Abstract
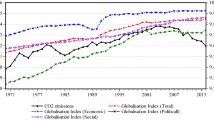
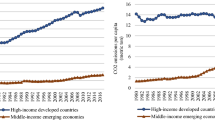
This paper analyzes the role of international cooperation on CO2 emissions growth in 36 OECD economies over the period 1970–2016. The indices of political globalization are the benchmark measure of international cooperation since a higher value of the index of political globalization is an indicator of collaboration in the world. The paper finds that political globalization decreases CO2 emissions growth. The findings remain robust when we consider the sub-indices of political globalization and include various controls. Also, the findings of the panel quantile regressions with the fixed-effects via the method of moments indicate that the effects of per capita income and the initial level of CO2 emissions are higher in more pollutant countries. However, the impact of political globalization on CO2 emissions is stable at different quantiles. The paper also discusses the potential implications for the role of international cooperation on climate change.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Theoretically speaking, natural resource rents (particularly oil rents) lead to greater CO2 emissions. However, the impact of energy usage on CO2 emissions is mixed, depending on the sample of countries (see, e.g., Acheampong 2018).
There are also game-theory approaches to the relationship between climate change and international governance (see, e.g., Hammitt and Adams 1996).
Bu et al. (2016) have reviewed the previous papers for the impacts of the KOF indices of globalization on environmental variables until 2015. Therefore, our review of the previous literature will focus on the empirical studies conducted after 2015.
There are also empirical studies to use different indicators of international political integration, rather than the KOF indices of globalization, to analyze their effects on environmental indicators (see, e.g., Longhofer and Jorgenson 2017).
In this paper, we consider a 5-year (average) growth rate in non-overlapping periods in random-effects estimations since the index value of political globalization can significantly vary only in the long term.
For more details, visit the website of the KOF Institute.
Note that the effects of the related control variables on CO2 emissions should be positive in developing countries.
Note that we run the cross-sectional dependence (CD) test of Pesaran (2004). Following the findings, we utilize the second generation unit root test of Pesaran (2007). All findings confirm that all series are stationary. Related findings are not provided to save space, but they are available upon request.
That is, greater CO2 can negatively affect the level of political globalization.
References
Acheampong AO (2018) Economic growth, CO2 emissions, and energy consumption: what causes what and where? Energy Econ 74:677–692
Ahmed K, Shahbaz M, Kyophilavong P (2016) Revisiting the emissions-energy-trade Nexus: evidence from the newly industrializing countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(8):7676–7691
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2016) The investigation of environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in the advanced economies: the role of energy prices. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:1622–1631
Apergis N, Can M, Gozgor G, Lau CKM (2018) Effects of export concentration on CO2 emissions in developed countries: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(14):14106–14116
British Petroleum (2019) BP statistical review of world energy June 2019. British Petroleum, London
Bu M, Lin C-T, Zhang B (2016) Globalization and climate change: new empirical panel data evidence. J Econ Surv 30(3):577–595
Can M, Gozgor G (2017) The impact of economic complexity on carbon emissions: evidence from France. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(19):16364–16370
Chang CP, Dong M, Sui B, Chu Y (2019) Driving forces of global carbon emissions: from time-and spatial-dynamic perspectives. Econ Model 77:70–80
Chen GQ, Chen ZM (2011) Greenhouse gas emissions and natural resources use by the world economy: ecological input–output modeling. Ecol Model 222(14):2362–2376
Chen X, Chen YE, Chun-Ping C (2019a) The effects of environmental regulation and industrial structure on carbon dioxide emission: a non-linear investigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(29):30252–30267
Chen YE, Fu Q, Zhao X, Yuan X, Chang CP (2019b) International sanctions’ impact on energy efficiency in target states. Econ Model 82:21–34
Destek MA (2019) Investigation on the role of economic, social, and political globalization on environment: evidence from CEECs. Environ Sci Pollut Res, forthcoming:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04698-x
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49(4):431–455
Dreher A (2006) Does globalization affect growth? Evidence from a new index of globalization. Appl Econ 38(10):1091–1110
Farhani S, Ozturk I (2015) Causal relationship between CO2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption, financial development, trade openness, and urbanization in Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):15663–15676
