Abstract
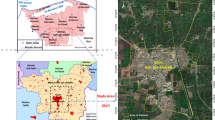
The amount of municipal solid waste (MSW) has been increasing rapidly in the urban centres of developing countries during the last few decades; however, municipal solid waste management (MSWM) remains inadequate. One of the largest aspects of cost of the MSWM system is the collection of waste. This paper describes a methodology that combines geographic information systems (GIS), hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set (HFLTS), and the full multiplicative form of multi-objective optimization by ratio analysis (MULTIMOORA), to determine suitable locations for waste collection boxes (named AYPIKUT), which have been designed specifically for collection of domestic waste vegetable oil and waste batteries. It takes as case study, Atakum, a district of Samsun city, Turkey. As a solution to the problem, first, a total of 88 items have been identified for consideration by seven criteria elicited from the insights of experts, and spatial analyses were performed. Multi-criteria HFLTS was then used to determine weights of the criteria. Population density was the most significant criterion affecting the selection process, and proximity to housing complexes with more than 150 dwellings was the least important. According to the weights of the seven criteria, and three rules determined by the experts, 15 AYPIKUT locations were identified using GIS. As a final step, the alternative locations (A1–A15) were ranked with the MULTIMOORA method. A5 was the most suitable site, and A6 was the least suitable site for an AYPIKUT. The results indicated the ability of the proposed model to select the suitable locations for waste collection box.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Afzali A, Sabri S, Rashid M, Jamal MVS, Ludin ANM (2014) Inter-municipal landfill site selection using analytic network process. Water Resour Manag 28:2179–2194
Aksoy E, San BT (2019) Geographical information systems (GIS) and multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) integration for sustainable landfill site selection considering dynamic data source. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:779–791
Altuntaş S, Dereli T, Yılmaz MK (2015) Evaluation of excavator technologies: application of data fusion based MULTIMOORA methods. J Civ Eng Manag 21(8):977–997
Amal L, Son LH, Chabchoub H (2018) SGA: spatial GIS-based genetic algorithm for route optimization of municipal solid waste collection. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:27569–27582
Atici KB, Simsek AB, Ulucan A, Tosun MU (2015) A GIS-based multiple criteria decision analysis approach for windpower plant site selection. Util Policy 37:86–96
Aydi A (2018) Evaluation of groundwater vulnerability to pollution using a GIS based multi-criteria decision analysis. Groundw Sustain Dev 7:204–211
Bahrani S, Ebadi T, Ehsani H, Yousefi H, Maknoon R (2016) Modeling landfill site selection by multi-criteria decision making and fuzzy functions in GIS, case study: Shabestar, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 75:337
Baležentis T, Zeng S (2013) Group multi-criteria decision making based upon interval-valued fuzzy numbers: an extension of the MULTIMOORA method. Expert Syst Appl 40:543–550
Baležentis A, Baležentis T, Brauers WKM (2012) Personnel selection based on computing with words and fuzzy MULTIMOORA. Expert Syst Appl 39:7961–7967
Balta MÖ, Ülgen Yenil H (2019) Multi criteria decision making methods for urban greenway: the case of Aksaray, Turkey. Land Use Policy 89:104224
Barzehkar M, Dinan NM, Mazaheri S, Tayebi RM, Brodie G (2019) Landfill site selection using GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation (case study: SaharKhiz Region located in Gilan Province in Iran). SN Appl Sci 1:1082
Brauers WKM, Zavadskas EK (2006) The MOORA method and its application to privatization in a transition economy. Control Cybern 35(2):445–469
Brauers WKM, Zavadskas EK (2010) Project management by MULTIMOORA as an instrument for transition economies. Technol Econ Dev Econ 16(1):5–24
Brauers WKM, Zavadskas EK (2013) Multi-objective decision making with a large number of objectives. An application for Europe 2020. Int J Oper Res 10(2):67–79
Burrough PA, McDonnell RA (1998) Principles of geographical information systems. Oxford University Press.
