Abstract
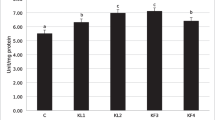
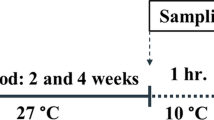
The present study was designed to investigate the protective role of dietary supplementation of Spirulina platensis (SP) against cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of lead nitrate in Clarias gariepinus. Four groups of fishes were used: first group as control which fed on basal diet, second group fed on basal diet and exposed to (1 mg/L of lead nitrate), third group fed on diet containing 0.25% SP and exposed to (1 mg/L of lead nitrate), and fourth group fed on diet containing 0.5%SP and exposed to (1 mg/L of lead nitrate). Fish samples were taken at 2nd and 4th week of exposure. The hematological indices of lead nitrate–exposed group were decreased significantly compared to the control group at 2nd and 4th week of exposure. Lead nitrate caused a significant increase in the percentage of poikilocytosis, micronuclei, and apoptotic cells as well as comet tail length and olive tail moment compared with the control group at 2nd and 4th week of exposure. The highest level of damage was found on 4th week of exposure with all parameters. Dietary inclusion of SP ameliorated these cytotoxic and genetic changes, as well as this amelioration was concentration and time dependent. Consequently, the present study proposed that the addition of SP to the fish diet can be used as a promising protective agent to oppose cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of lead nitrate in aquaculture.

Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Satar AM, Ali MH, Goher ME (2017) Indices of water quality and metal pollution of Nile River, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:21–29
Adeyemo OK (2007) Haematological profile of Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) exposed to lead. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 7
Alkahemal-Balawi HF et al (2011) Toxicity bioassay of lead acetate and effects of its sub-lethal exposure on growth, haematological parameters and reproduction in Clarias gariepinus. Afr J Biotechnol 10:11039–11047
Al-Sabti K, Metcalfe CD (1995) Fish micronuclei for assessing genotoxicity in water. Mutat Res 343:121–135
Ayllon F, Garcia-Vazquez E (2000) Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in European minnow Phoxinus phoxinus and Mollie Poeciliala tipinna: an assessment of the fish micronucleus test. Mutat Res 467:177–186
Bangeppagari M, Gooty JM, Tirado JO, Mariadoss S, Thangaswamy S, Maddela NR, Ortiz DR (2014) Therapeutic efficiency of Spirulina against lead acetate toxicity on the fresh water fish Labeo rohita. American Journal of Life Sciences 2(6):389–394.
Bhat VB, Madyastha KM (2001) Scavenging of peroxynitrite by phycocyaninphycocyanobilin from Spirulina platensis: protection against oxidative damage to DNA. Biochem Bioph Res Co 285:262–266
Bhilave MP, Muley DV (2008) Biochemical changes in the fish Cirrhinus mrigala after acute and chronic exposure of heavy metals. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 7
Bike RL (1993) Haematology: clinical and laboratory practice 1:12 Morphology of erythron, St. Louis, Missouri
Bonacker D, Stoiber T, Böhm KJ, Prots I, Wang M, Unger E, Thier R, Bolt HM, Degen GH (2005) Genotoxicity of inorganic lead salts and disturbance of microtubule function. Environ Mol Mutagen 45:346–353
Cantrell SM, Joy-Schlezinger J, Stegeman JJ, Tillitt DE, Hannink M (1998) Correlation of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced apoptotic cell death in the embryonic vasculature with embryotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 148:24–34
Chavan VR, Muley D (2014) Effect of heavy metals on liver and gill of fish Cirrhinus mrigala. International Journal of CurrentMicrobiology and Applied Sciences 3(5):277–288
Chu WL, Lim YW, Radhakrishnan AK, Lim PE (2010) Protective effect of aqueous extract from Spirulina platensis against cell death induced by free radicals. BMC Complement Altern Med 10:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-10-53
Cogun HY, Şahin M (2013) The effect of lead and zeolite on hematological and some biochemical parameters in Nile fish (Oreochromis niloticus)
Çoğun HY Şahin M (2013) The effect of lead and zeolite on hematological and some biochemical parameters in Nile fish (Oreochromis niloticus). In Current Progress in biological research. IntechOpen 277-286
Collins AR (2004) The comet assay for DNA damage and repair. Mol Biotechnol 26:249–261
Cooper RA (1980) Hemolytic syndromes and red cell membrane abnormalities in liver disease. Semin.Hematol. 17:103–112
Dacie JU, Lewis SM (1975) Basic hematology techniques. Dacie JU, Lewis SM: practical haematology. Churchill Livingston, London, pp 21–96
Dutta B et al (2015) Lead nitrate toxicity on haematological changes in a live fish species Channa punctatus (Bloch). J Int J Fish Aquat Stud:196–198
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Ghazaly KS (1991) Influences of thiamin on lead intoxication, lead deposition in tissues and lead hematological responses of Tilapia zillii. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 100:417–421
Goyer RA, Moore JF (1974) Cellular effects of lead. Adv Exp Med Biol 48:447–462
Habib MAB (2008) Review on culture, production and use of Spirulina as food for humans and feeds for domestic animals and fish. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1034
Hemalatha K et al (2012) Studies on the protective efficacy of Spirulina against lead acetate induced hepatotoxicity in Rattus norvegicus. Int J Chem Anal Sci 3:1509–1512
Hesser EF (1960) Methods for routine fish hematology. Prog Fish Cult 22:164–171
Hidaka M et al (2010) Cell lines derived from a Medaka radiation-sensitive mutant have defects in DNA double-Strand break responses. J Radiat Res 51:165–171
Hironobu W et al (2006) Immunostimulant effects of dietary Spirulinaplatensis on carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture. 258:157–163
Hofer RS, Köck WG, Pittracher H (1992) Heavy metal intoxication of arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) in a Remote Acid Alpine Lake. FAO/EIFAC/XVII/92/Symp. E31, Lugano, Switzerland.