Feng GF, Dong M, Wen J, Chang CP (2018) The impacts of environmental governance on political turnover of municipal party secretary in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(25):24668–24681
Frank DJ, Hironaka A, Schofer E (2000) The nation-state and the natural environment over the twentieth century. Am Sociol Rev 65(1):96–116
Gozgor G (2017) Does trade matter for carbon emissions in OECD countries? Evidence from a new trade openness measure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(36):27813–27821
Gozgor G, Can M (2017) Does export product quality matter for CO2 emissions? Evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(3):2866–2875
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Gygli S, Haelg F, Potrafke N, Sturm J-E (2019) The KOF globalisation index – revisited. Rev Int Organ 14(3):543–574
Hammitt JK, Adams JL (1996) The value of international cooperation for abating global climate change. Resour Energy Econ 18(3):219–241
Haseeb A, Xia E, Baloch MA, Abbas K (2018) Financial development, globalization, and CO2 emission in the presence of EKC: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(31):31283–31296
Jackson R, Sørensen G, Møller J (2018) Introduction to international relations: theories and approaches, 7th edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Khan D, Ullah A (2019) Testing the relationship between globalization and carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan: does environmental Kuznets curve exist? Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(15):15194–15208
Ling CH, Ahmed K, Muhamad RB, Shahbaz M (2015) Decomposing the trade-environment Nexus for Malaysia: what do the technique, scale, composition, and comparative advantage effect indicate? Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(24):20131–20142
Longhofer W, Jorgenson A (2017) Decoupling reconsidered: does world society integration influence the relationship between the environment and economic development? Soc Sci Res 65:17–29
Machado JAF, Santos Silva JMC (2019) Quantiles via moments. J Econ 213(1):145–173
Meyer JW (2010) World society, institutional theories, and the actor. Annu Rev Sociol 36:1–20
Ozcan B, Apergis N, Shahbaz M (2018) A revisit of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Turkey: new evidence from bootstrap rolling window causality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(32):32381–32394
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. In: Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) Discussion Papers, no. 1240. Institute for the Study of labor (IZA), Bonn
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22(2):265–312
Rahman S-U, Chen S, Saud S, Bano S, Haseeb A (2019) The Nexus between financial development, globalization, and environmental degradation: fresh evidence from central and eastern European countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(24):24733–24747
Scott WR (2008) Institutions and organizations: ideas and interests, 3rd edn. Sage Publications, Los Angeles
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017) The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. Singap Econ Rev 62(4):929–957
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecol Indic 52:379–393
Shahbaz M, Muhammad Q, Hye A, Tiwari AK, Leitão NC (2013) Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade, and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:109–121
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK (2018) Is globalization detrimental to CO2 emissions in Japan? New threshold analysis. Environ Model Assess 23(5):557–568
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U (2018) Influence of foreign direct investment on indicators of environmental degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(25):24845–24859
United Nations (2015) Adoption of the Paris agreement: proposal by the President. In: Draft decision -/CP.21, December 12, 2015. United Nations, Paris
Wang Y, Zhou T, Chen H, Rong Z (2019) Environmental homogenization or heterogenization? The effects of globalization on carbon dioxide emissions, 1970–2014. Sustainability 11(10):2752
World Bank (2019) World development indicators database. World Bank, Washington, D.C.
Zafar MW, Saud S, Hou F (2019) The impact of globalization and financial development on environmental quality: evidence from selected countries in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(13):13246–13262
Zaidi SAH, Zafar MW, Shahbaz M, Hou F (2019) Dynamic linkages between globalization, financial development and carbon emissions: evidence from Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation Countries. J Clean Prod 228:533–543
Zhang S, Liu X, Bae J (2017) Does trade openness affect CO2 emissions: evidence from ten newly industrialized countries? Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(21):17616–17625
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Gozgor, G., Koo, C.K. et al. Does international cooperation affect CO2 emissions? Evidence from OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 8548–8556 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07324-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07324-y