Abstract
This study uncovers the role of regulatory quality, energy use, and globalization in the conventional environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) for South Africa by incorporating structural breaks in the series based on quarterly frequency data between 1996:Q1 and 2016:Q4. Applying the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) model, we confirm a cointegration between the variables. The empirical results suggest the validity of the EKC hypothesis in South Africa. In addition, while energy use exerts positive pressure on ecological footprint, globalization and regulatory quality exert negative pressure on ecological footprint. However, the effect of globalization is weak in the long run while the effect of regulatory quality is weak in short run. The results further reveal that the structural break years are statistically insignificant. The causality result establishes a causal link flowing from all the variables to ecological footprint in the long run. In the short run, economic growth and energy use Granger-cause regulatory quality. Also, while energy use causes ecological footprint, globalization is a predictor of energy use. The policy implication of this study is that increasing the pace of globalization and strengthening regulatory quality are efficient strategies to improve environmental quality and sustain a stable EKC in South Africa.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the repositories:
- Ecological Footprint per capita is available at Global Footprint Network
- Globalization index is available at KOF Swiss Economic Institute via http://globalization.kof.ethz.ch/
- Regulatory Quality is available at World Development Indicators (WDI)/World - Bank Database
- GDP per capita is available at World Development Indicators database
- Energy use available at OECD database
Notes
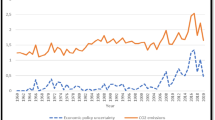
The results of the unit root tests are supported by the time-plots of the variables presented already in Fig. 1.
References
Abid M (2016) Impact of economic, financial, and institutional factors on CO2 emissions: evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa economies. Util Policy 41:85–94
Acemoglu D, Johnson S, Robinson JA (2002) Reversal of fortune: geography and institutions in the making of the modern world income distribution. Q J Econ 117(4):1231–1294
Acemoglu D, Johnson S, Robinson J, Thaicharoen Y (2003) Institutional causes, macroeconomic symptoms: volatility, crises and growth. J Monet Econ 50(1):49–123
Adedoyin FF, Gumede MI, Bekun FV, Etokakpan MU, Balsalobre-lorente D (2020) Modelling coal rent, economic growth and CO2 emissions: does regulatory quality matter in BRICS economies? Sci Total Environ 710:136284
Alhassan A, Usman O, Ike GN, Sarkodie SA (2020) Impact assessment of trade on environmental performance: accounting for the role of government integrity and economic development in 79 countries. Heliyon 6(9):e05046
Alege PO, Jolaade A, Adu O (2018) Is there co-integration between renewable energy and economic growth in selected Sub-Saharan African counties? Int J Energy Econ Policy 8(4):219–226
Al-Mulali U, Saboori B, Ozturk I (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Vietnam. Energy Policy 76:123–131
Apergis N, Payne JE (2009a) CO2 emissions, energy usage, and output in Central America. Energy Policy 37(8):3282–3286
Apergis N, Payne JE (2010) The emissions, energy consumption, and growth nexus: evidence from the commonwealth of independent states. Energy Policy 38(1):650–655
Apergis N, Payne JE (2009b) Energy consumption and economic growth in Central America: evidence from a panel cointegration and error correction model. Energy Econ 31(2):211–216
Apergis N, Ozturk I (2015) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol Indic 52:16–22
Asghari M (2013) Does FDI promote MENA region’s environment quality? Pollution halo or pollution haven hypothesis. Int J Sci Res Environ Sci 1(6):92–100
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Toward a sustainable environment: Nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029
Bhattacharya M, Paramati SR, Ozturk I, Bhattacharya S (2016) The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: evidence from top 38 countries. Appl Energy 162:733–741
Black WR (2010) Sustainable transportation: problems and solutions. Guilford Press, New York
Bokpin GA (2017) Foreign direct investment and environmental sustainability in Africa: the role of institutions and governance. Res Int Bus Financ 39:239–247
Cole MA (2004) Trade, the pollution haven hypothesis and the environmental Kuznets curve: examining the linkages. Ecol Econ 48(1):71–81
Cole MA, Elliott RJ, Fredriksson PG (2006) Endogenous pollution havens: does FDI influence environmental regulations? Scand J Econ 108(1):157–178
Copeland BR (2013) Trade and the environment. In: Palgrave handbook of international trade. Palgrave Macmillan, London, pp 423–496
