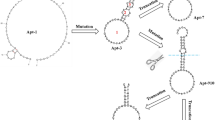
Abstract
The diversity of aquatic ecosystems impacted by toxic metals is widely distributed throughout the world. The application of metallothionein (MT) as an early warning sign of metal exposure in freshwater fish is important in biomonitoring, but a more accessible, sensitive, safe, and efficient new methodological strategy is necessary. On this way, a fish MT synthetic gene from Oreochromis aureos was expressed in Escherichia coli to produce polyclonal antibodies against the protein. In the validation assays, these antibodies were able to detect hepatic MT from freshwater fishes Oreochromis niloticus, Pimelodus maculatus, Prochilodus lineatus, and Salminus brasiliensis showing a potential tool for toxic metals biomarker in biomonitoring of aquatic ecosystems. The current results showed the applicability of this molecule in quantitative immunoassays as a sensor for monitoring aquatic environments impacted by toxic metals. Due to the lack of methods focusing on metal pollution diagnostics in aquatic ecosystems, the current proposal revealed a promising tool to applications in biomonitoring programs of water resources, mainly in Brazil where the mining activity is very developed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam MA, Maftuch KY, Risjani Y (2019) Detection of metallothionein protein biomarkers (MTs) and pinocytosis activity in Gambusia Fish (Gambusia affinis) exposed to cadmium. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 18(3):989–994
Alberto C, Ribeiro DO, Katsumiti A, França P, Maschio J, Zandoná E, Cestari MM, Vicari T, Roche H, Cristina H et al (2013) Biomarkers responses in fish (Atherinella brasiliensis ) of Paranaguá bay, Southern Brazil, for assessment of pollutant effects. Braz J Oceanogr 61(December 2004):1–11
ANM – Agencia Nacional de Mineração. (2012) TECHNICAL ADVICE N° 07/2019 –GSBM/SPM/ANM-ESGJ/LHPR/LPN/WAN Reference: Process 931. 194 p. Capdevila, M., et al. State-of-the-art of metallothioneins at the beginning of the 21st century. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, v.256, p. 46–62.
Bhandari S, Melchiorre C, Dostie K, Laukens D, Devisscher L, Louwrier A, Thees A, Lynes MA (2017) Detection and manipulation of the stress response protein metallothionein. Curr Protoc Toxicol 2017(February):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/cptx.17
Boelsterli UA (2007) Mechanistic toxicology: the molecular basis of how chemicals disrupt biological targets, 2ed edn. Taylor and Francis, London, 312 p
Bussolaro D, Filipak Neto F, Glinski A, Roche H, Guiloski IC, Mela M, Silva De Assis HC, Oliveira Ribeiro CA (2012) Bioaccumulation and related effects of PCBs and organochlorinated pesticides in freshwater fish Hypostomus commersoni. J Environ Monit 14(8):2154–2163. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em10863a
Capdevila M, Bofill R, Palacios O, Atrian S (2012) State-of-the-art of metallothioneins at the beginning of the 21st century. Coord Chem Rev 256(1–2):46–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.07.006
Chu MM, Guo ZQ, Muto N, Itoh N, Tanaka K, Ren HW (2006) Development of ELISA for metallothionein-II allows determination of heavy metal pollution of fresh water. Front Biosci 11(SUPPL. 1):2113–2122. https://doi.org/10.2741/1954
Costa DDM, Neto FF, Costa MDM, Morais RN, Garcia JRE, Esquivel BM, Ribeiro CAO (2010) Vitellogenesis and other physiological responses induced by 17-β-estradiol in males of freshwater fish Rhamdia quelen. Comp Biochem Physiol - C Toxicol Pharmacol 151(2):248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2009.11.002
Doering JA, Beitel SC, Eisner BK, Heide T, Hollert H, Giesy JP, Hecker M, Wiseman SB (2015) Identification and response to metals of metallothionein in two ancient fishes: white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) and lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens). Comp Biochem Physiol Part - C Toxicol Pharmacol 171:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.03.002
Doria HB, Voigt CL, Sandrini-Neto L, Campos SX, de Oliveira-Ribeiro CA, Randi MAF (2017) How and where to perform biomonitoring studies: different levels of toxic metal pollution are detected in the Alagados Reservoir in Southern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(14):13080–13094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8953-1
