Abstract
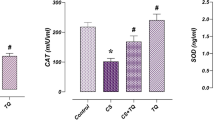
Testicular damage has been described as a common side effect of cisplatin (CDDP), which limits its clinical uses. Since oxidative injury and inflammatory response are the most pathological impact, estimation of natural antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents like trans-ferulic acid (TFA) could protect against CDDP-induced testicular damage. In the current investigation, rats were assigned into four groups: normal, TFA (50 mg/kg/day, P.O), CDDP (10 mg/kg) as single intraperitoneal (I.P) injection at the end of the 5th day, and TFA+CDDP where TFA was administered 5 days before CDDP injection and 5 days after. Interestingly, TFA significantly restored testosterone levels and abrogated oxidative stress injury. Additionally, TFA effectively suppressed inflammatory cytokines. It also counteracted the inflammation via downregulation of TLR4 and IRF3, P38-MAPK, NF-κB-p65, JAK1, STAT3, ERK1, and ERK2. Besides, TFA can modulate AKT and p-AKT protein expressions. In parallel, TFA mitigated the histopathological aberration of the testis and prevented spermatogenesis disruption. On the other hand, TFA augmented the in vitro CDDP cytotoxicity on Caco-2 and MCF-7 cells. Interestingly, TFA enhanced the cytotoxic effect of CDDP via apoptosis induction in both the early and late stages of apoptosis. Collectively, TFA exhibited a potential protective effect against CDDP-induced testicular injury by inhibiting oxidative stress as well as TLR4/IRF3/INF-γ, P38-MAPK/NF-κB-p65/TNF-α, and JAK1/STAT-3/ERK1/2 inflammatory signaling pathways with enhancing its in vitro cytotoxic activity.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdel-Daim MM, Abdel-Rahman HG, Dessouki AA, el-Far AH, Khodeer DM, Bin-Jumah M, Alhader MS, Alkahtani S, Aleya L (2020) Impact of garlic (Allium sativum) oil on cisplatin-induced hepatorenal biochemical and histopathological alterations in rats. Sci Total Environ 710:136338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136338
Abdel-Daim MM, Abushouk AI, Donia T, Alarifi S, Alkahtani S, Aleya L, Bungau SG (2019) The nephroprotective effects of allicin and ascorbic acid against cisplatin-induced toxicity in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:13502–13509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04780-4
Abdel-Daim MM, El-Sayed YS, Eldaim MA, Ibrahim A (2017) Nephroprotective efficacy of ceftriaxone against cisplatin-induced subchronic renal fibrosis in rats. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1332-5
Abdellatief SA, Galal AA, Farouk SM, Abdel-Daim MM (2017) Ameliorative effect of parsley oil on cisplatin-induced hepato-cardiotoxicity: a biochemical, histopathological, and immunohistochemical study. Biomed Pharmacother 86:482–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.038
Adelakun SA, Akinola BK, Akingbade GT (2018) Fertility enhancing activities of bioactive components of Cochlospermum planchonii rhizome on cisplatin induced reproductive dysfunctions in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Family Reprod Health 12:148–159
Al-Maghrebi M, Renno WM, Al-Somali HF, Botras MS, Qadhi IN (2016) Lutein modulates transcription dysregulation of adhesion molecules and spermatogenesis transcription factors induced by testicular ischemia reperfusion injury: it could be SAFE. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1223-9
Ali FE, Bakr AG, Abo-youssef AM, Azouz AA, Hemeida RA (2018a) Targeting Keap-1/Nrf-2 pathway and cytoglobin as a potential protective mechanism of diosmin and pentoxifylline against cholestatic liver cirrhosis. Life Sci 207:50–60
Ali FEM, Azouz AA, Bakr AG, Abo-Youssef AM, Hemeida RAM (2018b) Hepatoprotective effects of diosmin and/or sildenafil against cholestatic liver cirrhosis: the role of Keap-1/Nrf-2 and P(38)-MAPK/NF-κB/iNOS signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 120:294–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.07.027
Anand H, Misro MM, Sharma SB, Prakash S (2015) Protective effects of Eugenia jambolana extract versus N-acetyl cysteine against cisplatin-induced damage in rat testis. Andrologia 47:194–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12247
Ateşşahin A, Sahna E, Türk G, Ceribaşi AO, Yilmaz S, Yüce A, Bulmuş O (2006) Chemoprotective effect of melatonin against cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in rats. J Pineal Res 41:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00327.x
Azab SS, Kamel I, Ismail NN, El Din HH, El Fatah MA (2020) The defensive role of taurine against gonadotoxicity and testicular apoptosis effects induced by cisplatin in rats. J Infect Chemother 26:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2019.07.004
