Abstract
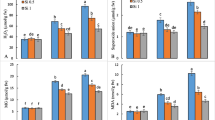
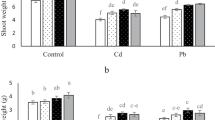
Lead (Pb) is among the most abundant toxic trace elements which causes direct and indirect negative effects on humans, animals, and plants. Thus, there is a need to alleviate the Pb toxicity in plants for good quality food production especially from marginal soils. In this study, the effects of silicon nanoparticles (Si NPs) were investigated on coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) biomass, vitamin C, flavonoid, antioxidant enzyme activities (i.e., catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and super oxide dismutase (SOD)), malondialdehyde (MDA), and Pb concentration in plants subjected to different Pb concentrations. Treatments included four levels of Pb (0, 500, 1000, and 1500 mg/kg of soil), and two levels of Si NPs (0 and 1.5 mM) in all combinations. The Pb treatments alone decreased the plant biomass and vitamin C while increased the flavonoid, MDA, antioxidant enzyme activities, and Pb concentration in tissues depending upon the Pb treatments. The foliar-applied 1.5 mM Si NPs alleviated the adverse impacts of Pb on coriander plants which were due to the minimization of Pb concentration in plants and improvements in the plant defense system. Si NPs minimized accumulation of MDA in plant tissues and adjusted the activities of POD, CAT, and SOD in plants under Pb stress. Overall, Si NP foliar application might be a suitable approach in reducing the Pb concentrations in plants. However, field studies with various plant species and environmental conditions are required to highlight the role of Si NPs on the plant under toxic trace element stress.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Rehman MZ, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015a) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MF, Irshad MK (2015b) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:186–197
Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Kanwal S, Ali Q, Ibrahim M, Gill RA, Khan MD (2015) Fulvic acid mediates chromium (Cr) tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant defense system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10601–10609
Ali S, Rizwan M, Hussain A, ur Rehman MZ, Ali B, Yousaf B, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019) Silicon nanoparticles enhanced the growth and reduced the cadmium accumulation in grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 140:1–8
Alzahrani Y, Kuşvuran A, Alharby HF, Kuşvuran S, Rady MM (2018) The defensive role of silicon in wheat against stress conditions induced by drought, salinity or cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 154:187–196
Asgari F, Majd A, Jonoubi P, Najafi F (2018) Effects of silicon nanoparticles on molecular, chemical, structural and ultrastructural characteristics of oat (Avena sativa L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 127:152–160
Beketov E, Pakhomov V, Nesterova O (2005) Improved method of flavonoid extraction from bird cherry fruits. Pharm Chem J 39:316–318
Bharwana S, Ali S, Farooq M, Iqbal N, Abbas F, Ahmad M (2013) Alleviation of lead toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes suppressed lead uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. J Bioremed Biodeg 4:1–12
Chalmardi ZK, Abdolzadeh A, Sadeghipour HR (2014) Silicon nutrition potentiates the antioxidant metabolism of rice plants under iron toxicity. Acta Physiol Plant 36:493–502
Chance B, Maehly A (1955) Assay of catalases and peroxidases. 764-775
Chen Q, Zhang X, Liu Y, Wei J, Shen W, Shen Z, Cui J (2017) Hemin-mediated alleviation of zinc, lead and chromium toxicity is associated with elevated photosynthesis, antioxidative capacity; suppressed metal uptake and oxidative stress in rice seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 81:253–264
Cui J, Liu T, Li F, Yi J, Liu C, Yu H (2017) Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: mechanisms and size effects. Environ Pollut 228:363–369
da Cunha KPV, do Nascimento CWA (2009) Silicon effects on metal tolerance and structural changes in maize (Zea mays L.) grown on a cadmium and zinc enriched soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 197:323
Dallas S, Ho G (2005) Subsurface flow reedbeds using alternative media for the treatment of domestic greywater in Monteverde, Costa Rica, Central America. Water Sci Technol 51:119–128