Çalış Boyacı A (2020) Selection of eco-friendly cities in Turkey via a hybrid hesitant fuzzy decision making approach. Appl Soft Comput 89:106090
Chalkias C, Lasaridi K (2009) A GIS based model for the optimisation of municipal solid waste collection: the case study of Nikea, Athens, Greece. WSEAS Trans Environ Dev 10(5):640–650
Chang NB, Parvathinathan G, Breeden JB (2008) Combining GIS with fuzzy multicriteria decision-making for landfillsiting in a fast-growing urban region. J Environ Manag 87:139–153
Chen Y, Yu J, Khan S (2010) Spatial sensitivity analysis of multi-criteria weights in GIS-based land suitability evaluation. Environ Model Softw 25:1582–1591
Cromley RG, Hanink DM (2003) Scale-independent land-use allocation modeling in raster GIS. Cartogr Geogr Inf Sci 30(4):343–350
Dahooie JH, Zavadskas EK, Firoozfar HR, Vanaki AS, Mohammadi N, Brauers WKM (2019) An improved fuzzy MULTIMOORA approach for multi-criteria decision making based on objective weighting method (CCSD) and its application to technological forecasting method selection. Eng Appl Artif Intell 79:114–128
Datta S, Sahu N, Mahapatra S (2013) Robot selection based on grey-MULTIMOORA approach. Grey Syst: Theory and Application 3(2):201–232
Eghtesadifard M, Afkhami P, Bazyar A (2020) An integrated approach to the selection of municipal solid waste landfills through GIS, K-means and multi-criteria decision analysis. Environ Res 185:109348
Erbaş M, Kabak M, Özceylan E, Çetinkaya C (2018) Optimal siting of electric vehicle charging stations: a GIS-based fuzzy multi-criteria decision analysis. Energy 163:1017–1031
Eskandari M, Homaee M, Mahmoodi S, Pazira E, Genuchten MTV (2015) Optimizing landfill site selection by using land classification maps. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:7754–7765
Fahmi A, Kahraman C, Bilen Ü (2016) Electre I method using hesitant linguistic term sets: an application to supplier selection. Int J Comput Intell Syst 9(1):153–167
Feng XQ, Tan QY, Wei CP (2018) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic multi-criteria decision making based on possibility theory. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 9:1505–1517
Feyzi S, Khanmohammadi M, Abedinzadeh N, Aalipour M (2019) Multi- criteria decision analysis FANP based on GIS for siting municipal solid waste incineration power plant in the north of Iran. Sustain Cities Soc 47:101513
GDLRC, (2020) General Directorate of Land Registry and Cadastre https://www.tkgm.gov.tr/tr/icerik/iste-konutta-en-cok-satis-yapilan-ilceler, Accessed 19 June 2020
Ghadikolaei AS, Madhoushi M, Divsalar M (2018) Extension of the VIKOR method for group decision making with extended hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Neural Comput & Applic 30:3589–3602
Gorsevski PV, Donevska KR, Mitrovski CD, Frizado JP (2012) Integrating multi-criteria evaluation techniques with geographic information systems for landfill site selection: a case study using ordered weighted average. Waste Manag 32:287–296
Guiqin W, Li Q, Guoxue L, Lijun C (2009) Landfill site selection using spatial information technologies and AHP: a case study in Beijing, China. J Environ Manag 90:2414–2421
Hafezalkotob A, Hafezalkotob A (2015) Comprehensive MULTIMOORA method with target-based attributes and integrated significant coefficients for materials selection in biomedical applications. Mater Design 87:949–959
Hariz HA, Dönmez CÇ, Sennaroglu B (2017) Siting of a central healthcare waste incinerator using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. J Clean Prod 166:1031–1042
Henry RK, Yongsheng Z, Jun D (2006) Municipal solid waste management challenges in developing countries – Kenyan case study. Waste Manag 26:92–100
Jamshidi-Zanjani A, Rezaei M (2017) Landfill site selection using combination of fuzzy logic and multiattribute decision-making approach. Environ Earth Sci 76:448
Kabak M, Erbaş M, Çetinkaya C, Özceylan E (2018) A GIS-based MCDM approach for the evaluation of bike-share stations. J Clean Prod 201:49–60
Kallel A, Serbaji MM, Zairi M (2016) Using GIS-based tools for the optimization of solid waste collection and transport: case study of Sfax City, Tunisia. J Eng 10:1–7