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques. Elsevier health sciences,
Bilgic Y, Akbulut S, Aksungur Z, Erdemli M, Ozhan O, Parlakpinar H, Vardi N, Turkoz Y (2018) Protective effect of dexpanthenol against cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Exp Ther Med 16:4049–4057. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6683
Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard JC (1997) Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu Rev Immunol 15:749–795. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.749
Bumrungpert A, Lilitchan S, Tuntipopipat S, Tirawanchai N, Komindr S (2018) Ferulic acid supplementation improves lipid profiles, oxidative stress, and inflammatory status in hyperlipidemic subjects: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients 10 https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060713
Cheng CY, Kao ST, Lee YC (2019a) Ferulic acid ameliorates cerebral infarction by activating Akt/mTOR/4E-BP1/Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic signaling in the penumbral cortex following permanent cerebral ischemia in rats. Mol Med Rep 19:792–804. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9737
Cheng Q, Li YW, Yang CF, Zhong YJ, Li L (2019b) Ethanol-induced hepatic insulin resistance is ameliorated by methyl ferulic acid through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 10:949. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00949
Chowdhury S, Ghosh S, Das AK, Sil PC (2019) Ferulic acid protects hyperglycemia-induced kidney damage by regulating oxidative insult, inflammation and autophagy. Front Pharmacol 10:27. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00027
Darzynkiewicz Z, Huang X, Zhao H (2017) Analysis of cellular DNA content by flow cytometry. Curr Protoc Immunol 119:5.7.1–5.7.20. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpim.36
Dasari S, Tchounwou PB (2014) Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740:364–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
Dev A, Iyer S, Razani B, Cheng G (2010) NF-κB and innate immunity. NF-kB in health and disease. Springer, In, pp 115–143
Eid AH, Abdelkader NF, Abd El-Raouf OM, Fawzy HM, El-Denshary ES (2016) Carvedilol alleviates testicular and spermatological damage induced by cisplatin in rats via modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Arch Pharm Res 39:1693–1702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0833-6
Eid AH, Gad AM, Fikry EM, Arab HH (2019) Venlafaxine and carvedilol ameliorate testicular impairment and disrupted spermatogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting AMPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 364:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.12.014
El-Mesallamy HO, Gawish RA, Sallam AM, Fahmy HA, Nada AS (2018) Ferulic acid protects against radiation-induced testicular damage in male rats: impact on SIRT1 and PARP1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:6218–6227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0873-6
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Eren H, Mercantepe T, Tumkaya L, Mercantepe F, Dil E, Horsanali MO, Yilmaz A (2020) Evaluation of the protective effects of amifostine and melatonin against cisplatin induced testis injury via oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats. Exp Mol Pathol 112:104324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104324
Fadaly WAA, Elshaier Y, Hassanein EHM, Abdellatif KRA (2020) New 1,2,4-triazole/pyrazole hybrids linked to oxime moiety as nitric oxide donor celecoxib analogs: synthesis, cyclooxygenase inhibition anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenicity, anti-proliferative activities, apoptosis, molecular modeling and nitric oxide release studies. Bioorg Chem 98:103752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103752
Fan Y, Mao R, Yang J (2013) NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer. Protein Cell 4:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-013-2084-3
Fouad AA, Abdel-Aziz AM, Hamouda AAH (2020) Diacerein downregulates NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-6/STAT3 pathways of inflammation and apoptosis in a rat model of cadmium testicular toxicity. Biol Trace Elem Res 195:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01865-6
Fouad AA, Qutub HO, Fouad AEA, Audeh AM, Al-Melhim WN (2017) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate counters cisplatin toxicity of rat testes. Pharm Biol 55:1710–1714. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2017.1322618