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Ishaque W, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2013) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 96:242–249
Fatemi H, Pour BE, Rizwan M (2020a) Isolation and characterization of lead (Pb) resistant microbes and their combined use with silicon nanoparticles improved the growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant capacity of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) under Pb stress. Environ Pollut:114982
Fatemi H, Esmaielpour B, Sefidkon F, Soltani AA, Nematollahzadeh A (2020b) How mycorrhiza symbiosis help coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) plants grow better under contaminated soil? J Plant Nutr:1–14
Feleafel MN, Mirdad ZM (2013) Hazard and effects of pollution by lead on vegetable crops. J Agri Environ 26(3):547–567
Fenech M, Amaya I, Valpuesta V, Botella MA (2019) Vitamin C content in fruits: biosynthesis and regulation. Front Plant Sci 9:2006
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gill RA et al (2015) Chromium-induced physio-chemical and ultrastructural changes in four cultivars of Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 120:154–164
Gunes A, Inal A, Bagci E, Coban S, Pilbeam D (2007) Silicon mediates changes to some physiological and enzymatic parameters symptomatic for oxidative stress in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) grown under B toxicity. Sci Hortic 113:113–119
Habibi G (2015) Effects of soil-and foliar-applied silicon on the resistance of grapevine plants to freezing stress. Acta Biol Szegediensis 59:109–117
Hattab S, Hattab S, Flores-Casseres ML, Boussetta H, Doumas P, Hernandez LE, Banni M (2016) Characterisation of lead-induced stress molecular biomarkers in Medicago sativa plants. Environ Exp Bot 123:1–12
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hou X, Liu A, Call L, Zhou C, Wu P, Zou X, Ma X (2014) Effects of Pb stress on growth and Pb accumulation of Paspalum notatum. J Agro-Environ Sci 4
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SA, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Hussain A, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Ali S (2019) Seed priming with silicon nanoparticles improved the biomass and yield while reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat grains. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:7579–7588
Ibrahim MM, Bafeel SO (2011) Molecular and physiological aspects for Lepidium sativum tolerance in response to lead toxicity. Fresenius Environ Bull 20:1871–1879
Iqbal MM, Murtaza G, Saqib ZA, Rashid A (2015) Growth and physiological responses of two rice varieties to applied lead in normal and salt-affected soils. Int J Agric Biol 17:1–10
Iwasaki K, Maier P, Fecht M, Horst WJ (2002) Leaf apoplastic silicon enhances manganese tolerance of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). J Plant Physiol 159:167–173
Karimi J, Mohsenzadeh S (2016) Effects of silicon oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of wheat seedlings. Russ J Plant Physiol 63:119–123
Kaur G, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2015) Adaptations to oxidative stress in Zea mays roots under short-term Pb2+ exposure. Biol 70:190–197
Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky O, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier J-D (2015) Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM Cu. Planta 241:847–860
Keunen E, Remans T, Bohler S, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2011) Metal-induced oxidative stress and plant mitochondria. Int J Mol Sci 12:6894–6918
Kidd P, Llugany M, Poschenrieder C, Gunse B, Barcelo J (2001) The role of root exudates in aluminium resistance and silicon-induced amelioration of aluminium toxicity in three varieties of maize (Zea mays L.). J Exp Bot 52:1339–1352
Kroukamp E, Wondimu T, Forbes PB (2016) Metal and metalloid speciation in plants: overview, instrumentation, approaches and commonly assessed elements. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 77:87–99
Kushwaha A, Hans N, Kumar S, Rani R (2018) A critical review on speciation, mobilization and toxicity of lead in soil-microbe-plant system and bioremediation strategies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:1035–1045
Lal N (2010) Molecular mechanisms and genetic basis of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants. In: Plant adaptation and phytoremediation. Springer, pp 35–58
