Abstract
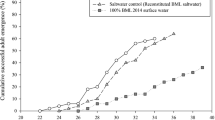
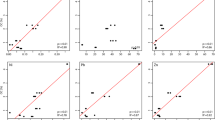
We carried out field studies and laboratory experiments to assess the impact of fluoride (F−) and turbidity on the freshwater snail Physella acuta in a polluted river receiving an industrial effluent (the middle Duraton River, Central Spain). Fluoride concentrations and turbidity levels significantly increased downstream from the industrial effluent (with the highest values being 0.6 mg F−/L and 55.2 nephelometric turbidity unit). In addition, higher deposition of fine inorganic matter was evident at polluted sampling sites. Conversely, the abundance of P. acuta significantly declined (until its virtual disappearance) downstream from the industrial effluent. Toxicity bioassays showed that P. acuta is a relatively tolerant invertebrate species to fluoride toxicity, with estimated safe concentrations (expressed as LC0.10 values for infinite hours of exposure) for juvenile and adult snails being 2.4 and 3.7 mg F−/L, respectively. Furthermore, juvenile snails (more sensitive than adult snails) did not show significant alterations in their behavior through 15 days of exposure to 2.6 mg F−/L: mean values of the proportion of test snails located on the water surface habitat, as well as mean values of the sliding movement rate (velocity) of test snails, never showed significant differences when comparing control and treatment glass vessels. It is concluded that instream habitat degradation, derived from increased turbidity levels, might be a major cause for significant reductions in the abundance of P. acuta downstream from the industrial effluent. The presence of the competing gastropod Ancylus fluviatilis could also affect negatively the recovery of P. acuta abundance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre-Sierra A, Alonso A, Camargo JA (2011) Contrasting sensitivities to fluoride toxicity between juveniles and adults of the aquatic snail Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Hydrobiidae, Mollusca). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:476–479
Albrecht C, Kroll O, Terrazas EM, Wilke T (2009) Invasion of ancient Lake Titicaca by the globally invasive Physa acuta (Gastropoda: Pulmonata: Hygrophila). Biol Inv 11:1821–1826
Alonso A, Camargo JA (2012) A video-based trackling analysis to assess the chronic toxic effects of fluoride ion on the aquatic snail Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Hydrobiidae, Mollusca). Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 81:70–75
American Public Health Association (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA-AWWA-WPCF, Washington, DC
Anderson R (2003) Physella (Costatella) acuta Draparnaud in Britain and Ireland. Its taxonomy, origins and relationships to other introduced Physidae. J Conchol 38:7–21
Appleton CC (2003) Alien and invasive freshwater Gastropoda in South Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 28:69–81
Benítez-Mora A, Camargo JA (2014) Ecological responses of aquatic macrophytes and benthic macroinvertebrates to dams in the Henares River Basin (Central Spain). Hydrobiologia 728:167–178
Benítez-Mora A, Aguirre-Sierra A, Alonso A, Camargo JA (2014) Ecotoxicological assessment of the impact of nitrate (NO3 −) on the European endangered white-clawed crayfish Austropotamobius italicus (Faxon). Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 101:220–225
Bernot RJ, Brandenburg M (2013) Freshwater snail vital rates affected by non-lethal concentrations of silver nanoparticles. Hydrobiologia 714:25–34
Bernot RJ, Kennedy EE, Lamberti GA (2005) Effects of ionic liquids on the survival, movement, and feeding behavior of the freshwater snail, Physa acuta. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1759–1765
Bilotta GS, Brazier RE (2008) Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res 42:2849–2861
Bryce SA, Lomnicky GA, Kaufmann PR (2010) Protecting sediment-sensitive aquatic species in mountain streams through the application of biologically based streambed sediment criteria. J N Am Benthol Soc 29:657–672
Burch JB (1989) North American freshwater snails. Hamburg, Michigan, The University of Michigan, Malacological Publications
Camargo JA (2003) Fluoride toxicity to aquatic organisms: a review. Chemosphere 50:251–264
Camargo JA (2004) Effects of body size and sodium chloride on the tolerance of net-spinning caddisfly larvae to fluoride toxicity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 72:579–585
Camargo JA, Tarazona JV (1990) Acute toxicity to freshwater macroinvertebrates of fluoride ion (F−) in soft water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:883–887
Camargo JA, Ward JV, Martin KL (1992) The relative sensitivity of competing hydropsychid species to fluoride toxicity in the Cache la Poudre River (Colorado). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:107–113
Camargo JA, Alonso A, de la Puente M (2005) Eutrophication downstream from small reservoirs in mountain rivers of Central Spain. Water Res 39:3376–3384
