Abstract
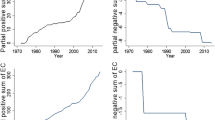
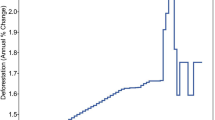
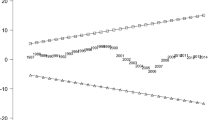
The multi-dimensional pollutions in the earth zone due to the degradation of the environmental levels have been emerging as an urgent issue in the developing economies. The BRICS group of countries holds a unique position in the emerging economies, playing a leading role in reinforcing political power globally and domestically. This study examines the annual time series over the period of 1971–2017 for Brazil, India, China, and South Africa, and 1990–2017 for Russia, to explore the relationship between environmental quality and economic growth in correspondence with the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis as well as the Decoupling Index (DI). The presence of an EKC strongly supports any of the individualistic environmental determinants effected in the long run by Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL), building linkage with the approach of the co-integration and the DI, which brings about economic growth as well as CO2 emission and environmental degradation simultaneously. A short-run relationship and presence of the EKC hypothesis are observed in Brazil, Russia, and India with 92%, while China’s (55%) and South Africa’s (79%) have a slower speed of adjustment to long-run equilibrium. This study concludes that economic expansion and environmental degradation are interrelated in the long run. Environment degradation (CO2 emission) can be eradicated by continuous economic growth, management of energy demands and energy crises, implementation of environmentally sustainable policies, application of green technologies for the use of natural resources, and controllability of urban population growth with immediate and effective actions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aboagye S (2017) Economic expansion and environmental sustainability nexus in Ghana. African Dev Rev 29:155–168
Al-Mulali U, Sab CNBC (2012) The impact of energy consumption and CO2 emission on the economic growth and financial development in the Sub Saharan African countries. Energy 39:180–186
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Lean HH (2015) The influence of economic growth, urbanization, trade openness, financial development, and renewable energy on pollution in Europe. Nat Hazards 79:621–644
Andreoni J, Levinson A (2001) The simple analytics of the environmental Kuznets curve. J Public Econ 80:269–286
Antweiler W, Copeland BR, Taylor MS (2001) Is free trade good for the environment? Am Econ Rev 91:877–908
Arouri MEH, Ben YA, M’henni H, Rault C (2012) Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Middle East and North African countries. Energy Policy 45:342–349
Baek J (2015) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: the case of Arctic countries. Energy Econ 50:13–17
Baek J, Cho Y, Koo WW (2009) The environmental consequences of globalization: A country-specific time-series analysis. Ecol Econ 68:2255–2264
Baloch MA, Ozturk I, Bekun FV, Khan D (2021) Modeling the dynamic linkage between financial development, energy innovation, and environmental quality: Does globalization matter? Bus Strateg Environ 30:176–184
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Leitão NC, Murshed M (2021) The carbon dioxide neutralizing effect of energy innovation on international tourism in EU-5 countries under the prism of the EKC hypothesis. J Environ Manage 298:113513
Bello MO, Solarin SA, Yen YY (2018) The impact of electricity consumption on CO2 emission, carbon footprint, water footprint and ecological footprint: the role of hydropower in an emerging economy. J Environ Manage 219:218–230
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S, Ozturk I (2015) The role of renewable energy consumption and trade: Environmental kuznets curve analysis for sub-saharan Africa countries. African Dev Rev 27:288–300
Bhattarai GR, Hite D, Hatch LU, Thompson H (2003) Endogenous Growth Models And The Environmental Kuznets Curve: An Analysis Of Global Environmental Sustainability. (No. 376-2016-20403)
Boopen S, Vinesh S (2011) On the relationship between CO2 emissions and economic growth: the Mauritian experience. In: University of Mauritius, Mauritius Environment Outlook Report, http://www. csae. ox. ac. uk/conferences/2011-EDiA/papers/776-Seetanah. pdf. p 2015
Charfeddine L, Kahia M (2019) Impact of renewable energy consumption and financial development on CO2 emissions and economic growth in the MENA region: a panel vector autoregressive (PVAR) analysis. Renew Energy 139:198–213
Cole MA, Neumayer E (2004) Examining the impact of demographic factors on air pollution. Popul Environ 26:5–21
Costantini V, Martini C (2010) The causality between energy consumption and economic growth: A multi-sectoral analysis using non-stationary cointegrated panel data. Energy Econ 32:591–603
Elmawazini K, Manga P, Nwankwo S, AlNaser B (2019) Health gap between developed and developing countries: Does globalization matter? Econ Chang Restruct 52:123–138