Leiva-Brondo M, Valcárcel M, Cortés-Olmos C, Roselló S, Cebolla-Cornejo J, Nuez F (2012) Exploring alternative germplasm for the development of stable high vitamin C content in tomato varieties. Sci Hortic 133:84–88
Li L, Zheng C, Fu Y, Wu D, Yang X, Shen H (2012) Silicate-mediated alleviation of Pb toxicity in banana grown in Pb-contaminated soil. Biol Trace Elem Res 145:101–108
Liu M, Huang B, Bi X, Ren Z, Sheng G, Fu J (2013) Heavy metals and organic compounds contamination in soil from an e-waste region in South China. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:919–929
Malar S, Vikram SS, Favas PJ, Perumal V (2016) Lead heavy metal toxicity induced changes on growth and antioxidative enzymes level in water hyacinths [Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.)]. Bot Stud 55:1–11
Miao B-H, Han X-G, Zhang W-H (2010) The ameliorative effect of silicon on soybean seedlings grown in potassium-deficient medium. Ann Bot 105:967–973
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi R, Govindarajan R, Kuriakose S, Prasad M (2006) Phytochelatin synthesis and response of antioxidants during cadmium stress in Bacopa monnieri L. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:25–37
Noman A, Ali S, Naheed F, Ali Q, Farid M, Rizwan M, Irshad MK (2015) Foliar application of ascorbate enhances the physiological and biochemical attributes of maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars under drought stress. Arch Agron Soil Sci 61:1659–1672
Norton GJ et al (2014) Lead in rice: analysis of baseline lead levels in market and field collected rice grains. Sci Total Environ 485:428–434
Omaye ST, Turnbull JD, Sauberlich HE (1979) Selected methods for the determination of ascorbic acid in animal cells, tissues, and fluids. In: Methods in enzymology, vol 62. Elsevier, pp 3–11
Parys E, Wasilewska W, Siedlecka M, Zienkiewicz M, Drożak A, Romanowska E (2014) Metabolic responses to lead of metallicolous and nonmetallicolous populations of Armeria maritima. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67:565–577
Polle A, Otter T, Seifert F (1994) Apoplastic peroxidases and lignification in needles of Norway spruce (Picea abies L.). Plant Physiol 106:53–60
Prakash V (1990) Leafy spices. CRC Press, Inc.
Rameshaiah G, Pallavi J, Shabnam S (2015) Nano fertilizers and nano sensors–an attempt for developing smart agriculture. Int J Engin Res General Sci 3:314–320
Reddy AM, Kumar SG, Jyothsnakumari G, Thimmanaik S, Sudhakar C (2005) Lead induced changes in antioxidant metabolism of horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.) and bengalgram (Cicer arietinum L.). Chemosphere 60:97–104
Ren S-C, Sun J-T (2014) Changes in phenolic content, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) activity, and antioxidant capacity of two buckwheat sprouts in relation to germination. J Funct Foods 7:298–304
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Rehman MZ, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17859–17879
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Farid M, Abbas F (2017a) Effect of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of globally important food crops: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 322:2–16
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Tsang DC, Rehman MZ, Zahir ZA, Rinklebe J, Tack FM, Ok YS (2017b) A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 182:90–105
Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Bashir A (2018) Lead toxicity in cereals and its management strategies: a critical review. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:1–16
Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Malik S, Adrees M, Qayyum MF, Alamri SA, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019) Effect of foliar applications of silicon and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on growth, oxidative stress, and cadmium accumulation by rice (Oryza sativa). Acta Physiol Plant 41:1–9
Rogalla H, Römheld V (2002) Role of leaf apoplast in silicon-mediated manganese tolerance of Cucumis sativus L. Plant Cell Environ 25:549–555
Sefidkon F (1999) Effect of essential oil in shoot and fruit of coriander. Iran J Med Aromat Plant 13:32–38
Semane B, Cuypers A, Smeets K, Van Belleghem F, Horemans N, Schat H, Vangronsveld J (2007) Cadmium responses in Arabidopsis thaliana: glutathione metabolism and antioxidative defence system. Physiol Plant 129:519–528