Chai L, Dong S, Zhao H, Deng H, Wang H (2016) Effects of fluoride on development and growth of Rana chensinensis embryos and larvae. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 126:129–137
Chapman JM, Proulx CI, Veilleux MAN, Levert C, Bliss S, André ME, Lapointe NWR, Cooke SJ (2014) Clear as mud: a meta-analysis on the effects of sedimentation on freshwater fish and the effectiveness of control measures. Water Res 56:190–202
Cope NJ, Winterbourn MJ (2004) Competitive interactions between two successful molluscan invaders of freshwaters: an experimental study. Aquat Ecol 38:83–91
Dalesman S, Rundle SD, Cotton PA (2007) Predator regime influences innate anti-predator behaviour in the freshwater gastropod Lymnaea stagnalis. Freshw Biol 52:2134–2140
Damkaer DM, Dey DB (1989) Evidence for fluoride effects on salmon passage at John Day dam, Columbia river, 1982-1986. N Am J Fish Manage 9:154–162
Dillon RT Jr (2000) The ecology of freshwater mollusks. Cambridge University Press, New York
Dillon RT Jr, Wethington AR, Rhett JM, Smith TP (2002) Populations of the European freshwater pulmonate Physa acuta are not reproductively isolated from American Physa heterostropha or Physa integra. Invert Biol 121:226–234
Extence CA, Chadd RP, England J, Dunbar MJ, Wood PJ, Taylor ED (2013) The assessment of fine sediment accumulation in rivers using macro-invertebrate community response. River Res Appl 29:17–55
Fernandes M, Amorim J, Vasconcelos V, Teles LO (2016) Resilience assessment of a biological early warning system based on the locomotor behavior of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:18858–18868
Gonzalo C, Camargo JA (2013) The impact of an industrial effluent on the water quality, submersed macrophytes and benthic macroinvertebrates in a dammed river of Central Spain. Chemosphere 93:1117–1124
Gonzalo C, Camargo JA, Masiero L, Casellato S (2010) Fluoride toxicity and bioaccumulation in the invasive amphipod Dikerogammarus villosus (Sowinsky, 1894): a laboratory study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:472–475
Hansen LR, Roslev P (2016) Behavioral responses of juvenile Daphnia magna after exposure to glyphosate and glyphosate-copper complexes. Aquat Toxicol 179:36–43
Hauer FR, Lamberti GA (eds) (1996) Methods in stream ecology. Academic, San Diego
Hellou J (2011) Behavioural ecotoxicology, an “early warning” signal to assess environmental quality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1–11
Henley WF, Patterson MA, Neves RJ, Lemly AD (2000) Effects of sedimentation and turbidity on lotic food webs: a concise review for natural resource managers. Rev Fish Sci 8:125–139
Jha SK, Mishra VK, Sharma DK, Damodaran T (2011) Fluoride in the environment and its metabolism in humans. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 211:121–142
Jones JI, Murphy JF, Collins AI, Sear DA, Naden PS, Armitage PD (2012) The impact of fine sediment on macro-invertebrates. River Res Appl 28:1055–1071
Lombardo P, Cooke GD (2004) Resource use and partitioning by two co-occurring freshwater gastropod species. Arch Hydrobiol 159:229–251
López-Doval JC, Poquet M, Muñoz I (2014) Sublethal effects of the herbicide Diuron on the freshwater snail Physella acuta. Limnetica 33:205–216
Maqboul A, Aoujdad R, Fadli M, Fekhaoui M (2014) Population dynamics of Physa acuta (Mollusca: Pulmonata) in the lakes of Rif mountains (northern Morocco, Ouergha watershed). J Entomol Zool Stud 2:240–245
Mbaka JG, Mwaniki MW (2015) A global review of the downstream effects of small impoundments on stream habitat conditions and macroinvertebrates. Environ Rev 23:257–262
Metcalfe-Smith JL, Holtze KE, Sirota GR, Reid JJ, De Solla SR (2003) Toxicity of aqueous and sediment associated fluoride to freshwater organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:161–166
Murphy JF, Jones JI, Pretty JL, Duerdoth CP, Hawczak A, Arnold A, Blackburn JH, Naden PS, Old G, Sear DA, Hornby D, Clarke RT, Collins AL (2015) Development of a biotic index using stream macroinvertebrates to assess stress from deposited fine sediment. Freshw Biol 60:2019–2036
Musee N, Oberholster PJ, Sikhwivhilu L, Botha AM (2010) The effects of engineered nanoparticles on survival, reproduction, and behavior of freshwater snail, Physa acuta (Draparnaud, 1805). Chemosphere 81:1196–1203
Naden PS, Murphy JF, Old GH, Newman J, Scarlett P, Harman M, Duerdoth CP, Hawczak A, Pretty JL, Arnold A, Laizé C, Hornby DD, Collins AL, Sear DA, Jones JI (2016) Understanding the controls on deposited fine sediment in the streams of agricultural catchments. Sci Total Environ 547:366–381
Pauget B, Gimbert F, Coeurdassier M, Crini N, Pérès G, Faure O, Douay F, Richard A, Grand C, de Vaufleury A (2013) Assessing the in situ bioavailability of trace elements to snails using accumulation kinetics. Ecol Indic 34:126–135
Payton ME, Greenstone MH, Schenker N (2003) Overlapping confidence intervals or standard error intervals: what do they mean in terms of statistical significance? J Insect Sci 3:34
Quinn JM, Davies-Colley RJ, Hickey CW, Vickers ML, Ryan PA (1992) Effects of clay discharges on streams 2. Benthic invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 248:235–247