Kamdar I, Ali S, Bennui A, Techato K, Jutidamrongphan W (2019) Municipal solid waste landfill siting using an integrated GIS-AHP approach: a case study from Songkhla, Thailand. Resour Conserv Recycl 149:220–235
Kanani-Sadat Y, Arabsheibani R, Karimipour F, Nasseri M (2019) A new approach to flood susceptibility assessment in data-scarce and ungauged regions based on GIS-based hybrid multi criteria decision-making method. J Hydrol 572:17–31
Kanchanabhan TE, Mohaideen JA, Srinivasan S, Sundaram VLK (2010) Optimum municipal solid waste collection using geographical information system (GIS) and vehicle tracking for Pallavapuram municipality. Waste Manag Res 29(3):323–339
Kapilan S, Elangovan K (2018) Potential landfill site selection for solid waste disposal using GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA). J Cent South Univ 25:570–585
Karimi H, Amiri S, Huang J, Karimi A (2019) Integrating GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis for landfll site selection, case study: Javanrood County in Iran. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:7305–7318
Khan D, Samadder SR (2016) Allocation of solid waste collection bins and route optimisation using geographical information system: a case study of Dhanbad City, India. Waste Manag Res 34(7):666–676
Khishtandar S, Zandieh M, Dorri B (2017) A multi criteria decision making framework for sustainability assessment of bioenergy production technologies with hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets: the case of Iran. Renew Sust Energ Rev 77:1130–1145
Khodaparast M, Rajabi AM, Edalat A (2018) Municipal solid waste landfill siting by using GIS and analytical hierarchy process (AHP): a case study in Qom city, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 77:52
Lella J, Mandla VR, Zhu X (2017) Solid waste collection/transport optimization and vegetation land cover estimation using Geographic Information System (GIS): a case study of a proposed smart-city. Sustain Cities Soc 35:336–349
Lin M, Huang C, Xu Z (2020) MULTIMOORA based MCDM model for site selection of car sharing station under picture fuzzy environment. Sustain Cities Soc 53:101873
Liu HB, Rodríguez RM (2014) A fuzzy envelope for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and its application to multicriteria decision making. Inf Sci 258:220–238
Liu HC, You JX, Li P, Su Q (2016) Failure mode and effect analysis under uncertainty: an integrated multiple criteria decision making approach. IEEE Trans Reliab 65(3):1380–1392
Mian MM, Zeng X, Nasry ANB, Al-Hamadani SMZF (2017) Municipal solid waste management in China: a comparative analysis. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 19:1127–1135
Miglietta PP, Micale R, Sciortino R, Caruso T, Giallanza A, La Scalia G (2019) The sustainability of olive orchard planting management for different harvesting techniques: an integrated methodology. J Clean Prod 238:117989
Mokhtara C, Negrou B, Settou N, Gouareh A, Settou B (2019) Pathways to plus-energy buildings in Algeria: design optimization method based on GIS and multi-criteria decision-making. Energy Procedia 162:171–180
Montes R, Sánchez AM, Villar P, Herrera F (2015) A web tool to support decision making in the housing market using hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Appl Soft Comput 35:949–957
Nas B, Cay T, Iscan F, Berktay A (2010) Selection of MSW landfill site for Konya, Turkey using GIS and multi-criteria evaluation. Environ Monit Assess 160:491–500
Nguyen-Trong K, Nguyen-Thi-Ngoc A, Nguyen-Ngoc D, Dinh-Thi-Hai V (2017) Optimization of municipal solid waste transportation by integrating GIS analysis, equation-based, and agent-based model. Waste Manag 59:14–22
Onar SÇ, Büyüközkan G, Öztayşi B, Kahraman C (2016) A new hesitant fuzzy QFD approach: an application to computer workstation selection. Appl Soft Comput 46:1–16
Ostovari Y, Honarbakhsh A, Sangoony H, Zolfaghari F, Maleki K, Ingram B (2019) GIS and multi-criteria decision-making analysis assessment of land suitability for rapeseed farming in calcareous soils of semi-arid regions. Ecol Indic 103:479–487