Farhani S, Shahbaz M, Arouri MEH (2013) Panel analysis of CO2 emissions, GDP, energy consumption, trade openness and urbanization for MENA countries. 2013:1-19
Gao J, Zhang L (2014) Electricity consumption–economic growth–CO2 emissions nexus in sub-Saharan Africa: Evidence from panel cointegration. African Dev Rev 26:359–371
Hassan ST, Xia E, Khan NH, Shah SMA (2019) Economic growth, natural resources, and ecological footprints: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:2929–2938
Hossain S (2012) An econometric analysis for CO 2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, foreign trade and urbanization of Japan. Vol. 3 No. 3A (2012) , Article ID: 25022 , 4 pages DOI:https://doi.org/10.4236/lce.2012.323013
Hu J, Gui S, Zhang W (2017) Decoupling analysis of China’s product sector output and its embodied carbon emissions—an empirical study based on non-competitive IO and Tapio decoupling model. Sustainability 9:815
Jenkıns HP, Katırcıoglu ST (2010) The bounds test approach for cointegration and causality between financial development, international trade and economic growth: the case of Cyprus. Appl Econ 42:1699–1707
Jevrejeva S, Moore JC, Grinsted A (2010) How will sea level respond to changes in natural and anthropogenic forcings by 2100? Geophys Res Lett 37(7)
Kaushal LA, Pathak N (2015) The causal relationship among economic growth, financial development and trade openness in Indian economy. Int J Econ Perspect 9:5–22
Khoshnevis Yazdi S, Golestani Dariani A (2019) CO 2 emissions, urbanisation and economic growth: evidence from Asian countries. Econ Res istraživanja 32:510–530
Lau LC, Tan KT, Lee KT, Mohamed AR (2009) A comparative study on the energy policies in Japan and Malaysia in fulfilling their nations’ obligations towards the Kyoto Protocol. Energy Policy 37:4771–4778
Lise W, Van Montfort K (2007) Energy consumption and GDP in Turkey: Is there a co-integration relationship? Energy Econ 29:1166–1178
Marques AC, Fuinhas JA, Leal PA (2018) The impact of economic growth on CO 2 emissions in Australia: the environmental Kuznets curve and the decoupling index. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:27283–27296
McMichael AJ, Campbell-Lendrum D, Kovats S, et al (2004) Global climate change
Mehrara M (2007) Energy consumption and economic growth: the case of oil exporting countries. Energy Policy 35:2939–2945
Mohsin M, Zhu Q, Naseem S et al (2021) Mining Industry Impact on Environmental Sustainability, Economic Growth, Social Interaction, and Public Health: An Application of Semi-Quantitative Mathematical Approach. Processes 9:972
Murshed M (2020a) Are Trade Liberalization policies aligned with Renewable Energy Transition in low and middle income countries? An Instrumental Variable approach. Renew Energy 151:1110–1123
Murshed M (2020b) An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:36254–36281
Murshed M, Alam MS (2021) Estimating the macroeconomic determinants of total, renewable, and non-renewable energy demands in Bangladesh: the role of technological innovations. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–21
Murshed M, Rahman MA, Alam MS et al (2021) The nexus between environmental regulations, economic growth, and environmental sustainability: linking environmental patents to ecological footprint reduction in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–22
Naseem S, Fu GL, Mohsin M et al (2020) Semi-Quantitative Environmental Impact Assessment of Khewra Salt Mine of Pakistan: an Application of Mathematical Approach of Environmental Sustainability. Mining, Metall Explor 37:1185–1196
Naseem S, Mohsin M, Hui W et al (2021) The investor psychology and stock market behavior during the initial era of COVID-19: a study of China, Japan, and the United States. Front Psychol 12:16
Nuroglu E, Kunst RM (2018) Kuznets and environmental Kuznets curves for developing countries. Ind policy Sustain Growth Sustain Dev. Springer, Singapore
Omri A, Daly S, Rault C, Chaibi A (2015) Financial development, environmental quality, trade and economic growth: What causes what in MENA countries. Energy Econ 48:242–252
Onafowora OA, Owoye O (2014) Bounds testing approach to analysis of the environment Kuznets curve hypothesis. Energy Econ 44:47–62
Oyinlola MA, Adedeji A (2019) Human capital, financial sector development and inclusive growth in sub-Saharan Africa. Econ Chang Restruct 52:43–66
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2013) The long-run and causal analysis of energy, growth, openness and financial development on carbon emissions in Turkey. Energy Econ 36:262–267
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U, Saboori B (2016) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1916–1928
Pata UK (2018) Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J Clean Prod 187:770–779
Pesaran B, Pesaran MH (2010) Time series econometrics using Microfit 5.0: A user’s manual. Oxford University Press, Inc.
