Abstract
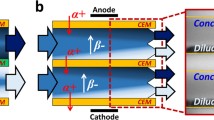
As water scarcity has become a serious global issue, seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) is considered as a promising technique to expand traditional water supplies. However, the reject brine from SWRO systems is still a major environmental concern. In this research, the monovalent selective electrodialysis (S-ED) was used to separate and recover one of the primary components, i.e., sodium chloride, from the SWRO brine, thereby avoiding the direct discharge of the brine and achieving the brine valorization. The permselectivity of selective ion-exchange membranes (IEMs) was elucidated by comparing with the standard IEMs in structure-property via membrane characterization techniques. Results indicated that the permselectivity of Selemion CSO membrane was attributed to the positive-charged layer with a low sulfonate/ammonium ratio of 1.28. Whereas the permselectivity of Selemion ASV membrane resulted from the highly cross-linked layer, according to the similar content of the fixed quaternary amines and the shift of the C‑N absorption peak. In addition, the effects of the current density and temperature on the membrane performance were studied, including permselectivity (\( {P}_{{\mathrm{Mg}}^{2+}}^{{\mathrm{Na}}^{+}} \) and \( {P}_{{\mathrm{SO}}_4^{2-}}^{{\mathrm{Cl}}^{-}} \)), Na+ recovery, and specific energy consumption (ESEC). Finally, the NaCl-rich brine with the total dissolved solid (TDS) value of 167.5 ± 3.3 g/L was obtained using SWRO brine with the initial TDS of 76.8 g/L. The Na+/Mg2+ mass ratio of the concentrate was 222.4, compared with the initial value of 9.7 in SWRO brine.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdu S, Marti-Calatayud MC, Wong JE, Garcia-Gabaldon M, Wessling M (2014) Layer-by-layer modification of cation exchange membranes controls ion selectivity and water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:1843–1854. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4048317
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Tkachev A, Galunin E, Burakov A, Grachev VA (2018) Water treatment by new-generation graphene materials: hope for bright future. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:7315–7329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1315-9
Amara M, Kerdjoudj H (2002) Modified membranes applied to metallic ion separation and mineral acid concentration by electrodialysis. Sep Purif Technol 29:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5866(02)00084-9
Amy G, Ghaffour N, Li Z, Francis L, Linares RV, Missimer T, Lattemann S (2017) Membrane-based seawater desalination: present and future prospects. Desalination 401:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.10.002
Barbosa M, Vale N, Costa FM, Martins MC, Gomes P (2017) Tethering antimicrobial peptides onto chitosan: optimization of azide-alkyne “click” reaction conditions. Carbohydr Polym 165:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.050
Casas S, Bonet N, Aladjem C, Cortina JL, Larrotcha E, Cremades LV (2011) Modelling sodium chloride concentration from seawater reverse osmosis brine by electrodialysis: preliminary results solvent extraction and ion exchange. 29:488–508 doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/07366299.2011.573451
Chen Q-B, Ji Z-Y, Liu J, Zhao Y-Y, Wang S-Z, Yuan J-S (2018) Development of recovering lithium from brines by selective-electrodialysis: effect of coexisting cations on the migration of lithium. J Membr Sci 548:408–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.040
Cowan DA, Brown JH (1959) Effect of turbulence on limiting current in electrodialysis cells. Ind Eng Chem 51:1445–1448. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50600a026
Fan H, Yip NY (2019) Elucidating conductivity-permselectivity tradeoffs in electrodialysis and reverse electrodialysis by structure-property analysis of ion-exchange membranes. J Membr Sci 573:668–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.11.045
Farrokhzad H, Moghbeli MR, Van Gerven T, Van der Bruggen B (2015) Surface modification of composite ion exchange membranes by polyaniline. React Funct Polym 86:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2014.08.003
Firdaous L, Malériat JP, Schlumpf JP, Quéméneur F (2007) Transfer of monovalent and divalent cations in salt solutions by electrodialysis separation. For Sci Technol 42:931–948. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390701206413
Fontananova E, Zhang W, Nicotera I, Simari C, van Baak W, di Profio G, Curcio E, Drioli E (2014) Probing membrane and interface properties in concentrated electrolyte solutions. J Membr Sci 459:177–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.01.057
Galama AH, Daubaras G, Burheim OS, Rijnaarts HHM, Post JW (2014) Seawater electrodialysis with preferential removal of divalent ions. J Membr Sci 452:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.10.050