dos Coimbra RSC, dos Santos CR, Saraiva VB, Oliveira MM (2013) Biomarkers as tools in quality assessment of fish contaminated with trace metals. Bol do Obs Ambient Alberto Ribeiro Lamego 7(1):153–172. https://doi.org/10.5935/2177-4560.20130011
dos Santos DR, Yamamoto FY, Filipak Neto F, Randi MAF, Garcia JE, Costa DDM, Liebel S, Campos SX, Voigt CL, de Oliveira Ribeiro CA (2016) The applied indicators of water quality may underestimate the risk of chemical exposure to human population in reservoirs utilized for human supply—Southern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(10):9625–9639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5995-0
Drira N, Trefry JH, Trocine RP (2017) Interrelationships among trace metals and metallothionein in 11 digestive glands and gills for field samples of Merceneria merceneria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12 24(36):27897–27904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0368-5
Duan L, Yu J, Xu L, Tian P, Hu X, Song X, Pan Y (2019) Functional characterization of a type 4 metallothionein gene (CsMT4) in cucumber. Hortic Plant J 5(3):120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpj.2019.04.002
Fabrin TMC, Diamante NA, Mota TFM, de Ghisi NC, Prioli SMAP, Prioli AJ (2018) Performance of biomarkers metallothionein and ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase in aquatic environments: A meta-analytic approach. Chemosphere 205:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.069
Gao D, Wang GT, Chen XT, Nie P (2009) Metallothionein-2 gene from the mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi: cDNA cloning, tissue expression, and immunohistochemical localization. CompBiochem Physiol - C Toxicol Pharmacol 149(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.05.014
Ghisi NDC, Ramsdorf WA, Ferraro MVM, De Almeida MIM, Ribeiro CADO, Cestari MM (2011) Evaluation of genotoxicity in Rhamdia quelen (Pisces, Siluriformes) after sub-chronic contamination with Fipronil. Environ Monit Assess 180(1–4):589–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1807-7
Hamilton SJ, Mehrle PM (1986) Metallothionein in Fish: Review of Its Importance in Assessing Stress from Metal Contaminants. Trans Am Fish Soc 115(4):596-609. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8659(1986)115<596:MIF>2.0.CO;2
Hauser-Davis RA, Bastos FF, Tuton B, Chávez Rocha R, Pierre TS, Ziolli RL, Arruda MAZ (2014) Bile and liver metallothionein behavior in copper-exposed fish. J Trace Elem Med Biol 28(1):70–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2013.09.003
Joseph BC, Pichaimuthu S, Srimeenakshi S (2015) An overview of the parameters for recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci Ther 06(05). https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7013.1000221
Kado Y, Mizohata E, Nagatoishi S, Iijima M, Shinoda K, Miyafusa T, Nakayama T, Yoshizumi T, Sugiyama A, Kawamura T, Lee YH, Matsumura H, Doi H, Fujitani H, Kodama T, Shibasaki Y, Tsumoto K, Inoue T (2016) Epiregulin recognition mechanisms by anti-epiregulin antibody 9E5: structural, functional, and molecular dynamics simulation analyses. J Biol Chem 291(5):2319–2330. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.656009
Kim N, Son SH (2015) Development of antigen-immobilized metallothionein sensor that exploits gold nanoparticle-based enhancement of signal. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15(8):6188–6192. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2015.10297
Lacorn M, Lahrssen A, Rotzoll N, Simat TJ, Steinhart H (2001) Quantification of metallothionein isoforms in fish liver and its implications for biomonitoring. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(1):140–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620200115
LaVallie ER, DiBiasio EA, Kovacic S, Grant KL, Schandel PF, McCoy JM (1993) © 199 3 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/naturebiotechnology. Nat Biotechnol 11:187–193
Lee E, Jeon H, Kang C, Woo S, Yum S, Kwon Y. (2018). Detection of metallothionein in javanese medaka (Oryzias javanicus), using a scFv-immobilized protein chip. Sensors (Switzerland). 18(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041069.