Fouad AA, Refaie MMM, Abdelghany MI (2019) Naringenin palliates cisplatin and doxorubicin gonadal toxicity in male rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 29:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2018.1512180
Gawish RA, Fahmy HA, Abd El Fattah AI, Nada AS (2020) The potential effect of methylseleninic acid (MSA) against γ-irradiation induced testicular damage in rats: impact on JAK/STAT pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 679:108205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.108205
Guvvala PR, Ravindra JP, Selvaraju S, Arangasamy A, Venkata KM (2019) Ellagic and ferulic acids protect arsenic-induced male reproductive toxicity via regulating Nfe2l2, Ppargc1a and StAR expressions in testis. Toxicology 413:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2018.11.012
Hamza AA, Elwy HM, Badawi AM (2016) Fenugreek seed extract attenuates cisplatin-induced testicular damage in Wistar rats. Andrologia 48:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12435
Hasanein P, Fazeli F, Parviz M, Roghani M (2018) Ferulic acid prevents lead-induced testicular oxidative stress and suppressed spermatogenesis in rats. Andrologia 50:50. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12798
Hassanein EHM, Ali FEM, Kozman MR, Abd El-Ghafar OAM (2020) Umbelliferone attenuates gentamicin-induced renal toxicity by suppression of TLR-4/NF-κB-p65/NLRP-3 and JAK1/STAT-3 signaling pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:11558–11571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11416-5
Hassanein EHM, Shalkami AS, Khalaf MM, Mohamed WR, Hemeida RAM (2019) The impact of Keap1/Nrf2, P(38)MAPK/NF-κB and Bax/Bcl2/caspase-3 signaling pathways in the protective effects of berberine against methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother 109:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.088
He S, Guo Y, Zhao J, Xu X, Song J, Wang N, Liu Q (2019) Ferulic acid protects against heat stress-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in IEC-6 cells via the PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Int J Hyperthermia 35:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2018.1483534
Hu S, Hosey KL, Derbigny WA (2015) Analyses of the pathways involved in early- and late-phase induction of IFN-beta during C. muridarum infection of oviduct epithelial cells. PLoS One 10:e0119235. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119235
Ibrahim A, Al-Hizab FA, Abushouk AI, Abdel-Daim MM (2018) Nephroprotective effects of benzyl isothiocyanate and resveratrol against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress and inflammation. Front Pharmacol 9:1268. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01268
Ibrahim A, Eldaim MA, Abdel-Daim MM (2016) Nephroprotective effect of bee honey and royal jelly against subchronic cisplatin toxicity in rats. Cytotechnology 68:1039–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-015-9860-2
Idriss HT, Naismith JH (2000) TNF alpha and the TNF receptor superfamily: structure-function relationship(s). Microsc Res Tech 50:184–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0029(20000801)50:3<184::Aid-jemt2>3.0.Co;2-h
Kelainy EG, Ibrahim Laila IM, Ibrahim SR (2019) The effect of ferulic acid against lead-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in kidney and testes of rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:31675–31684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06099-6
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger C, Kuijten G, Keehnen R, Pals S, Van Oers M (1994) Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis
Köroğlu KM, Çevik Ö, Şener G, Ercan F (2019) Apocynin alleviates cisplatin-induced testicular cytotoxicity by regulating oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats. Andrologia 51:e13227. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13227
Koshiguchi M, Komazaki H, Hirai S, Egashira Y (2017) Ferulic acid suppresses expression of tryptophan metabolic key enzyme indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase via NFκB and p38 MAPK in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglial cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:966–971. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2016.1274636
Kumar P, Sulakhiya K, Barua CC, Mundhe N (2017) TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 expressions, responsible for disparity in action of curcumin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 431:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2981-5
