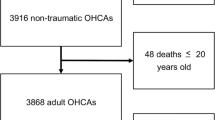
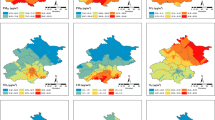
Abstract
Ambient air pollution (AAP) has been widely associated with increased morbidity of ischemic heart disease (IHD). However, no prior studies have investigated the effects of AAP exposure on the length of stay (LOS) due to IHD. Hospital data during 2015–2017 were obtained from hospital information system in five cities of Hubei province, China. We collected daily mean concentrations of air pollutants, including PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, O3, and CO, and meteorological data during the same time period. Poisson regression was applied to estimate the acute impacts of AAP on the LOS of IHD inpatients. A total of 42,114 inpatients with primary diagnosis of IHD were included, 50.63% of which were chronic IHD inpatients. Annual average concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, O3, and CO were 61.93 μg/m3, 95.47 μg/m3, 18.59 μg/m3, 35.87 μg/m3, 100.30 μg/m3, and 1.117 mg/m3, respectively. After adjusting for temperature, relative humidity, gender, age group, payment method, number of hospital beds, location of hospital, and surgery or not, exposures to PM2.5, PM10, SO2, O3, and CO were associated with increased LOS for all IHD patients in both single- and multi-pollutant models, and stronger associations were observed among chronic IHD patients. In addition, subgroup analyses demonstrated that males and the group aged 65+ years were more vulnerable to air pollution, and the adverse effects were also promoted by low temperature in cold season. This study provides the first investigation of the adverse effects of AAP on the LOS for IHD patients. In order to shorten the LOS of IHD, measures should be taken to strengthen the AAP management and protect the high-risk population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arjomandi M, Wong H, Donde A, Frelinger J, Dalton S, Ching W, Power K, Balmes JR (2015) Exposure to medium and high ambient levels of ozone causes adverse systemic inflammatory and cardiac autonomic effects. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 308:H1499–H1509
Aronow WS, Harris CN, Isbell MW, Rokaw SN, Imparto B (1972) Effect of freeway travel on angina pectoris. Ann Intern Med 77:669–676. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-77-5-669
Aryal KK, Mehata S, Neupane S, Vaidya A, Dhimal M, Dhakal P, Rana S, Bhusal CL, Lohani GR, Paulin FH and others (2015) The burden and determinants of non-communicable diseases risk factors in Nepal: findings from a Nationwide STEPS Survey. PLoS One 10: e0134834
Babatola SS (2018) Global burden of diseases attributable to air pollution. J Public Health Afr 9:813
Bell ML, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM, Dominici F (2004) Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities, 1987-2000. JAMA 292:2372–2378
Bennett DA (2001) How can I deal with missing data in my study? Aust N Z J Public Health 25:464–469
Bhatia S, Bhatia S, Mears J, Dibu G, Deshmukh A (2017) Seasonal periodicity of ischemic heart disease and heart failure. Heart Fail Clin S1551713617300521
Brook DR, Franklin B, Cascio W, Hong Y, Howard G, Lipsett M, Luepker R, Mittleman M, Samet J, Sidney C, Smith CS, Tager I (2004) Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the expert panel on population and prevention science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 109:2655–2671
Cao J, Qin G, Shi R, Bai F, Yang G, Zhang M, Lv J (2016) Overproduction of reactive oxygen species and activation of MAPKs are involved in apoptosis induced by PM2.5 in rat cardiac H9c2 cells. J Appl Toxicol 36:609–617
Chen R, Zhang Y, Yang C, Zhao Z, Xu X, Kan H (2013) Acute effect of ambient air pollution on stroke mortality in the China air pollution and health effects study. Stroke 44:954–960
Chen D, Mayvaneh F, Baaghideh M, Entezari A, Ho HC, Xiang Q, Jiao A, Zhang F, Hu K, Chen G, Zhao Q, Sun S, Zhang Y (2019) Utilizing daily excessive concentration hours to estimate cardiovascular mortality and years of life lost attributable to fine particulate matter in Tehran, Iran. Sci Total Environ 703:134909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134909
Cheng J, Xu Z, Zhang X, Zhao H, Hu W (2019) Estimating cardiovascular hospitalizations and associated expenses attributable to ambient carbon monoxide in Lanzhou, China: scientific evidence for policy making. Sci Total Environ 682:514–522
Chuang KJ, Chan CC, Su TC, Lee CT, Tang CS (2007) The effect of urban air pollution on inflammation, oxidative stress, coagulation, and autonomic dysfunction in young adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:370–376
Chuang KJ, Coull BA, Zanobetti A, Suh H, Schwartz J, Stone PH, Litonjua A, Speizer FE, Gold DR (2008) Particulate air pollution as a risk factor for ST-segment depression in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 118:1314–1320
Dales R (2005) Ambient carbon monoxide may influence heart rate variability in subjects with coronary artery disease. J Occup Environ Med 46:1217–1221
