Abstract
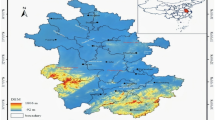
Considering the shortage of per capita water resources in China, the paper established a fractional order accumulated grey prediction model (FGM(1,1)) to predict per capita water consumption of 31 regions (provinces, municipalities, and autonomous regions) in China from 2019 to 2024. The results show that per capita water consumption varies greatly across the different regions. Among them, per capita water consumption of nine regions (i.e., Beijing, Tianjin, Inner Mongolia, Jiangsu, Henan, Hubei, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Shaanxi) shows an increasing trend, whereas per capita water consumption in other 22 regions shows a downward trend. The predictive results can provide a basis for water resource management in China.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2009) Long Beach Water Department; Long Beach achieves 20% reduction in per capita water consumption 11 years ahead of 2020 statewide conservation mandate. Energy Weekly News:1945–6999
Cao S, Hu Q, Sijia J, Wang Y, Zhu X, Yong L (2019) 1995-2016 Shenzhen water consumption change and water saving potential analysis. Water Resources Protection 35:76–81
Du F, Wenkang S, Liangzhou C, Deng Y, Zhu Z (2004) Infrared image segmentation with 2-D maximum entropy method based on particle swarm optimization (PSO). Pattern Recogn Lett 26(5):597–603
Duman GM, Kongar E, Gupta SM (2020) Predictive analysis of electronic waste for reverse logistics operations: a comparison of improved univariate grey models. Soft Comput 24:15747–15762
Fatemeh S, Hashemi NS (2019) Improving performance evaluation based on balanced scorecard with grey relational analysis and data envelopment analysis approaches: case study in water and wastewater companies. Evaluation and program planning 79:101762
Gharabaghi S, Stahl E, Bonakdari H (2019) Integrated nonlinear daily water demand forecast model (case study: City of Guelph, Canada). J Hydrol 579:124182
He S, Hongjun D, Yang L (2019) Based on GM (1,1) model of Hebei Province per capita water consumption forecast research. Industry and Technology Forum 18:46–47
Hongying Z, Wu L (2020) Forecasting the non-renewable energy consumption by an adjacent accumulation grey model. J Clean Prod 275:124113
Hua E, Wang X, Engel BA, Sun S, Wang Y (2020) The competitive relationship between food and energy production for water in China. J Clean Prod 247:119103
Huang L (2020) Current situation of water resource management and countermeasures. Science and Technology Innovation and Application (3):193–194
Hussien WA, Memon FA, Savic DA (2016) Assessing and Modelling the influence of household characteristics on per capita water consumption. Water Resour Manag 30:2931–2955
Kamali M, Persson KM, Costa ME, Capela I (2019) Sustainability criteria for assessing nanotechnology applicability in industrial wastewater treatment: current status and future outlook. Environ Int 125:261–276
Karamaziotis PI, Raptis A, Nikolopoulos K, Litsiou K, Assimakopoulos V (2020) An empirical investigation of water consumption forecasting methods. Int J Forecast 36:588–606
Li J (2019) Analysis of the current situation of water resource management in China. China water transport (second half) 19(10):39–40
Li H, Wang X, Liu D’e (2010) GM (1,1) based water resources prediction model library system design. People’s Yellow River 32:51–53
Liu W, Xu B et al (2018) China statistical yearbook on environment −2018. China Statistics Press:4–5
Liu J, Bao Z, Liu C, Wang G, Liu Y, Wang J, Guan X (2019) China’s water resources and water consumption changes in the past 20 years and analysis of their causes. Journal of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering:31–41
Ma X, Li L (2018) Based on linear regression method to predict the legal water consumption of residents in the south at night. Water Supply and Drainage 54:87–93
Maamar S (2016) Forecasting urban water demand: a meta-regression analysis. J Environ Manag 183:777–785
Meng W, Yang D, Huang H (2018) Prediction of China’s sulfur dioxide emissions by discrete grey model with fractional order generation operators. Complexity. 2018:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8610679
Meng X, Fan F, Wu L (2021) Prediction of major pollutants discharge from wastewater in 31 cities of China. Sustainable Production and Consumption 26:54–64
Peng P (2020) Analysis of the current situation of water resources in China based on regression analysis. Modern communication (5):49–50
Roushangar K, Alizadeh F (2018) Investigating effect of socio-economic and climatic variables in urban water consumption prediction via Gaussian process regression approach. Water Science & Technology: Water Supply 18(1):84–93
Shenlin L, Xiaohong C, Singh VP, Qi X, Zhang L (2020) Tradeoff for water resources allocation based on updated probabilistic assessment of matching degree between water demand and water availability. Science of the Total Environment:716
Wang Y, Suiqing L, Dong W (2009) Non-equidistant GM (1,1) model with improved background values to predict water consumption. China Water Supply and Drainage 25:57–59
Wei T, Lou I, Yang Z, Li Y (2016) A system dynamics urban water management model for Macau. China Journal of Environmental Sciences 50:117–126
Wu H (2019) Analysis of the status quo of sustainable development of water resources in China. Land and. Natural Resources Research (3):5–6
Wu L, Sifeng L, Ligen Y, Shuli Y, Dinglin L (2013) Grey system model with the fractional order accumulation. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(7):1775–1785
Wu L, Liu S, Fang Z, Xu H (2015) Properties of the GM (1, 1) with fractional order accumulation. Appl Math Comput 252:287–293
Wu H, Zeng B, Zhou M (2017) Forecasting the water demand in Chongqing, China using a grey prediction model and recommendations for the sustainable development of urban water consumption. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute 14(11):1386
Yang Y (2019) Based on SCS-CN model of Urumqi water resources prediction research. Shaanxi Water Resources:48–50
Yang W, Li Q (2004) A review of particle swarm optimization algorithms. Chinese Engineering Science:87–94
Yang X, Xiaoling S, Lihua M (2009) Prediction of water consumption in Guanzhong area based on artificial neural network model. Water Saving Irrigation:4–6
Yuan Y, Zhao H, Yuan X et al (2019) Application of fractional order-based grey power model in water consumption prediction. Environ Earth Sci 78(8):1–8
Yuan D, Liu X, Zhang X (2020) Forecasting of domestic water consumption based on modified grey model GM(1,1). Shaanxi Water Conservancy (7):1–3
Zhai C, Zhang H, Wang L (2009) Industrial production function method for the study of urban industrial water consumption forecast. Journal of Tianjin University of Technology 28:79–81
Zhang B, Jiaxiang T, Yuan Y (2011) Water consumption forecast of Nanjing based on improved GM (1,1) model. Hydropower and Energy Science 29:24–26
Zhu M, Chenjing L, Ni G (2017) Regional structure characteristics of FDI in seven regions of China in recent ten years based on geographical regionalization. Economic Research Guide (23):81–83
Funding
The relevant researches are supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71871084) and the Excellent Young Scientist Foundation of Hebei Education Department (SLRC2019001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Meng Xiangmei: Data curation, investigation, methodology, project administration, formal analysis, resources, validation, visualization, editing, writing—original draft.
Wu Lifeng: Conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Wu, L. Prediction of per capita water consumption for 31 regions in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 29253–29264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12368-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12368-0