Li J, Luo G, Xu J (2019) Fate and ecological risk assessment of nutrients and metals in sewage sludge from ten wastewater treatment plants in Wuxi City, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102(2):259–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2525-z
Margoshes M, Vallee BL (1957) A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex. J Am Chem Soc 79:4813–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01574a064
M’Kandawire E, Mierek-Adamska A, Stürzenbaum SR, Choongo K, Yabe J, Mwase M, Saasa N, Blindauer CA (2017) Metallothionein from wild populations of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus: from sequence, protein expression and metal binding properties to transcriptional biomarker of metal pollution. Int J Mol Sci 18(7):1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071548
McCoy J; LaVallie E (1997). Purification of recombinant proteins. Curr Protocols Protein Sci 1–14.
McNiff ML, Haynes EP, Dixit N, Gao FP, Laurence JS (2016) Thioredoxin fusion construct enables high-yield production of soluble, active matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 122(5):64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2016.02.012
Moura Costa DD, Bozza DA, Rizzo LE, Garcia J, Costa MDM, de Oliveira Ribeiro CA (2016) Characterization, specificity and sensibility of produced anti-Rhamdia quelen vitellogenin in Brazilian fish species. Fish Physiol Biochem 42(6):1721–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0252-0
Nakazato K, Tomioka S, Nakajima K, Saito H, Kato M, Kodaira T, Ichi YS, Shimomura Y, Hiroki T, Motoyama K et al (2014) Determination of the serum metallothionein (MT)1/2 concentration in patients with Wilson’s disease and Menkes disease. J Trace Elem Med Biol 28(4):441–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.07.013
Rosano GL, Ceccarelli EA (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5(APR):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
Ryvolova M, Krizkova S, Adam V, Beklova M, Trnkova L, Hubalek J, Kizek R (2011) Analytical methods for metallothionein detection. Curr Anal Chem 7(3):243–261. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573411011107030243
Shim YN, Paeng IR (2003) Development of bioluminescence immunoassay using photoprotein, aequorin and site-directed immobilization. Bull Kor Chem Soc 24(1):70–74. https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2003.24.1.070
Song Y, Li P, Du Y (2011) Overexpression of TrxA::BjMT2 (Thioredoxin::Metallothionein type 2 from Brassica Juncea) fusion protein in Escherichia coli and in vitro cleavage by TEV protease. Adv Mater Res 183–185:947–951. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.183-185.947
Tenório-Daussat CL, Resende MCM, Ziolli RL, Hauser-Davis RA, Schaumloffel D, Saint’Pierre TD (2014) Evaluation and standardization of different purification procedures for fish bile and liver metallothionein quantification by spectrophotometry and SDS-PAGE analyses. Talanta 120:491–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.11.070
Valiyari S, Mahdian R, Salami M, Oloomi M, Golshani M, Shokrgozar MA, Bouzari S (2017) Expression, purification and functional assessment of smallest isoform of human interleukin-24 in Escherichia coli. Braz Arch Biol Technol 60:e17160621. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2017160621
Vardhan KH, Kumar PS, Panda RC (2019) A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: current trends and future perspectives. J Mol Liq 290:111197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111197
Vergani L, Grattarola M, Borghi C, Dondero F, Viarengo A (2005) Fish and molluscan metallothioneins: a structural and functional comparison. FEBS J 272(23):6014–6023. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04993.x
Viarengo A, Burlando B, Evangelisti V, Mozzone S, Dondero F. (2001). Sensitivity and specificity of metallothionein as a biomarker for aquatic environment biomonitoring. Biomarkers Mar Org 29–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-044482913-9/50004-3.