Desai MM, Stauffer BD, Feringa HH, Schreiner GC (2009) Statistical models and patient predictors of readmission for acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2:500–507
Fakhri AA, Ilic LM, Wellenius GA, Urch B, Silverman F, Gold DR, Mittleman MA (2009) Autonomic effects of controlled fine particulate exposure in young healthy adults: effect modification by ozone. Environ Health Perspect 117:1287–1292
Filleul L, Cassadou S, Medina S, Fabres P, Lefranc A, Eilstein D, Le Tertre A, Pascal L, Chardon B, Blanchard M et al (2006) The relation between temperature, ozone, and mortality in nine French cities during the heat wave of 2003. Environ Health Perspect 11:1344–1347
Glick AF, Tomopoulos S, Fierman AH, Elixhauser A, Trasande L (2019) Association between outdoor air pollution levels and inpatient outcomes in pediatric pneumonia hospitalizations, 2007 to 2008. Acad Pediatr 19:414–420
Grigorakis N, Floros C, Tsangari H, Tsoukatos E (2016) Out of pocket payments and social health insurance for private hospital care: evidence from Greece. Health Policy 120:948–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2016.06.011
Guo Y, Jia Y, Pan X, Liu L, Wichmann HE (2009) The association between fine particulate air pollution and hospital emergency room visits for cardiovascular diseases in Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 407:4826–4830
Huang J, Li G, Qian X, Xu G, Zhao Y, Huang J, Liu Q, He T, Guo X (2018) The burden of ischemic heart disease related to ambient air pollution exposure in a coastal city in South China. Environ Res 164:255–261
Kinjo K, Sato H, Nakatani D, Nakatani D, Mizuno H, Shimizu M, Hishida E, Ezumi A, Hoshida S, Koretsune Y, Hori M (2004) Predictors of length of hospital stay after acute myocardial infarction in Japan. Circ J 68:809–815
Kowalska M, Kocot K (2016) Short-term exposure to ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) and the risk of heart rhythm abnormalities and. Stroke 70:1017
Kuwabara K, Imanaka Y, Matsuda S, Fushimi K, Hashimoto H, Ishikawa KB, Horiguchi H, Hayashida K, Fujimori K (2008) Impact of age and procedure on resource use for patients with ischemic heart disease 85:0–206
Li B, Gao H, Li X, Liu Y, Wang M (2006) Correlation between brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and arterial compliance and cardiovascular risk factors in elderly patients with arteriosclerosis. Hypertens Res 29:309–314
Liu T, Zeng W, Lin H, Rutherford S, Xiao J, Li X, Li Z, Qian Z, Feng B, Ma W (2016) Tempo-spatial variations of ambient ozone-mortality associations in the USA: results from the NMMAPS data. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13090851
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, AlMazroa MA, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker-Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Abdulhak AB, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, Burney P, Carapetis J, Chen H, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahodwala N, de Leo D, Degenhardt L, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ezzati M, Feigin V, Flaxman AD, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FGR, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gonzalez-Medina D, Halasa YA, Haring D, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Hoen B, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Keren A, Khoo JP, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Ohno SL, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Mallinger L, March L, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGrath J, Memish ZA, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Michaud C, Miller M, Miller TR, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Mokdad AA, Moran A, Mulholland K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KMV, Nasseri K, Norman P, O'Donnell M, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Phillips D, Pierce K, Pope CA III, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Raju M, Ranganathan D, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Rivara FP, Roberts T, de León FR, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Segui-Gomez M, Shepard DS, Singh D, Singleton J, Sliwa K, Smith E, Steer A, Taylor JA, Thomas B, Tleyjeh IM, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Undurraga EA, Venketasubramanian N, Vijayakumar L, Vos T, Wagner GR, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Wilkinson JD, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh PH, Yip P, Zabetian A, Zheng ZJ, Lopez AD, Murray CJL (2012) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380:2095–2128
Luo L, Ren J, Zhang F, Zhang W, Li C, Qiu Z, Huang D (2018) The effects of air pollution on length of hospital stay for adult patients with asthma. Int J Health Plann Manag 33:e751–e767. https://doi.org/10.1002/hpm.2532
Ma Y, Yang S, Yu Z, Jiao H, Zhang Y, Ma B (2019) A study on the short-term impact of fine particulate matter pollution on the incidence of cardiovascular diseases in Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 215:116889