Ibrahem MD, Ibrahim MA (2014) The potential effects of Spirulinaplatensis (Arthrospiraplatensis) on tissue protection of Nile tilapia (Oreochromisniloticus) through estimation of P53 level. J Adv Res 5:133–136
Jaat A et al (2013) Ameliorative effect of Spirulina on the histology of ovary of mercuric chloride effected fish, Clarias gariepinus. IJGHC 2:130–138
Jagetia GC, Ganapathi NG (1993) Radiation-induced micronucleus formation in mouse bone marrow after low dose exposures. Mutat Res 16:235–242
Johansson-Sjöbeck ML, Larsson Å (1979) Effects of inorganic lead on delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity and hematological variables in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdnerii. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 8:419–431
Johnson FM (1998) The genetic effects of environmental lead. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 410:123–140
Khafaga AF, El-Sayed YS (2018) Spirulina ameliorates methotrexate hepatotoxicity via antioxidant, immune stimulation, and proinflammatory cytokines and apoptotic proteins modulation. Life Sci 196:9–17
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Góźdź S, Koza Z, Wojcik A (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 534:15–20
Lal Shah S (2010) Hematological changes in Tinca tinca after exposure to lethal and sublethal doses of mercury, cadmium and Lead. Iran J Fish Sci 9:434–443
Latif A et al (2014) Evaluation of toxic stress of copper sulphate and lead nitrate on hematological and serum biochemical characteristics of freshwater cyprinid (Labeo rohita). Int J Current Engg Technol 4:366–372
Lee GR et al (1999) Wintrobe’s clinical hematology 10th. Lippincort Williams and Wilkins, Bethseda, Maryland
Li XL et al (2009) Phycocyanin protects INS-1E pancreatic beta cells against human islet amyloid polypeptide-induced apoptosis through attenuating oxidative stress and modulating JNK and p38 mitogenactivated protein kinase pathways. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol 41:1526–1535
Mahmoud MU et al (2013) Effect of lead on some haematological and biochemical characteristics of Clarias gariepinus dietary supplemented with lycopene and vitamin E. Egypt Acad J Biolog Sci 5:67–89
Mekkawy IA, Mahmoud UM, Sayed AH (2011) Effects of 4-nonylphenol on blood cells of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Tissue Cell 43:223–229
Mohamed WA, Ismail SA, el-Hakim YMA (2014) Spirulina platensis ameliorative effect against GSM 900-MHz cellular phone radiation-induced genotoxicity in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Comp Clin Pathol 23:1719–1726
Mustafa MG, Nakagawa H (1995) A review: dietary benefits of algae as an additive in fish feed. Isr J Aquacult Bamidgeh 47:155–162
Nan P et al (2013) Genotoxic effects of 8-hydroxylquinoline in loach (Misgurnusanguillicaudatus) assessed by the micronucleus test, comet assay and RAPD analysis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:434–443
Oluah NS, Omerebele UAM (2010) Changes in haematological parameters of Clarias gariepinus exposed to lead poisoning. J fisher Inter 5:72–76
Osman AGM, Mekkawy IA, Verreth J, Kirschbaum F (2007) Effects of lead nitrate on the activity of metabolic enzymes during early developmental stages of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Fish Physiol Biochem 33:1–13
Poblete-Naredo I, Albores A (2016) Molecular biomarkers to assess health risks due to environmental contaminants exposure. Biomedica 36:309–335
Ramalingam V et al (2000) Effect of Lead on Haematological and biochemical changes in fresh water fish Cirrhina mrigala. Pollut Res 19:81–84
Roche H, Bogé G (1996) Fish blood parameters as a potential tool for identification of stress caused by environmental factors and chemical intoxication. Mar Environ Res 41:27–43
Rosenberg CE, Perí SI, Arrieta MA, Fink NE, Salibián A (1998) Red blood cell osmotic fragility in Bufo arenarum exposed to lead. Arch Physiol Biochem 106:19–24
Sayed AH, Authman MMN (2018) The protective role of Spirulina platensis to alleviate the sodium dodecyl sulfate toxic effects in the catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:136–144
Sayed AH, Fawzy MA (2014) Effect of dietary supplementation of Spirulinaplatensis on the growth and haematology of the catfish Clarias gariepinus. Journal of Advances in Biology 5(2):625-635.