Othman AN, Naim WM, Noraini S (2012) GIS based multi criteria decision making for landslide hazard zonation. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 35:595–602
Özkan B, Özceylan E, Sarıçiçek İ (2019) GIS-based MCDM modeling for landfill site suitability analysis: a comprehensive review of the literature. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:30711–30730
Özkan B, Özceylan E, Kabak M, Dağdeviren M (2020) Evaluating the websites of academic departments through SEO criteria: a hesitant fuzzy linguistic MCDM approach. Artif Intell Rev 53:875–905
Pham Phu ST, Fujiwara T, Hoang MG, Pham VD, Tran MT (2019) Waste separation at source and recycling potential of the hotel industry in Hoi An city, Vietnam. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:23–34
Phua MH, Minowa M (2005) A GIS-based multi-criteria decision making approach to forest conservation planning at a landscape scale: a case study in the Kinabalu Area, Sabah, Malaysia. Landsc Urban Plan 71:207–222
Priti, Mandal K (2019) Review on evolution of municipal solid waste management in India: practices, challenges and policy implications. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:1263–1279
Qiu L, Zhu J, Pan Y, Hu W, Amable GS (2017) Multi-criteria land use suitability analysis for livestock development planning in Hangzhou metropolitan area, China. J Clean Prod 161:1011–1019
Rahimi S, Hafezalkotob A, Monavari SM, Hafezalkotob A, Rahimi R (2020) Sustainable landfill site selection for municipal solid waste based on a hybrid decision-making approach: fuzzy group BWM-MULTIMOORA-GIS. J Clean Prod:248, 119186
Ramya S, Devadas V (2019) Integration of GIS, AHP and TOPSIS in evaluating suitable locations for industrial development: a case of Tehri Garhwal district, Uttarakhand, India. J Clean Prod 238:117872
Rezaeisabzevar Y, Bazargan A, Zohourian B (2020) Landfill site selection using multi criteria decision making: Influential factors for comparing locations. J Environ Sci 93:170–184
Ripa M, Fiorentino G, Vacca V, Ulgiati S (2017) The relevance of site-specific data in life cycle assessment (LCA). The case of the municipal solid waste management in the metropolitan city of Naples (Italy). J Clean Prod 142:445–460
Rızvanoğlu O, Kaya S, Ulukavak M, Yeşilnacar Mİ (2020) Optimization of municipal solid waste collection and transportation routes, through linear programming and geographic information system: a case study from Şanlıurfa, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 192:9
Rodríguez RM, Martínez L, Herrera F (2012) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(1):109–119
Rodríguez RM, Martínez L, Herrera F (2013) A group decision making model dealing with comparative linguistic expressions based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Inf Sci 241:28–42
Rupani PF, Delarestaghi RM, Abbaspour M, Rupani MM, EL-Mesery HS, Shao W (2019) Current status and future perspectives of solid waste management in Iran: a critical overview of Iranian metropolitan cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:32777–32789
Sánchez-Lozano JM, Bernal-Conesa JA (2017) Environmental management of Natura 2000 network areas through the combination of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) methods. Case study in south-eastern Spain. Land Use Policy 63:86–97
Sánchez-Lozano JM, Teruel-Solano J, Soto-Elvira PL, García-Cascales MS (2013) Geographical information systems (GIS) and multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) methods for the evaluation of solar farms locations: case study in south-eastern Spain. Renew Sust Energ Rev 24:544–556
Sánchez-Lozano JM, García-Cascales MS, Lamata MT (2016a) GIS-based onshore wind farm site selection using fuzzy multi-criteria decision making methods. Evaluating the case of southeastern Spain. Appl Energy 171:86–102
Sánchez-Lozano JM, García-Cascales MS, Lamata MT (2016b) Comparative TOPSIS-ELECTRE TRI methods for optimal sites for photovoltaic solar farms. Case study in Spain. J Clean Prod 127:387–398
Selim S, Koc San D, Selim C, San BT (2018) Site selection for avocado cultivation using GIS and multi-criteria decision analyses: case study of Antalya, Turkey. Comput Electron Agric 154:450–459