Warnes A, Fooks AR, Stephenson JR (2004) Design and preparation of recombinant antigens as diagnostic reagents in solid-phase immunosorbent assays. Methods Mol Med 94:373–391
Yamamoto FY, Garcia JRE, Kupsco A, Oliveira Ribeiro CA (2017) Vitellogenin levels and others biomarkers show evidences of endocrine disruption in fish species from Iguaçu River - Southern Brazil. Chemosphere. 186:88–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.111
Yamamoto FY, Diamante GD, Santana MS, Santos DR, Bombardeli R, Martins CC, Oliveira Ribeiro CA, Schlenk D (2018) Alterations of cytochrome P450 and the occurrence of persistent organic pollutants in tilapia caged in the reservoirs of the Iguaçu River. Environ Pollut 240:670–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.019
Yang J, Sun H, Zhang H, Zhou H (2017) Expression, purification of metallothionein genes from freshwater crab (Sinopotamon yangtsekiense) and development of an antimetallothionein ELISA. PLoS One 12(3):e0174482. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174482
Yap CK, Jusoh A, Leong WJ, Karami A, Ong GH (2015) Potential human health risk assessment of heavy metals via the consumption of tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus collected from contaminated and uncontaminated ponds. Environ Monit Assess 187(9):584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4812-z
Yudkovski Y, Rogowska-Wrzesinska A, Yankelevich I, Shefer E, Herut B, Tom M (2008) Quantitative immunochemical evaluation of fish metallothionein upon exposure to cadmium. Mar Environ Res 65(5):427–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2008.02.001
Ziller A, Yadav RK, Capdevila M, Reddy MS, Vallon L, Marmeisse R, Atrian S, Palacios Ò, Fraissinet-Tachet L (2017) Metagenomics analysis reveals a new metallothionein family: sequence and metal-binding features of new environmental cysteine-rich proteins. J Inorg Biochem 167:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.11.017
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Carlos Chagas Institute (ICC-Fiocruz/PR) for allowing MT recombinant expression and purification and the Production and Research Centre of Immunobiological Products (CPPI), Health Department of the Paraná State for housing the rabbits during the immunization period. Thanks also to Extracellular Matrix and Biotechnology of Venoms (UFPR) by Thrombin donation.
Funding
The current study presents part of the results related to the execution of the ANEEL code R&D project PD-06491-0265/2012 carried out by UFPR for COPEL Generation and Transmission SA under the Research and Technological Development Program of the Brazilian Electric sector regulated by the National Agency of Electricity - ANEEL. This research received financial support from Paranaense Energy Company (COPEL) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PCN: Investigation, protein expression and purification, rabbits immunizations, immunoassay, data curation, and writing ± original draft.
DARV: Polyclonal antibody purification, biological samples preparation, and immunoassay procedure.
MMP: Conceptualization, data analysis, and writing review and editing.
IO: Project supervision and manuscript review.
FCASF: Project supervision and manuscript review.
NITZ: Synthetic gene design, supervision of the protein expression, and purification procedure and manuscript review.
CAOR: Project administration, funding acquisition, general supervision, and writing ± review & editing.
CS: Conceptualization, cleavage reaction, immunoassay supervision, data analysis, figures elaboration, and writing ± review & editing.
Finally, all authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Use Ethics Committee (CEUA) from Biological Sciences Sector at the Federal University of Paraná (CEUA/BIO Number 662, 15/12/2013).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of the interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Severine Le Faucheur
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagamatsu, P.C., Vargas, D.Á.R., Prodocimo, M.M. et al. Synthetic fish metallothionein design as a potential tool for monitoring toxic metals in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 9517–9528 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11427-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11427-2