Abstract
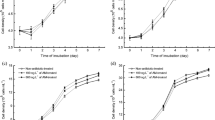
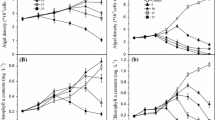
Due to changing global climatic conditions, a lot of attention has been given to cyanobacteria and their bioactive secondary metabolites. These conditions are expected to increase the frequency of cyanobacterial blooms, and consequently, the concentrations of cyanotoxins in aquatic ecosystems. Unfortunately, there are very few studies that address the effects of cyanotoxins on the physiology of phytoplankton species under different environmental conditions. In the present study, we investigated the effect of the cyanotoxin anatoxin-a (ATX-A) on Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanobacteria) and Acutodesmus acuminatus (chlorophyta) under varying light and nitrogen conditions. Low light (LL) and nitrogen limitation (LN) resulted in significant cell density reduction of the two species, while the effect of ATX-A on M. aeruginosa was not significant. However, under normal (NN) and high nitrogen (HN) concentrations, exposure to ATX-A resulted in significantly (p < 0.05) lower cell density of A. acuminatus. Pigment content of M. aeruginosa significantly (p < 0.05) declined in the presence of ATX-A, regardless of the light condition. Under each light condition, exposure to ATX-A caused a reduction in total microcystin (MC) content of M. aeruginosa. The detected MC levels varied as a function of nitrogen and ATX-A concentrations. The production of reactive oxygen species (H2O2) and antioxidant enzyme activities of both species were significantly altered by ATX-A under different light and nitrogen conditions. Our results revealed that under different light and nitrogen conditions, the response of M. aeruginosa and A. acuminatus to ATX-A was variable, which demonstrated the need for different endpoints of environmental factors during ecotoxicological investigations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sammak MA, Hoagland KD, Cassada D, Snow DD (2014) Co-occurrence of the cyanotoxins BMAA, DBA and anatoxin-a in Nebraska reservoirs, fish, and aquatic plants. Toxins 6:488–508
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:235–241
Babica P, Kohoutek J, Bláha L, Adamovsky O, Marsálek B (2006) Evaluation of extraction approaches linked to ELISA and HPLC for analyses of microcystin-LR, -RR and -YR in freshwater sediments with different organic material contents. Anal Bioanal Chem 85:1545–1551
Bártova K, Hilscherova K, Babica P, Marsalek B, Bláha L (2011) Effects of microcystin and complex cyanobacterial samples on the growth and oxidative stress parameters in green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and comparison with the model oxidative stressor herbicide paraquat. Environ Toxicol 26:641–648
Bittencourt-Oliveira MC, Chia AM, de Oliveira HSB, Cordeiro-Araújo MK, Molica RJR, Dias CTS (2015) Allelopathic interactions between microcystin-producing and non-microcystin-producing cyanobacteria and green microalgae: implications for microcystins production. J Appl Phycol 27:275–284
Bláhová L, Oravec M, Marsálek B, Sejnohová L, Simek Z, Bláha L (2009) The first occurrence of the cyanobacterial alkaloi toxin cylindrospermopsin in the Czech Republic as determined by immunochemical and LC/MS methods. Toxicon 53:519–524
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91:179–194
Botes DP, Wessels PL, Kruger H, Runnegar MTC, Santikarn S, et al. (1985) Structural studies on cyanoginosins-LR, -YR, -YA, and –YM, peptide toxins from Microcystis aeruginosa. J Chem Soc, Perkin Transactions I:2747–2748
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Chem 72:243–254
Briand E, Bormans M, Quiblier C, Salençon MJ, Humbert JF (2012) Evidence of the cost of the production of microcystins by Microcystis aeruginosa under differing light and nitrate environmental conditions. PLoS One 7(1):e29981
Campos A, Araújo P, Pinheiro C, Azevedo J, Osório H, Vasconcelos V (2013) Effect on growth, antioxidant enzyme activity and levels of extracellular proteins in the green alga Chlorella vulgaris exposed to crude cyanobacterial extracts and pure microcystin and cylindrospermopsin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 94:45–53
Carmichael WW, Biggs DF, Gorham PR (1975) Toxicology and pharmacological action of Anabaena flos-aquae toxin. Science 187:542–544
Chia AM, Cordeiro-Araújo MK, Bittencourt-Oliveira MC (2015a) Growth and antioxidant response of Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanobacteria) exposed to anatoxin-a. Harmful Algae 49:135–146
Chia AM, Chimdirim PK, Japhet WS (2015b) Lead induced antioxidant response and phenotypic plasticity of Scenedesmus quadricauda (Turp.) de Brebisson under different nitrogen conditions. J Appl Phycol 27:293–302
Chia AM, Lombardi AT, Melão MGG, Parrish CC (2015c) Combined nitrogen limitation and cadmium stress stimulate total carbohydrates, lipids, protein and amino acid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris (Trebouxiophyceae). Aquat Toxicol 160:87–95
Deng L, Senseman SA, Gentry TJ, Zuberer DA, Weiss TL, Devarenne TP, Camargo ER (2012) Effect of selected herbicides on growth and hydrocarbon content of Botryococcus braunii (race B). Ind Crop Prod 39:154–161