Phimphanthavong H (2013) The impacts of economic growth on environmental conditions in laos. Int J Bus Manag Econ Res 4:766–774
Rasoulinezhad E, Saboori B (2018) Panel estimation for renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, CO 2 emissions, the composite trade intensity, and financial openness of the commonwealth of independent states. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:17354–17370
Ruffing K (2007) Indicators to measure decoupling of environmental pressure from economic growth. Sustain Indic A Sci Assess 67:211
Saboori B, Bin SJ, Mohd S (2012) An empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions in Indonesia: the role of energy consumption and foreign trade. Int J Econ Financ 4:243–251
Sadorsky P (2010) The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 38:2528–2535
Saidi K, Mbarek MB (2017) The impact of income, trade, urbanization, and financial development on CO 2 emissions in 19 emerging economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:12748–12757
Sarfraz M, Mohsin M, Naseem S, Kumar A (2021) Modeling the relationship between carbon emissions and environmental sustainability during COVID-19: a new evidence from asymmetric ARDL cointegration approach. Environ Dev Sustain:1–19
Sarkodie SA, Ozturk I (2020) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Kenya: a multivariate analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 117:109481
Seetanah B, Sannassee RV, Fauzel S et al (2019) Impact of economic and financial development on environmental degradation: evidence from small island developing states (SIDS). Emerg Mark Financ Trade 55:308–322
Solarin SA, Bello MO (2018) Persistence of policy shocks to an environmental degradation index: the case of ecological footprint in 128 developed and developing countries. Ecol Indic 89:35–44
Sulaiman C, Abdul-Rahim AS (2018) Population growth and CO2 emission in Nigeria: a recursive ARDL approach. Sage Open 8:2158244018765916
Tamazian A, Rao BB (2010) Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evidence from transitional economies. Energy Econ 32:137–145
Ullah S, Ozturk I, Majeed MT, Ahmad W (2021) Do technological innovations have symmetric or asymmetric effects on environmental quality? Evidence from Pakistan. J Clean Prod 316:128239
Ulucak R, Lin D (2017) Persistence of policy shocks to Ecological Footprint of the USA. Ecol Indic 80:337–343
Usman A, Ozturk I, Hassan A et al (2021) The effect of ICT on energy consumption and economic growth in South Asian economies: an empirical analysis. Telemat Informatics 58:101537
Yan Y, Wang C, Ding D et al (2016) Industrial carbon footprint of several typical Chinese textile fabrics. Acta Ecol Sin 36:119–125
Yasin I, Ahmad N, Chaudhary MA (2020) Catechizing the environmental-impression of urbanization, financial development, and political institutions: a circumstance of ecological footprints in 110 developed and less-developed countries. Soc Indic Res 147:621–649
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Muhammad Mohsin, Sobia Naseem and Muddassar Sarfraz; Methodology: Muhammad Zia-UR-Rehman; Formal analysis and investigation: Muddassar Sarfraz and Sajjad Ahmad Baig; Writing—original draft preparation: Sobia Naseem, Muhammad Mohsin; Writing—review and editing: Muhammad Zia-UR- Rehman; Funding acquisition: Muddassar Sarfraz; Resources: Sajjad Ahmad Baig; Supervision: Muhammad Zia-UR- Rehman and Muddassar Sarfraz. All authors approved the current study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standard.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naseem, ., Mohsin, M., Zia-UR-Rehman, M. et al. The influence of energy consumption and economic growth on environmental degradation in BRICS countries: an application of the ARDL model and decoupling index. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 13042–13055 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16533-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16533-3