Reddy SLN, Venu Gopal NBRK (1990) Effect of fluoride on acetylcholinesterase activity and oxygen consumption in a freshwater field crab, Barytelphusa guerini. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:760–766
Reddy SLN, Venu Gopal NBRK, Nagender Reddy A, Ramana Rao JV (1989) Fluoride-induced changes in carbohydrate metabolism in the tissue of freshwater crab Barytelphusa guerini. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 18:59–67
Riley LA, Dybdahl MF (2015) The roles of resource availability and competition in mediating growth rates of invasive and native freshwater snails. Freshw Biol 60:1308–1315
Riley LA, Dybdahl MF, Hall RO (2008) Invasive species impact: asymmetric interactions between invasive and endemic freshwater snails. J N Am Benthol Soc 27:509–520
Robinson PD (2009) Behavioral toxicity of organic chemical contaminants in fish: application to ecological risk assessments (ERAs). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 66:1179–1188
Rowe DK, Suren AM, Martin ML, Smith JP, Smith BJ, Williams E (2002) Lethal turbidity levels for common freshwater fish and invertebrates in Auckland streams. Auckland Regional Council Technical Publication Number 337, New Zealand
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 3rd edn. W.H. Freeman, New York
Soler J, Moreno D, Araujo R, Ramos MA (2006) Diversidad y distribución de los moluscos de agua dulce en la Comunidad de Madrid (España). Graellsia 62:201–252
Strong EE, Gargominy O, Ponder WF, Bouchet P (2008) Global diversity of gastropods (Gastropoda; Mollusca) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595:149–166
Suren AM, Martin ML, Smith BJ (2005) Short-term effects of high suspended sediments on six common New Zealand steam invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 548:67–74
Tachet H, Richoux P, Bournaud M, Usseglio-Polatera P (2003) Invertebrés d’Eau Douce (Systematique, Biologie, Écologie). CNRS Editions, Paris
Thorp JH, Covich AP (eds) (2010) Ecology and classification of north American freshwater invertebrates, 3rd edn. San Diego, Academic
Turner AM, Bernot RJ, Boes CM (2000) Chemical cues modify species interactions: the ecological consequences of predator avoidance by freshwater snails. Oikos 88:148–158
Turner AM, Turner RR, Ray SR (2007) Competition and intraguild egg predation among freshwater snails: re-examining the mechanism of interspecific interactions. Oikos 116:1895–1903
US Environmental Protection Agency (1991) Multifactor probit analysis. US EPA 600/X-91-101, Washington DC
Vaikasas S, Palaima K, Pliuraite V (2013) Influence of hydropower dams on the state of macroinvertebrates assemblages in the Virvyte River, Lithuania. J Environ Eng Landsc Manage 21:305–315
Wagner N, Lötters S, Veith M, Viertel B (2015) Acute toxic effects of the herbicide formulation Focus® Ultra on embryos and larvae of the Moroccan painted frog, Discoglossus scovazzi. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69:535–544
Weinstein LH, Davison AW (2004) Fluorides in the environment: effects on plants and animals. CABI Publishing, Cambridge
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: Lake and rivers ecosystems, 3rd edn. Academic, San Diego
Wetzel RG, Likens GE (2000) Limnological analyses, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Wood PJ, Armitage PD (1997) Biological effects of fine sediment in the lotic environment. Environ Manag 21:203–217
World Health Organization (2002) Environmental health criteria 227. Fluorides. WHO, Geneva
Zala SM (2004) Abnormal behaviors induced by chemical pollution: a review of the evidence and new challenges. Anim Behav 68:649–664
Zalizniak L, Kefford BJ, Nugegoda D (2009) Effects of different ionic compositions on survival and growth of Physa acuta. Aquat Ecol 43:145–156
Zukowski S, Walker KF (2009) Freshwater snails in competition: alien Physa acuta (Physidae) and native Glyptophysa gibbosa (Planorbidae) in the River Murray, South Australia. Mar Freshw Res 60:999–1005
Acknowledgments
Funds for this research came from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (research project CGL2011-28585). The University of Alcala provided logistical support for carrying out field studies and laboratory experiments. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Cinta Porte
Highlights
- The bladder snail Physella acuta appears to be a tolerant invertebrate species to fluoride toxicity.
- Estimated safe concentrations for juvenile and adult snails are 2.4 and 3.7 mg F−/L, respectively.
- Behavioral toxicity testing is used to evaluate the suitability of estimated safe concentrations.
- Instream habitat degradation, derived from increased turbidity levels, might be a major cause for the impact of the industrial effluent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camargo, J.A., Alonso, Á. Ecotoxicological assessment of the impact of fluoride (F−) and turbidity on the freshwater snail Physella acuta in a polluted river receiving an industrial effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 15667–15677 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9208-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9208-x