance in a dryland maize cropping system. Eur J Soil Sci 72:400–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12954
West PC, Gerber JS, Engstrom PM, Mueller ND, Brauman KA, Carlson KM, Cassidy ES, Johnston M, MacDonald GK, Ray DK, Siebert S (2014) Leverage points for improving global food security and the environment. Science 345:325–328. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1246067
Wolf B (1982) A comprehensive system of leaf analyses and its use for diagnosing crop nutrient status. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 13:1035–1059. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103628209367332
Xiong T, Dumat C, Pierart A, Shahid M, Kang Y, Li N, Bertoni G, Laplanche C (2016) Measurement of metal bioaccessibility in vegetables to improve human exposure assessments: field study of soil–plant–atmosphere transfers in urban areas. South China Environ Geochem Health 38:1283–1301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9796-2
Zhang XX, Zhang T, Fang H (2009) Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:397–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1829-z
Zhuang P, Yang QW, Wang HB, Shu WS (2007) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by eight plant species in the field. Water Air Soil Pollut 184:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9412-2
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Institute of Soil and Environmental Sciences (University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan) for providing research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Naveed and Shah Fahad conceived the idea of the experiment and provided technical guidance. Allah Ditta, Maryum Ahmad, Adnan Mustafa, and Zulfiqar Ahmad had a major contribution to the overall preparation and carrying out of the research. Manuel Conde-Cid, Shermeen Tahir, Syed Atizaz Ali Shah, and Muhammad Mohsin Abrar contributed to arranging the data for different attributes and provided support for the experiment. Shah Fahad revised and edited the manuscript and provided technical guidance and editing support.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
We all declare that manuscript reporting studies do not involve any human participants, human data, or human tissue. So it is not applicable.
Consent for publication
Our manuscript does not contain data from any person, so it is “not applicable.”
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naveed, M., Ditta, A., Ahmad, M. et al. Processed animal manure improves morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics of Brassica napus L. under nickel and salinity stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 45629–45645 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14004-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14004-3