Kuzmich NN, Sivak KV, Chubarev VN, Porozov YB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN, Peri F (2017) TLR4 signaling pathway modulators as potential therapeutics in inflammation and sepsis. Vaccines 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines5040034
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.807
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a001651. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001651
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017a) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2:17023. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Liu YM, Shen JD, Xu LP, Li HB, Li YC, Yi LT (2017b) Ferulic acid inhibits neuro-inflammation in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Int Immunopharmacol 45:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.02.007
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods (San Diego, Calif) 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, Gulluni F, Hirsch E (2014) PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann Med 46:372–383. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2014.912836
Mihara M, Uchiyama M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(78)90342-1
Mir SM et al (2018) Ferulic acid protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing inflammatory events and upregulating antioxidant defenses in Balb/c mice. Biomed Pharmacother 100:304–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.169
Murray PJ (2007) The JAK-STAT signaling pathway: input and output integration. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 178:2623–2629. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.2623
Pabla N, Dong Z (2008) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int 73:994–1007. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002786
Ren Z, Zhang R, Li Y, Li Y, Yang Z, Yang H (2017) Ferulic acid exerts neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med 40:1444–1456. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.3127
Rezvanfar MA, Rezvanfar MA, Shahverdi AR, Ahmadi A, Baeeri M, Mohammadirad A, Abdollahi M (2013) Protection of cisplatin-induced spermatotoxicity, DNA damage and chromatin abnormality by selenium nano-particles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 266:356–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.11.025
Roy S, Metya SK, Rahaman N, Sannigrahi S, Ahmed F (2014) Ferulic acid in the treatment of post-diabetes testicular damage: relevance to the down regulation of apoptosis correlates with antioxidant status via modulation of TGF-β1, IL-1β and Akt signalling. Cell Biochem Funct 32:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.2983
Sadar SS, Vyawahare NS, Bodhankar SL (2016) Ferulic acid ameliorates TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis through modulation of cytokines, oxidative stress, iNOs, COX-2, and apoptosis in laboratory rats. EXCLI J 15:482–499. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2016-393
Sajadimajd S, Bahramsoltani R, Iranpanah A, Kumar Patra J, Das G, Gouda S, Rahimi R, Rezaeiamiri E, Cao H, Giampieri F, Battino M, Tundis R, Campos MG, Farzaei MH, Xiao J (2020) Advances on natural polyphenols as anticancer agents for skin cancer. Pharmacol Res 151:104584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104584
Salem EA, Salem NA, Maarouf AM, Serefoglu EC, Hellstrom WJ (2012) Selenium and lycopene attenuate cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity associated with oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Urology 79:1184.e1181–1184.e1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2011.12.006
Shati AA (2019) Resveratrol improves sperm parameter and testicular apoptosis in cisplatin-treated rats: effects on ERK1/2, JNK, and Akt pathways. Syst Biol Reprod Med 65:236–249. https://doi.org/10.1080/19396368.2018.1541114
Shen Q, Zhang X, Li Q, Zhang J, Lai H, Gan H, du X, Li M (2019) TLR2 protects cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury associated with autophagy via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 120:4366–4374. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27722
Shokri V, Jalili C, Raissi F, Akhshi N, Ghanbari A (2020) Evaluating the effects of acacetin versus a low dose of cisplatin drug on male reproductive system and kidney in mice: with emphasis on inflammation process. Andrologia 52:e13444. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13444
Sioud F, Ben Toumia I, Lahmer A, Khlifi R, Dhaouefi Z, Maatouk M, Ghedira K, Chekir-Ghedira L (2020) Methanolic extract of Ephedra alata ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity through reducing oxidative stress and genotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:12792–12801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07904-3