Meo SA, Suraya F (2016) Effect of environmental air pollution on cardiovascular diseases. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:4890–4897
Mohammadi Y, Parsaeian M, Mehdipour P, Khosravi A, Larijani B, Sheidaei A, Mansouri A, Kasaeian A, Yazdani K, Moradi-Lakeh M (2017) Measuring Iran’s success in achieving Millennium Development Goal 4: a systematic analysis of under-5 mortality at national and subnational levels from 1990 to 2015. Lancet Glob Health 5:e537–e544
Moran AE, Forouzanfar MH, Roth GA, Mensah GA, Ezzati M, Flaxman A, Murray CJ, Naghavi M (2014) The global burden of ischemic heart disease in 1990 and 2010: the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Circulation 129:1493–1501
Newby DE, Mannucci PM, Tell GS, Baccarelli AA, Brook RD, Donaldson K, Forastiere F, Franchini M, Franco OH, Graham I (2015) Expert position paper on air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J 36:83–93
Newell K, Kartsonaki C, Lam K, Kurmi O (2018) Cardiorespiratory health effects of gaseous ambient air pollution exposure in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Health 17:41
Nhung N, Schindler C, Dien TM, Probst-Hensch N, Kunzli N (2019) Association of ambient air pollution with lengths of hospital stay for Hanoi children with acute lower-respiratory infection, 2007-2016. Environ Pollut 247:752–762
Okere AN, Renier CM, Frye A (2016) Predictors of hospital length of stay and readmissions in ischemic stroke patients and the impact of inpatient medication management. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25:1939–1951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.04.011
Osman AM, Alsultan MS, Al-Mutairi MA (2011) The burden of ischemic heart disease at a major cardiac center in Central Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 32:1279–1284
Pattenden S, Armstrong B, Milojevic A, Heal MR, Chalabi Z, Doherty R, Barratt B, Kovats RS, Wilkinson P (2010) Ozone, heat and mortality: acute effects in 15 British conurbations. Occup Environ Med 67:699–707
Pekkanen J, Peters A, Hoek G, Tiittanen P, Brunekreef B (2002) Particulate air pollution and risk of ST-segment depression during repeated submaximal exercise tests among subjects with coronary heart disease: the exposure and risk assessment for fine and ultrafine particles in ambient air (ULTRA) study. Circulation 106:933–938
Peng RD, Dominici F, Louis TA (2006) Model choice in time series studies of air pollution and mortality. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-985X.2006.00410.x
Reese RL, Freedland KE, Steinmeyer BC, Rich MW, Rackley JW, Carney RM (2011) Depression and rehospitalization following acute myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 4:626–633
Ribeiro PC, Nascimento L, Almeida AA, Targa M, Cesar A (2019) Fine particulate matter and ischemic heart diseases in relation to sex. An ecological time series study. Sao Paulo Med J 137:60–65
Riojas-Rodríguez H, Escamilla-Cejudo JA, González-Hermosillo JA, Téllez-Rojo MM, Rojas-Bracho L (2006) Personal PM2.5 and CO exposures and heart rate variability in subjects with known ischemic heart disease in Mexico City. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 16:131–137
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS and others (2012) Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics--2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 125:188–197
Routledge HC, Manney S, Harrison R, Ayres JG, Townend JN (2006) Effect of inhaled Sulphur dioxide and carbon particles on heart rate variability and markers of inflammation and coagulation in human subjects. Heart 92:220–227
Scaife A, Barclay J, Hillis GS, Srinivasan J, Macdonald DW, Ross JA, Ayres JG (2012) Lack of effect of nitrogen dioxide exposure on heart rate variability in patients with stable coronary heart disease and impaired left ventricular systolic function. Occup Environ Med 69:587–591
Shepard D, VanderZanden A, Moran A, Naghavi M, Murray C, Roth G (2015) Ischemic heart disease worldwide, 1990 to 2013: estimates from the global burden of disease study 2013. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 8:455–456
Sheps DS (1990) Production of arrhythmias by elevated carboxyhemoglobin in patients with coronary artery disease
Silva RA, Adelman Z, Fry MM, West JJ (2016) The impact of individual anthropogenic emissions sectors on the global burden of human mortality due to ambient air pollution. Environ Health Perspect 124:1776–1784
Sohn J, You SC, Cho J, Choi YJ, Joung B, Kim C (2016) Susceptibility to ambient particulate matter on emergency care utilization for ischemic heart disease in Seoul, Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:19432–19439
Soleimani Z, Darvishi BA, Khalifeh R, Griffin DW, Mesdaghinia A (2019) Short-term effects of ambient air pollution and cardiovascular events in Shiraz, Iran, 2009 to 2015. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:6359–6367
Soyiri IN, Reidpath DD, Sarran C (2011) Asthma length of stay in hospitals in London 2001-2006: demographic, diagnostic and temporal factors. PLoS One 6:e27184
