Abstract
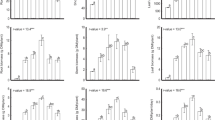
Phytoremediation of strontium contaminated soil by Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench was investigated, and the soil microbial community-level physiological profiles (CLPPs) were examined. The growth and the stable strontium (88Sr) accumulations of the energy crop S. bicolor grown on the Sr-spiked soil at the level of 0, 50, 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg soil were characterized through pot soil system after the entire growth period (140 days). Correspondingly, the available content of strontium in soil extracted by Mehlich III extraction solution reached 42.0, 71.9, 151.8, and 242.2 mg/kg, respectively. The Sr-polluted soil microbial community was assessed by a Biolog Eco-plate method. The results showed that the spiked Sr significantly increased the height and the stem biomass weight of the plant. Sr contents in roots, stems, and leaves of the sorghum increased linearly (R 2 > 0.95) with the elevation of the Sr-spiked level in soil. The average Sr concentration in roots, stems, and leaves reached 68.9, 61.3, and 132.6 mg/kg dry weight (DW) under Sr-spiked 400 mg/kg soil, respectively. Sr content in tissues decreased in the order of leaves > roots > stems. The bioconcentration factor (BCF; Sr contents in shoots to soil) values of S. bicolor in soil system was lower than 1 (0.21∼0.39) whether based on the spiked Sr level or on the available Sr level in soil. The transfer factor (TF; Sr contents in shoots to roots) values of S. bicolor in soil system usually is higher than 1 or near to 1 (0.92∼1.29). TF values increased while BCF values decreased as the soil Sr increased. The Biolog Eco-plate assay showed that Sr at the spiked level of 400 mg/kg soil enhanced the soil microbial diversity and activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achal V, Pan XL, Zhang DY (2012) Bioremediation of strontium (Sr) contaminated aquifer quartz sand based on carbonate precipitation induced by Sr resistant Halomonas sp. Chemosphere 89:764–768
Al Attar L, Al-Oudat M, Safia B, Ghani BA (2015) Transfer factor of Sr-90 and Cs-137 to lettuce and winter wheat at different growth stage applications. J Environ Radioact 150:104–110
Al Chami Z, Amer N, Al Bitar L, Cavoski I (2015) Potential use of Sorghum bicolor and Carthamus tinctorius in phytoremediation of nickel, lead and zinc. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:3957–3970
Bentley RA (2006) Strontium isotopes from the earth to the archaeological skeleton: a review. J Archaeol Method Theory 13:135–187
Brzostowski A, Falandysz J, Jarzynska G, Zhang D (2011) Bioconcentration potential of metallic elements by Poison Pax (Paxillus involutus) mushroom. J Environ Sci Health A 46:378–393
Calvino M, Messing J (2012) Sweet sorghum as a model system for bioenergy crops. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:323–329
Chapman SJ, Campbell CD, Artz R (2007) Assessing CLPPs using MicroResp™—a comparison with Biolog and multi-SIR. J Soils Sediments 7(6):406–410
Classen AT, Boyle SI, Haskins KE, Overby ST, Hart SC (2003) Community-level physiological profiles of bacteria and fungi: plate type and incubation temperature influences on contrasting soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44:319–328
Dushenkov S (2003) Trends in phytoremediation of radionuclides. Plant Soil 249:167–175
Eapen S, Singh S, Thorat V, Kaushik CP, Raj K, D’Souza SF (2006) Phytoremediation of radiostrontium (90Sr) and radiocesium (137Cs) using giant milky weed (Calotropis gigantea R.Br.) plants. Chemosphere 65:2071–2073
Entry JA, Vance NC, Hamilton MA, Zabowski D, Watrud LS, Adriano DC (1996) Phytoremediation of soil contaminated with low concentrations of radionuclides. Water Air Soil Pollut 88:167–176
Entry JA, Watrud LS, Reeves M (1999) Accumulation of 137Cs and 90Sr from contaminated soil by three grass species inoculated with mycorrhizal fungi. Environ Pollut 104:449–457
Epelde L, Mijangos I, Becerril JM, Garbisu C (2009) Soil microbial community as bioindicator of the recovery of soil functioning derived from metal phytoextraction with sorghum. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1788–1794
Fellet G, Marchiol L, Perosa D, Zerbi G (2007) The application of phytoremediation technology in a soil contaminated by pyrite cinders. Ecol Eng 31:207–214