Dean JM (1992) Trade and the Environment: A Survey of the Literature (No. 966). The World Bank, Washington D.C
Dogan E, Turkekul B (2016) CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1203–1213
Dreher A (2006) Does globalization affect growth? Evidence from a new index of globalization. Appl Econ 38(10):1091–1110
Dudka S, Adriano DC (1997) Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: a review. J Environ Qual 26(3):590–602
Fredriksson PG, Svensson J (2003) Political instability, corruption and policy formation: the case of environmental policy. J Public Econ 87(7–8):1383–1405
Galinato GI, Chouinard HH (2018) Strategic interaction and institutional quality determinants of environmental regulations. Resour Energy Econ 53:114–132
Gökmenoğlu K, Taspinar N (2016) The relationship between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth and FDI: the case of Turkey. J Int Trade Econ Develop 25(5):706–723
Grossman, G. M., & Krueger, A. B. (1991). Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement (No. w3914). National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1996) The inverted-U: what does it mean? Environ Dev Econ 1(1):119–122
Güngör H, Olanipekun IO, Usman O (2020) Testing the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of energy consumption and democratic accountability. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–15
Halicioglu F (2009) An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 37(3):1156–1164
Hamit-Haggar M (2012) Greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: A panel cointegration analysis from Canadian industrial sector perspective. Energy Econ 34(1):358–364
Harrison AE, Eskeland G (1997) Moving to greener pastures? Multinationals and the pollution-haven hypothesis. The World Bank, Wahington D.C
He J (2006) Pollution haven hypothesis and environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: the case of industrial emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces. Ecol Econ 60(1):228–245
Hoffmann R, Lee CG, Ramasamy B, Yeung M (2005) FDI and pollution: a granger causality test using panel data. J Int Develop 17(3):311–317
Hubbard R, O’Brien A (2013) Economics, 4th edn. Pearson International Edition, NewJersey/UK
Ibrahim MD, Alola AA (2020) Integrated analysis of energy-economic development environmental sustainability nexus: case study of MENA countries. Sci Total Environ 737:139768
Ike GN, Usman O, Sarkodie SA (2020a) Fiscal policy and CO2 emissions from heterogeneous fuel sources in Thailand: evidence from multiple structural breaks cointegration test. Sci Total Environ 702:134711
Ike GN, Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020b) Environmental quality effects of income, energy prices and trade: the role of renewable energy consumption in G-7 countries. Sci Total Environ 721:137813
Iorember PT, Jelilov G, Usman O, Işık A, Celik B (2020a) The influence of renewable energy use, human capital, and trade on environmental quality in South Africa: multiple structural breaks cointegration approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–13
Iorember PT, Goshit GG, Dabwor DT (2020b) Testing the nexus between renewable energy consumption and environmental quality in Nigeria: the role of broad-based financial development. Afr Dev Rev 32(2):163–175
Kahia M, Aïssa MSB, Lanouar C (2017) Renewable and non-renewable energy use-economic growth nexus: the case of MENA Net Oil Importing Countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 71:127–140
Katircioglu ST, Katircioglu S (2018) Testing the role of urban development in conventional environmental Kuznets curve: evidence from Turkey. Appl Econ Lett 25:741–746
Katircioglu ST (2014) International tourism, energy consumption, and environmental pollution: the case of Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 36:180–187
Liu M, Ren X, Cheng C, Wang Z (2020) The role of globalization in CO2 emissions: a semi-parametric panel data analysis for G7. Sci Total Environ 718:137379
Lopez R (1994) The environment as a factor of production: the effects of economic growth and trade liberalization. J Environ Econ Manag 27(2):163–184
Mesagan EP, Isola WA, Ajide KB (2018) The capital investment channel of environmental improvement: evidence from BRICS. Environ Dev Sustain:1–22
Nentjes A, de Vries FP, Wiersma D (2007) Technology-forcing through environmental regulation. Eur J Polit Econ 23(4):903–916
Olanipekun IO, Olasehinde-Williams GO, Alao RO (2019) Agriculture and environmental degradation in Africa: the role of income. Sci Total Environ 692:60–67
Panayotou T (2000) Population and environment. CID Working Paper Series 2000.53. Harvard University, Cambridge
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analyses of level relationships. J Appl Econom 16:289–326
Rafindadi AA, Usman O (2020) Toward sustainable electricity consumption in Brazil: the role of economic growth, globalization and ecological footprint using a nonlinear ARDL approach. J Environ Plan Manag:1–25