Shahid M, Pourrut B, Dumat C, Nadeem M, Aslam M, Pinelli E (2014) Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants. In: Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, vol 232. Springer, pp 1–44
Shakoor MB et al (2014) Citric acid improves lead (Pb) phytoextraction in Brassica napus L. by mitigating Pb-induced morphological and biochemical damages. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 109:38–47
Shi Z, Yang S, Han D, Zhou Z, Li X, Liu Y, Zhang B (2018) Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.) by reducing cadmium ion uptake and enhancing antioxidative capacity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7638–7646
Shu X, Yin L, Zhang Q, Wang W (2012) Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, antioxidant enzyme activities, and photosynthesis in cuttings and seedlings of Jatropha curcas L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:893–902
Siddiqui H, Ahmed KBM, Sami F, Hayat S (2020) Silicon nanoparticles and plants: current knowledge and future perspectives. In: Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 41. Springer, pp 129–142
Silva S, Pinto G, Santos C (2017) Low doses of Pb affected Lactuca sativa photosynthetic performance. Photosynthetica 55:50–57
Singh A, Parihar P, Singh R, Prasad SM (2016) An assessment to show toxic nature of beneficial trace metals: too much of good thing can be bad. Int J Curr Multidiscip Stud 2:141–144
Soares C, de Sousa A, Pinto A, Azenha M, Teixeira J, Azevedo RA, Fidalgo F (2016) Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on ROS content, antioxidant system, lipid peroxidation and Ni uptake in Solanum nigrum L. under Ni stress. Environ Exp Bot 122:115–125
Song A, Li P, Li Z, Fan F, Nikolic M, Liang Y (2011) The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant Soil 344:319–333
Souza JF, Dolder H, Cortelzaao A (2005) Influence of Mn toxicity on photosynthesis in Vigna umbellate seedlings. Phptosynthetica 38:449–453
Suzuki N, Koussevitzky S, Mittler R, Miller G (2012) ROS and redox signalling in the response of plants to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 35:259–270
Tang H et al (2015) Effects of selenium and silicon on enhancing antioxidative capacity in ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) under cadmium stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:9999–10008
Torabi F, Majd A, Enteshary SH, Ayrian S (2013) Study of effect of silicon on some anatomical and physiological characteristics of borage (Borago officinalis L.) in hydroponic conditions. J Cell Tissue 4:275–285
Tripathi P et al (2013) Silicon mediates arsenic tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) through lowering of arsenic uptake and improved antioxidant defence system. Ecol Eng 52:96–103
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK, Rai AK (2015) Silicon-mediated alleviation of Cr (VI) toxicity in wheat seedlings as evidenced by chlorophyll florescence, laser induced breakdown spectroscopy and anatomical changes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:133–144
Wan J et al (2016) Synthesis and evaluation of a new class of stabilized nano-chlorapatite for Pb immobilization in sediment. J Hazard Mater 320:278–288
Wang J, Li W, Zhang C, Ke S (2010) Physiological responses and detoxific mechanisms to Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in young seedlings of Paulownia fortunei. J Environ Sci 22:1916–1922
Wang S, Wang F, Gao S (2015) Foliar application with nano-silicon alleviates Cd toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2837–2845
Wohlrab C, Phillips E, Dachs GU (2017) Vitamin C transporters in cancer: current understanding and gaps in knowledge. Front Oncol 7:74
Xie L et al (2017) The cadmium and lead content of the grain produced by leading Chinese rice cultivars. Food Chem 217:217–224
Zhang H, Selim H (2008) Reaction and transport of arsenic in soils: equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Adv Agron 98:45–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatemi, H., Esmaiel Pour, B. & Rizwan, M. Foliar application of silicon nanoparticles affected the growth, vitamin C, flavonoid, and antioxidant enzyme activities of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) plants grown in lead (Pb)-spiked soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 1417–1425 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10549-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10549-x