Frostegard A, Tunlid A, Baath E (2011) Use and misuse of PLFA measurements in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1621–1625
Fuhrmann M, Lasat MM, Ebbs SD, Kochian LV, Cornish J (2002) Uptake of cesium-137 and strontium-90 from contaminated soil by three plant species; application to phytoremediation. J Environ Qual 31:904–909
Garland JL (1996) Analytical approaches to the characterization of samples of microbial communities using patterns of potential C source utilization. Soil Biol Biochem 28:213–221
Garland JL (1997) Analysis and interpretation of community-level physiological profiles in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 24:289–300
Garland JL, Mills AL, Young JS (2001) Relative effectiveness of kinetic analysis vs single point readings for classifying environmental samples based on community-level physiological profiles (CLPP). Soil Biol Biochem 33:1059–1066
Gomez E, Garland J, Conti M (2004) Reproducibility in the response of soil bacterial community-level physiological profiles from a land use intensification gradient. Appl Soil Ecol 26:21–30
He HH, Bleby TM, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Kuo J (2012) Precipitation of calcium, magnesium, strontium and barium in tissues of four Acacia species (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae). Plos One 7
IAEA (2010) Handbook of parameter values for the prediction of radionuclide transfer in terrestrial and freshwater environments. IAEA technical report series no. 472. IAEA, Vienna
Karpova EA, Gomonova NF (2006) Strontium in an agrocenosis on a soddy-podzolic soil under conditions of the long-term effect and aftereffect of fertilizers. Eurasian Soil Sci 39:779–784
Khan S, Hesham A, Qiao M, Rehman S, He JZ (2010) Effects of Cd and Pb on soil microbial community structure and activities. Environ Sci Pollut R 17:288–296
Krouglov SV, Filipas AS, Alexakhin RM, Arkhipov NP (1997) Long-term study on the transfer of 137Cs and 90Sr from Chernobyl-contaminated soils to grain crops. J Environ Radioactiv 34:267–286
Krutilina VS, Goncharova NA, Panov NP, Letchamo W (1999) Effect of zeolite and phosphogypsum on yield, plant uptake, and content of strontium in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 30:483–495
Lehman RM, Garland JL, Osborne SL (2013) Applying an oxygen-based respiratory assay to assess soil microbial responses to substrate and N availability. Appl Soil Ecol 64:127–134
Li GY, Hu N, Ding DX, Zheng JF, Liu YL, Wang YD, Nie XQ (2011) Screening of plant species for phytoremediation of uranium, thorium, barium, nickel, strontium and lead contaminated soils from a uranium mill tailings repository in South China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:646–652
Marchiol L, Fellet G, Perosa D, Zerbi G (2007) Removal of trace metals by Sorghum bicolor and Helianthus annuus in a site polluted by industrial wastes: a field experience. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:379–387
Margon A, Mondini C, Valentini M, Ritota M, Leita L (2013) Soil microbial biomass influence on strontium availability in mine soil. Chem Speciation Bioavail 25:119–124
Mehlich A (1984) Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: a modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 15(12):1409–1416
Moyen C, Roblin G (2010) Uptake and translocation of strontium in hydroponically grown maize plants, and subsequent effects on tissue ion content, growth and chlorophyll a/b ratio: comparison with Ca effects. Environ Exp Bot 68:247–257
Nadimi-Goki M, Wahsha M, Bini C, Kato Y, Vianello G, Antisari LV (2014) Assessment of total soil and plant elements in rice-based production systems in NE Italy. J Geochem Explor 147:200–214
Niedree B, Berns AE, Vereecken H, Burauel P (2013) Do Chernobyl-like contaminations with Cs-137 and Sr-90 affect the microbial community, the fungal biomass and the composition of soil organic matter in soil? J Environ Radioact 118:21–29
Pessacq J, Medina R, Terada C, Bianchini FE, Morelli IS, Del Panno MT (2015) Assessment of the responsiveness to different stresses of the microbial community from long-term hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:1–13
Phieler R, Merten D, Roth M, Buchel G, Kothe E (2015) Phytoremediation using microbially mediated metal accumulation in Sorghum bicolor. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:19408–19416