Sayed AH, Mitani H (2017) Immunostaining of UVA-induced DNA damage in erythrocytes of medaka (Oryzias latipes). J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 171:90–95
Sayed AH, Soliman HA (2017) Developmental toxicity and DNA damaging properties of silver nanoparticles in the catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 822:34–40
Sayed AH, Soliman HA (2018) Modulatory effects of green tea extract against the hepatotoxic effects of 4-nonylphenol in catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:159–165
Sayed AH, Abdel-Tawab HS, Abdel Hakeem SS, Mekkawy IA (2013) The protective role of quince leaf extract against the adverse impacts of ultraviolet-a radiation on some tissues of Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 119:9–14
Sayed AH et al (2015) Arsenic-induced genotoxicity in Nile tilapia (Orechromis niloticus); the role of Spirulina platensis extract. Environ Monit Assess 187
Sayed AH et al (2016a) Erythrocytes alterations of monosex tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Linnaeus, 1758) produced using methyltestosterone. Egypt J Aquat Res 42:83–90
Sayed AH et al (2016b) Apoptosis and morphological alterations after UVA irradiation in red blood cells of p53 deficient Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 161:1–8
Sayed AH et al (2017) Hepatoprotective efficacy of Spirulina platensis against lead-induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity in catfish; Clarias gariepinus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:344–350
Sayed AH et al (2018a) Sensitivity of medaka (Oryzias latipes) to 4-nonylphenol subacute exposure; erythrocyte alterations and apoptosis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 58:98–104
Sayed AH et al (2018b) Gamma-H2AX foci as indication for the DNA damage in erythrocytes of medaka (Oryzias latipes) intoxicated with 4-nonylphenol. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:018–2985
Schmid W (1975) The micronucleus test. Mutat Res 31:9–15
Schmitt CJ et al (2002) Inhibition of erythrocyte δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) activity in fish from waters affected by lead smelters. Environmental monitoring and assessment, vol 77, pp 99–119
Schuurhuis GJ, Hommes J, Vos J, Molenaar I, Konings AWT (1984) Radiation-induced structural changes in membrane proteins of human erythrocytes and ghosts and the relation to cellular morphology. International Journal of Radiation Biology and Related Studies in Physics, Chemistry and Medicine 45:159–177
Shah, S. L., 2006. Hematological parameters in tench Tinca tinca after short term exposure to lead. J Appl Toxicol: An International Journal. 26, 223–228
Sharaf, S. M., et al., 2011. Haematological, biochemical and histological alterations in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus exposed to sublethal concentrations of lead. In Proceedings of the 4th global fisheries and aquaculture research conference, the Egyptian International Center for Agriculture, Giza, Egypt, 3–5 October 2011 (pp. 425–439). Massive Conferences and Trade Fairs
Sharma J, Langer S (2014) Effect of manganese on haematological parameters of fish, Garragotylagotyla. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies 2:77–81
Shimizu N, Shimura T, Tanaka T (2000) Selective elimination of acentric double minutes from cancer cells through the extrusion of micronuclei. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 448:81–90
SPSS (1998) SPSS for Windows. SPSS Inc, Headquarters, Chicago
Stevens ML (1997) Fundamentals of clinical hematology. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA
Stivala LA, Savio M, Cazzalini O, Pizzala R, Rehak L, Bianchi L, Vannini V, Prosperi E (1996) Effect of β-carotene on cell cycle progression of human fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 17:2395–2401
Takeuchi TJ et al (2002) Effect on the growth and body composition of juvenile tilapia Oreochromisniloticus fed raw Spirulina platensis. Fish Sci 68:34–40
Tewari H, Gill TS, Pant J (1987) Impact of chronic lead poisoning on the hematological and biochemical profiles of a fish, Barbus conchonius (ham). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 38:748–752
Tort L et al (1987) Effects on dogfish haematology and liver composition after acute copper exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol 87:349–354
Vetrivel C, Pugazhendy K, Prabakaran S (2014) Protective effect of spirulina against the lead acetate induced ALP and ACP activity in the liver tissue of fresh water fish, Labeo rohita. Int J Modn Res Revs 2:226–228.
Wintrobe MM (1978) Clinical hematology. Henry Kimpton, London, p 448
Witeska M (2004) The effect of toxic chemicals on blood cell morphology in fish. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 13(12):1379–1384.
Witeska M et al (2010) Hematological changes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) after short-term lead (Pb) exposure. Pol J Environ Stud 19:825–831
Zhang, C. W., et al., 1994. The effect of polysaccharide and phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis var. on peripheral blood and hematopoietic system of bone marrow in mice, Paper presented to the 2nd Asia- Pacific conference on Algal Biotechnology, Malaysia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures involving experimental design and fish handling were approved by the Committee of Animal Care and Use, Faculty of Science, Assiut University.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamed, M., Soliman, H.A.M. & Sayed, A.ED.H. Ameliorative effect of Spirulina platensis against lead nitrate–induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in catfish Clarias gariepinus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 20610–20618 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05319-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05319-3