Thyagaraju BM (2008) Ferulic acid supplements abrogate oxidative impairments in liver and testis in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Zool Sci 25:854–860. https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.25.854
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:4350–4354
Van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ, Cloos J (2011) Cell sensitivity assays: the MTT assay. Cancer cell culture. Springer, In, pp 237–245
Van Weemen B, Schuurs A (1971) Immunoassay using antigen—enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett 15:232–236
Walczak-Jedrzejowska R, Wolski JK, Slowikowska-Hilczer J (2013) The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in male fertility. Cent European J Urol 66:60–67. https://doi.org/10.5173/ceju.2013.01.art19
Yahfoufi N, Alsadi N, Jambi M, Matar C (2018) The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols. Nutrients 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111618
Yamamoto M et al (2003) Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science (New York, NY) 301:640–643. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1087262
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R (2009) STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 9:798–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2734
Yucel C, Arslan FD, Ekmekci S, Ulker V, Kisa E, Erdogan Yucel E, Ucar M, Ilbey YO, Celik O, Basok BI, Kozacioglu Z (2019) Protective effect of all-trans retinoic acid in cisplatin-induced testicular damage in rats. World J Men's Health 37:249–256. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.180105
Zafeer MF, Firdaus F, Anis E, Mobarak Hossain M (2019) Prolong treatment with Trans-ferulic acid mitigates bioenergetics loss and restores mitochondrial dynamics in streptozotocin-induced sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Neurotoxicology 73:246–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2019.04.006
Zduńska K, Dana A, Kolodziejczak A, Rotsztejn H (2018) Antioxidant properties of ferulic acid and its possible application. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 31:332–336. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491755
Zhang K, Weng H, Yang J, Wu C (2020) Protective effect of Liuwei Dihuang Pill on cisplatin-induced reproductive toxicity and genotoxicity in male mice. J Ethnopharmacol 247:112269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.112269
Zhang S, Wang P, Zhao P, Wang D, Zhang Y, Wang J, Chen L, Guo W, Gao H, Jiao Y (2018) Pretreatment of ferulic acid attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 32:394632017750518. https://doi.org/10.1177/0394632017750518
Zhao Y, Song W, Wang Z, Wang Z, Jin X, Xu J, Bai L, Li Y, Cui J, Cai L (2018) Resveratrol attenuates testicular apoptosis in type 1 diabetic mice: role of Akt-mediated Nrf2 activation and p62-dependent Keap1 degradation. Redox Biol 14:609–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.007
Zheng RL, Zhang H (1997) Effects of ferulic acid on fertile and asthenozoospermic infertile human sperm motility, viability, lipid peroxidation, and cyclic nucleotides. Free Radic Biol Med 22:581–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(96)00272-9
Zhou Z, Shi T, Hou J, Li M (2020) Ferulic acid alleviates atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in mice via its potent anti-inflammatory effect. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 42:156–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923973.2020.1733012
Acknowledgements
The authors are greatly indebted to prof. Salah M. H. Afifi, Professor of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Assiut University, Egypt, for his kind help in the histopathological studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and experimental procedure: EHMH, BAA, and FEMA. Statistical analysis and data interpretation: OAMA and MRK. Writing of the manuscript: SMZS and EHMH. The final version of the manuscript has been revised and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University (No. IRB:17300459).
Consent for publication
The authors declared that the final version of the manuscript has been reviewed, approved, and consented to publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(RAR 133 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassanein, E.H.M., Abdel-Wahab, B.A., Ali, F.E.M. et al. Trans-ferulic acid ameliorates cisplatin-induced testicular damage via suppression of TLR4, P38-MAPK, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 41948–41964 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13544-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13544-y