Pinto AP, de Varennes A, Goncalves MLS, Mota AM (2006) Sorghum detoxification mechanisms. J Plant Nutr 29:1229–1242
Prasad M, Freitas H (2003) Metal hyperaccumulation in plants—biodiversity prospecting for phytoremediation technology. Electron J Biotechnol 6:285–321
Qi L, Qin XL, Li FM, Siddique K, Brandl H, Xu JZ, Li XG (2015) Uptake and distribution of stable strontium in 26 cultivars of three crop species: oats, wheat, and barley for their potential use in phytoremediation. Int J Phytoremediat 17:264–271
Roca MC, Vallejo VR, Roig M, Tent J, Vidal M, Rauret G (1997) Prediction of cesium-134 and strontium-85 crop uptake based on soil properties. J Environ Qual 26:1354–1362
Ros M, Goberna M, Pascual JA, Klammer S, Insam H (2008) 16S rDNA analysis reveals low microbial diversity in community level physiological profile assays. J Microbiol Methods 72:221–226
Sasmaz A, Sasmaz M (2009) The phytoremediation potential for strontium of indigenous plants growing in a mining area. Environ Exp Bot 67:139–144
Sahoo SK, Kavasi N, Sorimachi A, Arae H, Tokonami S, Mietelski JW, Lokas E, Yoshida S (2016) Strontium-90 activity concentration in soil samples from the exclusion zone of the Fukushima daiichi nuclear power plant. Sci Rep-UK 6(23925):1–10
Soudek P, Valenova S, Vavrikova Z, Vanek T (2006) 137Cs and 90Sr uptake by sunflower cultivated under hydroponic conditions. J Environ Radioactiv 88:236–250
Su Y, Sridhar B, Han FX, Diehl SV, Monts DL (2007) Effect of bioaccumulation of Cs and Sr natural isotopes on foliar structure and plant spectral reflectance of indian mustard (Brassica juncea). Water Air Soil Pollut 180:65–74
Tsukada H, Takeda A, Takahashi T, Hasegawa H, Hisamatsu S, Inaba J (2005) Uptake and distribution of 90Sr and stable Sr in rice plants. J Environ Radioactiv 81:221–231
Twining JR, Payne TE, Itakura T (2004) Soil-water distribution coefficients and plant transfer factors for 134Cs, 85Sr and 65Zn under field conditions in tropical Australia. J Environ Radioactiv 71:71–87
Von Fircks Y, Rosen K, Sennerby-Forsse L (2002) Uptake and distribution of 137Cs and 90Sr in Salix viminalis plants. J Environ Radioactiv 63:1–14
Wang D, Wen FP, Xu CH, Tang YL, Luo XG (2012) The uptake of Cs and Sr from soil to radish (Raphanus sativus L.)- potential for phytoextraction and remediation of contaminated soils. J Environ Radioactiv 110:78–83
Wang JJ, Wang CJ, Huang CC, Lin YM (1998) Transfer factors of 90Sr and 137Cs from paddy soil to the rice plant in Taiwan. J Environ Radioactiv 39:23–34
Wang X, Chen C, Wang JL (2016a) Bioremediation of cesium-contaminated soil by Sorghum bicolor and soil microbial community analysis. Geomicrobiol J 33:216–221
Wang X, Chen C, Wang JL (2016b) Cs phytoextraction by Sorghum bicolor in soil and in hydroponic system. Int J Phytoremed doi:10.1080/15226514.2016.1244158
Wang X, Chen C, Wang JL (2017) Cadmium phytoextraction from loam soil in tropical southern China by Sorghum bicolor. Int J Phytoremed (accepted)
Wang YP, Shi JY, Wang H, Lin Q, Chen XC, Chen YX (2007) The influence of soil heavy metals pollution on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and community composition near a copper smelter. Ecotox Environ Safe 67:75–81
Wen FP, Wang D, Xu CH, Xu FT, Zhang ZW, Zhang XX (2009) Uptake and distribution of 133Cs and 88Sr in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Bull Bot Res 29(5):592–596
Zhu YG, Shaw G (2000) Soil contamination with radionuclides and potential remediation. Chemosphere 41:121–128
Zhuang P, Shu W, Li Z, Liao B, Li J, Shao J (2009) Removal of metals by sorghum plants from contaminated land. J Environ Sci 21:1432–1437
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT-13026) and the National S&T Major Project (2013ZX06002001). The authors would also like to thank the financial support provided by the Open Research Fund Program of Key Laboratory of Advanced Reactor Engineering and Safety, Ministry of Education of China, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51338005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Chen, C. & Wang, J. Phytoremediation of strontium contaminated soil by Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench and soil microbial community-level physiological profiles (CLPPs). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 7668–7678 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8432-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8432-8