Srebot V, Gianicolo EA, Rainaldi G, Trivella MG, Sicari R (2009) Ozone and cardiovascular injury. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-7120-7-30
Su C, Breitner S, Schneider A, Liu LQ, Franck U, Peters A, Pan XC (2016) Short-term effects of fine particulate air pollution on cardiovascular hospital emergency room visits: a time-series study in Beijing, China. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 89:641–657
Suh HH, Zanobetti A (2010) Exposure error masks the relationship between traffic-related air pollution and heart rate variability. J Occup Environ Med 52:685–692
Sun J, Zhou T (2017) Health risk assessment of China’s main air pollutants. BMC Public Health 17:212
Tarkiainen TH, Timonen KL, Vanninen EJ, Alm S, Pekkanen J (2003) Effect of acute carbon monoxide exposure on heart rate variability in patients with coronary artery disease. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 23:98–102
Tsai TY, Lo LW, Liu SH, Cheng WH, Chou YH, Lin WL, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Hu YF, Chung FP et al (2019) Diurnal cardiac sympathetic hyperactivity after exposure to acute particulate matter 2.5 air pollution. J Electrocardiol 52:112–116
Vahedian M, Khanjani N, Mirzaee M, Koolivand A (2017) Ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for cardiovascular diseases in Arak, Iran. Arya Atheroscler 13:117–134
Versteeg H, Hoogwegt MT, Hansen TB, Pedersen SS, Zwisler A, Thygesen LC (2013) Depression, not anxiety, is independently associated with 5-year hospitalizations and mortality in patients with ischemic heart disease. J Psychosom Res 75:518–525
Wang Z, Li X, Chen M, Lei S (2018) Social health insurance, healthcare utilization, and costs in middle-aged and elderly community-dwelling adults in China. Int J Equity Health 17:17
Warburton D, Bredin S, Shellington EM, Cole C, de Faye A, Harris J, Kim DD, Abelsohn A (2019) A systematic review of the short-term health effects of air pollution in persons living with coronary heart disease. J Clin Med 8:274
Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Sullivan L, Parise H, Kannel WB (2002) Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Arch Intern Med 162:1867–1872
Wu Z, Chen X, Li G, Li G, Tian L, Wang Z, Xiong X, Yang C, Zhou Z, Pan X (2020) Attributable risk and economic cost of hospital admissions for mental disorders due to PM2.5 in Beijing. Sci Total Environ 718:137274
Xu A, Mu Z, Jiang B, Wang W, Yu H, Zhang L, Li J (2017a) Acute effects of particulate air pollution on ischemic heart disease hospitalizations in Shanghai, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:168
Xu Q, Wang S, Guo Y, Wang C, Huang F, Li X, Gao Q, Wu L, Tao L, Guo J et al (2017b) Acute exposure to fine particulate matter and cardiovascular hospital emergency room visits in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 220(Pt A):317–327
Zhang Y, Wu K, Zhu C, Feng R, Li C, Ma L (2015) Association between ambient air pollution and stroke mortality in Wuhan, China: a time-series analysis. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 49:605–610
Zhang A, Nikoloski Z, Mossialos E (2017) Does health insurance reduce out-of-pocket expenditure? Heterogeneity among China's middle-aged and elderly. Soc Sci Med 190:11–19
Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen W, Li X, Wang L, Wang L, Liu Y et al (2019) Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 394:1145–1158
Zhu B, Zhang Y, Chen N, Quan J (2019) Assessment of air pollution aggravation during straw burning in Hubei, Central China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081446
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Hubei National Environmental Monitoring Center for providing air pollution data and the China Meteorological Data Network for providing meteorological data. We greatly thank the hospitals of Wuhan, Yichang, Shiyan, Jingmen, and Huanggang in Hubei province for providing the hospitalization data and the Health Commission of Hubei Province (the former Health and Family Planning Commission of Hubei Province) for undertaking the organization and communication works.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81773552), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2018YFC1315302, 2017YFC1200502), and Key Research Center for Humanities and Social Sciences in Hubei Province (Hubei University of Medicine) (Grant Nos. 2020ZD001, 2016YB008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The study was approved to waive informed consent of the participants by the Ethics Committee of Medical Department of Wuhan University (No. 2019YF2037).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.32 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yu, Y., Yu, C. et al. Associations between acute exposure to ambient air pollution and length of stay for inpatients with ischemic heart disease: a multi-city analysis in central China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 43743–43754 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10256-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10256-7