Ghalloussi R, Garcia-Vasquez W, Chaabane L, Dammak L, Larchet C, Deabate SV, Nevakshenova E, Nikonenko V, Grande D (2013) Ageing of ion-exchange membranes in electrodialysis: a structural and physicochemical investigation. J Membr Sci 436:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.02.011
Güler E, van Baak W, Saakes M, Nijmeijer K (2014) Monovalent-ion-selective membranes for reverse electrodialysis. J Membr Sci 455:254–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.12.054
Ibanez R, Stamatialis DF, Wessling M (2004) Role of membrane surface in concentration polarization at cation exchange membranes. J Membr Sci 239:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2003.12.032
Jeppesen T, Shu L, Keir G, Jegatheesan V (2009) Metal recovery from reverse osmosis concentrate. J Clean Prod 17:703–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.11.013
Karimi L, Ghassemi A (2015) Effects of operating conditions on ion removal from brackish water using a pilot-scale electrodialysis reversal system. Desalin Water Treat 57:8657–8669. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1024748
Korngold E, Aronov L, Daltrophe N (2009) Electrodialysis of brine solutions discharged from an RO plant. Desalination 242:215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.008
Le XT (2013) Contribution to the study of properties of Selemion AMV anion exchange membranes in acidic media. Electrochim Acta 108:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.011
Le XT, Bui TH, Viel P, Berthelot T, Palacin S (2009) On the structure–properties relationship of the AMV anion exchange membrane. J Membr Sci 340:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.05.025
Le XT, Viel P, Jégou P, Garcia A, Berthelot T, Bui TH, Palacin S (2010) Diazonium-induced anchoring process: an application to improve the monovalent selectivity of cation exchange membranes. J Mater Chem 20:3750. https://doi.org/10.1039/b918915g
Lee H-J, Sarfert F, Strathmann H, Moon S-H (2002) Designing of an electrodialysis desalination plant. Desalination 142:267–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00208-4
Lee S, Choi J, Park Y-G, Shon H, Ahn CH, Kim S-H (2019) Hybrid desalination processes for beneficial use of reverse osmosis brine: Current status and future prospects. Desalination 454:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.02.002
Li Y, Xu T (2008) Permselectivities of monovalent anions through pyridine-modified anion-exchange membranes. Sep Purif Technol 61:430–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.12.009
Lu H-Y, Lin C-S, Lee S-C, Ku M-H, Hsu J-P, Tseng S, Lin S-H (2011) Preparation of mineral source water from deep sea water: reduction of sulfate ion using selemion ASV membrane. AICHE J 57:1033–1042. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12319
Mei Y, Tang CY (2018) Recent developments and future perspectives of reverse electrodialysis technology: a review. Desalination 425:156–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.10.021
Mei Y, Yao Z, Ji L, Toy PH, Tang CY (2018) Effects of hypochlorite exposure on the structure and electrochemical performance of ion exchange membranes in reverse electrodialysis. J Membr Sci 549:295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.12.016
Nayar KG, Fernandes J, McGovern RK, Dominguez KP, McCance A, Al-Anzi BS, Lienhard JH (2019) Cost and energy requirements of hybrid RO and ED brine concentration systems for salt production. Desalination 456:97–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.11.018
Nie X-Y, Sun S-Y, Song X, Yu J-G (2017) Further investigation into lithium recovery from salt lake brines with different feed characteristics by electrodialysis. J Membr Sci 530:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.02.020
Park K, Kim J, Yang DR, Hong S (2020) Towards a low-energy seawater reverse osmosis desalination plant: a review and theoretical analysis for future directions. J Membr Sci 595:117607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117607
Reig M et al (2014) Concentration of NaCl from seawater reverse osmosis brines for the chlor-alkali industry by electrodialysis. Desalination 342:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.12.021
Reig M, Valderrama C, Gibert O, Cortina JL (2016) Selectrodialysis and bipolar membrane electrodialysis combination for industrial process brines treatment: monovalent-divalent ions separation and acid and base production. Desalination 399:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.08.010
Ren Z et al (2016) FTIR, Raman, and XPS analysis during phosphate, nitrate and Cr(VI) removal by amine cross-linking biosorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 468:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.01.079
Rijnaarts T, Reurink DM, Radmanesh F, de Vos WM, Nijmeijer K (2019) Layer-by-layer coatings on ion exchange membranes: effect of multilayer charge and hydration on monovalent ion selectivities. J Membr Sci 570-571:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.10.074
Rubinstein I (1991) Electroconvection at an electrically inhomogeneous permselective interface. Phys Fluids A: Fluid Dynam 3:2301–2309. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.857869