Şener Ş, Şener E, Nas B, Karagüzel R (2010) Combining AHP with GIS for landfill site selection: a case study in the Lake Beysşehir catchment area (Konya, Turkey). Waste Manag 30:2037–2046
Singh LK, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2017) Multi-criteria analysis and GIS modeling for identifying prospective water harvesting and artificial recharge sites for sustainable water supply. J Clean Prod 142:1436–1456
Sumathi VR, Natesan U, Sarkar C (2008) GIS-based approach for optimized siting of municipal solid waste landfill. Waste Manag 28:2146–2160
Tavares G, Zsigraiová Z, Semiao V (2011) Multi-criteria GIS-based siting of an incineration plant for municipal solid waste. Waste Manag 31:1960–1972
TCA, Turkish Court of Accounts (2007) Waste management in Turkey: national regulations and evaluation of implementation results. Performance Audit Report, Ankara, pp 1–76
Terazono A, Oguchi M, Iino S, Mogi S (2015) Battery collection in municipal waste management in Japan: challenges for hazardous substance control and safety. Waste Manag 39:246–257
Tian ZP, Wang JQ, Wang J, Zhang HY (2018) A multi-phase QFD-based hybrid fuzzy MCDM approach for performance evaluation: a case of smart bike-sharing programs in Changsha. J Clean Prod 171:1068–1083
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25:529–539
TSI, Turkish Statistical Institute (2019) http://www.turkstat.gov.tr/PreTablo.do?alt_id=1019, Accessed 15April 2020
TSI, Turkish Statistical Institute (2020) https://biruni.tuik.gov.tr/medas/?kn=95&locale=tr, Accessed 17 September 2020
Tüysüz F, Şimşek B (2017) A hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets based AHP approach for analyzing the performance evaluation factors: an application to cargo sector. Complex Intell Syst 3:167–175
Vaissi S, Sharifi M (2019) Integrating multi-criteria decision analysis with a GIS based siting procedure to select a protected area for the Kaiser’s mountain newt, Neurergus kaiseri (Caudata: Salamandridae). Glob Ecol Conserv 20:e00738
Vijay R, Gautam A, Kalamdhad A, Gupta A, Devotta S (2008) GIS-based locational analysis of collection bins in municipal solid waste management systems. J Environ Eng Sci 7:39–43
Villacreses G, Gaona G, Martínez-Gómez J, Jijón DJ (2017) Wind farms suitability location using geographical information system (GIS), based on multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) methods: the case of continental Ecuador. Renew Energy 109:275–286
Wei C, Liao H (2016) A multigranularity linguistic group decision-making method based on hesitant 2-tuple sets. Int J Intell Syst 31(6):612–634
Wei CP, Ren ZL, Rodríguez RM (2015) A hesitant fuzzy linguistic TODIM method based on a score function. Int J Comput Intell Syst 8(4):701–712
Yavuz M, Öztayşi B, Onar SÇ, Kahraman C (2015) Multi-criteria evaluation of alternative-fuel vehicles via a hierarchical hesitant fuzzy linguistic model. Expert Syst Appl 42:2835–2848
Zhang DQ, Tan SK, Gersberg RM (2010) Municipal solid waste management in China: status, problems and challenges. J Environ Manag 91:1623–1633
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aslı Çalış Boyacı: Term, conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing (original draft), writing (review and editing), and visualization.
Aziz Şişman: Software, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, writing (original draft), writing (review and editing), and visualization.
Köksal Sarıcaoğlu: Writing (review and editing).
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix. Envelopes and collective preferences for HFLTS
Appendix. Envelopes and collective preferences for HFLTS
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çalış Boyacı, A., Şişman, A. & Sarıcaoğlu, K. Site selection for waste vegetable oil and waste battery collection boxes: a GIS-based hybrid hesitant fuzzy decision-making approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 17431–17444 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12080-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12080-5