Rafindadi AA, Usman O (2019) Globalization, energy use, and environmental degradation in South Africa: startling empirical evidence from the Maki-cointegration test. J Environ Manag 244:265–275
Raza SA, Sharif A, Wong WK, Karim MZA (2017) Tourism development and environmental degradation in the United States: evidence from wavelet-based analysis. Curr Issue Tour 20(16):1768–1790
Rodrik D (2008) One economics, many recipes: globalization, institutions, and economic growth. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Rondinelli D, Berry M (2000) Multimodal transportation, logistics, and the environment: managing interactions in a global economy. Eur Manag J 18(4):398–410
Saint Akadiri S, Alkawfi MM, Uğural S, Akadiri AC (2019) Towards achieving environmental sustainability target in Italy. The role of energy, real income and globalization. Sci Total Environ 671:1293–1301
Samimi AJ, Ahmadpour M, Ghaderi S (2012) Governance and environmental degradation in MENA region. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 62:503–507
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015a) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecol Indic 52:379–393
Shahbaz M, Nasreen S, Abbas F, Anis O (2015b) Does foreign direct investment impede environmental quality in high-, middle-, and low-income countries? Energy Econ 51:275–287
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Ozturk I (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis and the role of globalization in selected African countries. Ecol Indic 67:623–636
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017a) The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. Singapore Econ Rev 62(04):929–957
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Hammoudeh S, Shahzad SJH (2017b) Bounds testing approach to analyzing the environment Kuznets curve hypothesis with structural beaks: the role of biomass energy consumption in the United States. Energy Econ 68(2017):548–565
Shahbaz M, Mahalik MK, Shahzad SJH, Hammoudeh S (2019) Testing the globalization-driven carbon emissions hypothesis: international evidence. Int Econ 158:25–38
Soytas U, Sari R, Ewing BT (2007) Energy consumption, income, and carbon emissions in the United States. Ecol Econ 62(3–4):482–489
Stern DI (2004) The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev 32(8):1419–1439
Stern DI, Common MS, Barbier EB (1996) Economic growth and environmental degradation: the environmental Kuznets curve and sustainable development. World Dev 24(7):1151–1160
Taylor MS (2005) Unbundling the pollution haven hypothesis. BE J Econ Analys Polic 4(2)
Trébuil G (1995) Pioneer agriculture, green revolution and environmental degradation in Thailand. Count costs Econ Growth Environ Thailand:67–89
Usman O, Olanipekun IO, Iorember PT, Abu-Goodman M (2020a) Modelling environmental degradation in South Africa: the effects of energy consumption, democracy, and globalization using innovation accounting tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:8334–8349
Usman O, Akadiri SS, Adeshola I (2020b) Role of renewable energy and globalization on ecological footprint in the USA: implications for environmental sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:30681–30693
Usman O, Bekun FV, Ike GN (2020c) Democracy and tourism demand in European countries: does environmental performance matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(30):38353–38359
Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020d) Assessment of the role of renewable energy consumption and trade policy on environmental degradation using innovation accounting: evidence from the US. Renew Energy 150:266–277
Usman O, Iorember PT, Olanipekun IO (2019) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in India: the effects of energy consumption and democracy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(13):13390–13400
Woods WI (2004) Population nucleation, intensive agriculture, and environmental degradation: the Cahokia example. Agric Hum Values 21(2–3):255–261
Zhang XP, Cheng XM (2009) Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Ecol Econ 68(10):2706–2712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Maryam Abu-Goodman: data curation, writing—original draft, formal analysis, investigation. Ojonugwa Usman: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology. Ifedolapo Olabisi Olanipekun: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Hasan Güngör: writing—original draft, supervision, validation, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güngör, H., Abu-Goodman, M., Olanipekun, I.O. et al. Testing the environmental Kuznets curve with structural breaks: the role of globalization, energy use, and regulatory quality in South Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 20772–20783 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11843-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11843-4