Shahmansouri A, Min J, Jin L, Bellona C (2015) Feasibility of extracting valuable minerals from desalination concentrate: a comprehensive literature review. J Clean Prod 100:4–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.03.031
Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Elimelech M, Georgiadis JG, Mariñas BJ, Mayes AM (2008) Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 452:301. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06599
Shemer H, Semiat R (2017) Sustainable RO desalination – energy demand and environmental impact. Desalination 424:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.09.021
Strathmann H (2010) Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 264:268–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.04.069
Tanaka Y (2012) Ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis program and its application to multi-stage continuous saline water desalination. Desalination 301:10–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.06.007
Tanaka Y (2015) Limiting current. Density:199–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-63319-4.00009-2
Tanaka Y, Ehara R, Itoi S, Goto T (2003) Ion-exchange membrane electrodialytic salt production using brine discharged from a reverse osmosis seawater desalination plant. J Membr Sci 222:71–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0376-7388(03)00217-5
Tanaka Y, Reig M, Casas S, Aladjem C, Cortina JL (2015) Computer simulation of ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis for salt concentration and reduction of RO discharged brine for salt production and marine environment conservation. Desalination 367:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.03.022
Tang Y, Li M, Mu C, Zhou J, Shi B (2019) Ultrafast and efficient removal of anionic dyes from wastewater by polyethyleneimine-modified silica nanoparticles. Chemosphere 229:570–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.062
Teppen BJ, Miller DM (2006) Hydration energy determines isovalent cation exchange selectivity by clay minerals. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:31. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.0212
Tow EW, Warsinger DM, Trueworthy AM, Swaminathan J, Thiel GP, Zubair SM, Myerson AS, Lienhard V JH (2018) Comparison of fouling propensity between reverse osmosis, forward osmosis, and membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 556:352–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.03.065
Wang M, Y-x J, T-t Y, Wang K-k (2013) The endowment of monovalent selectivity to cation exchange membrane by photo-induced covalent immobilization and self-crosslinking of chitosan. J Membr Sci 442:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.04.027
Yamaguchi T, Ohzono H, Yamagami M, Yamanaka K, Yoshida K, Wakita H (2010) Ion hydration in aqueous solutions of lithium chloride, nickel chloride, and caesium chloride in ambient to supercritical water. J Mol Liq 153:2–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2009.10.012
Ye ZL, Ghyselbrecht K, Monballiu A, Pinoy L, Meesschaert B (2019) Fractionating various nutrient ions for resource recovery from swine wastewater using simultaneous anionic and cationic selective-electrodialysis. Water Res 160:424–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.085
Zhang J, Sun Y, Yu J (2017a) Qualitative discussion of prenucleation cluster role in crystallization of calcium carbonate under high concentration of magnesium based on experimental phenomena. J Cryst Growth 478:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2017.07.012
Zhang W, Miao M, Pan J, Sotto A, Shen J, Gao C, der Bruggen BV (2017b) Separation of divalent ions from seawater concentrate to enhance the purity of coarse salt by electrodialysis with monovalent-selective membranes. Desalination 411:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.02.008
Zhao Y, Tang K, Liu H, Van der Bruggen B, Sotto Díaz A, Shen J, Gao C (2016) An anion exchange membrane modified by alternate electro-deposition layers with enhanced monovalent selectivity. J Membr Sci 520:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.07.026
Zhao L-M, Chen Q-B, Ji Z-Y, Liu J, Zhao Y-Y, Guo X-F, Yuan J-S (2018) Separating and recovering lithium from brines using selective-electrodialysis: sensitivity to temperature. Chem Eng Res Des 140:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.10.009
Funding
The authors would like to thank the financial support from the National Key R&D Program (No. 2016YFC0401203), Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. U1507105), and Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader (No. 18XD1424600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Sun, Y., Song, X. et al. Separation of mono- and di-valent ions from seawater reverse osmosis brine using selective electrodialysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 18754–18767 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10014-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10014-9