Furey A, Crowley J, Hamilton B, Lehane M, James KJ (2005) Strategies to avoid the mis-identification of anatoxin-a using mass spectrometry in the forensic investigation of acute neurotoxic poisoning. J Chromatogr A 1082:91–97
Ger KA, Teh SJ, Baxa DV, Lesmeister S, Goldman CR (2010) The effects of dietary Microcystis aeruginosa and microcystin on the copepods of the upper San Franscisco estuary. Freshw Biol 55:1548–1559
Graham JL, Loftin KA, Meyer MT, Ziegler AC (2010) Cyanotoxin mixtures and taste-and-odor compounds in cyanobacterial blooms from the Midwestern United States. Environ Sci Technol 44:7361–7368
Gross EM (2003) Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:313–339
Ha MH, Pflugmacher S (2013a) Phytotoxic effects of the cyanobacterial neurotoxin anatoxin-a: morphological, physiological and biochemical responses in aquatic macrophyte, Ceratophyllum demersum. Toxicon 70:1–8
Ha MH, Pflugmacher S (2013b) Time-dependent alterations in growth, photosynthetic pigments and enzymatic defense systems of submerged Ceratophyllum demersum during exposure to the cyanobacterial neurotoxin anatoxin-a. Aquat Toxicol 138-139:26–34
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Harel M, Weiss G, Lieman-Hurwitz J, Gun J, Lev O, Lebendiker M, et al. (2013) Interactions between Scenedesmus and Microcystis may be used to clarify the role of secondary metabolites. Environ Microbiol Rep 5:97–104
Hereman TC, Bittencourt-Oliveira MC (2012) Bioaccumulation of microcystins in lettuce. Journal of Phycology J Phycol 48:1535–1537
Holland A, Kinnear S (2013) Interpreting the possible ecological role(s) of cyanotoxins: compounds for competitive advantage and/or physiological aide? Mar Drugs 11:2239–2258
Huang YL, Zhang P, Zhu C, Zhou ZH (2012) Vertical migration comparison of Scenedesmus and Microcystis. Adv Mat Res 518-523:558–564
James KJ, Sherlock IR, Stack MA (1997) Anatoxin-a in Irish fresh-water and cyanobacteria, determined using a new fluorimetric liquid chromatographic method. Toxicon 35:963–971
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1982) Glycolate metabolism of three submerged aquatic angiosperms during aging. Aquat Bot 12:345–354
Johansson LH, Borg LAH (1988) A spectrophotometric method for determination of catalase activity in small tissue samples. Anal Biochem 174:331–336
Juneja A, Ceballos RM, Murthy GS (2013) Effects of environmental factors and nutrient availability on the biochemical composition of algae for biofuels production: a review. Energies 6:4607–4638
Juttner F, Leonhardt J, Mohren S (1983) Environmental factors affecting the formation of mesityloxide dimethylallylic alcohol and other volatile compounds excreted by Anabaena cylindrical. J Gen Microbiol 129:407–412
Kearns KD, Hunter MD (2000) Green algal extracellular products regulate antialgal toxin production in a cyanobacterium. Environ Microbiol 2:291–297
Kearns KD, Hunter MD (2001) Toxin-producing Anabaena flos-aquae induces settling of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a competing motile alga. Microbial Ecol 42:80–86
Krienitz L, Hegewald E, Hepperle D, Wolf M (2003) The systematics of coccoid green algae: 18S rRNA gene sequence data versus morphology. Biologia 58:437–446
Larkum AWD, Douglas SE, Raven JA (2003) Photosynthesis in algae. Kluwer, Dordrecht Netherlands, p. 479
Leflaive J, Ten-Hage L (2007) Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: a comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw Biol 52:199–214
Liu Y, Xu Y, Yu YP, Yu R, Li P, Qiao D, Cao Y, Cao Y (2014) The biodiversity of oleaginous microalgae in northern Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Afr J Microbiol Res 8:66–74
Lozano P, Trombini C, Crespo E, Blasco J, Moreno-Garrido I (2014) ROI-scavenging enzyme activities as toxicity biomarkers in three species of marine microalgae exposed to model contaminants (copper, Irgarol and atrazine). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:294–301
Méjean A, Ploux O (2013) A genomic view of secondary metabolite production in cyanobacteria. Genomics of cyanobacteria. Adv Bot Res 65:189–234
Metcalf JS, Bell SG, Codd GA (2000) Production of novel polyclonal antibodies against the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR and their application for the detection and quantification of microcystins and nodularin. Water Res 34:2761–2769
Mikula P, Zezulka S, Jancula D, Marsalek B (2012) Metabolic activity and membrane integrity changes in Microcystis aeruginosa—new findings on hydrogen peroxide toxicity in cyanobacteria. Eur J Phycol 47:195–206
Miller AF (2012) Superoxide dismutases: ancient enzymes and new insights. FEBS Lett 586:585–595
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The generation of superoxide radical antioxidation of haemoglobin. J Biol Chem 247:6960–6962
Mitrovic SM, Pflugmacher S, James KJ, Furey A (2004) Anatoxin-a elicits an increase in peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase activity in aquatic plants. Aquat Toxicol 68:185–192
Mohamed ZA, Carmichael WW, Hussein AA (2003) Estimation of microcystins in the fresh water fish Oreochromis niloticus in an Egyptian fish farm containing a Microcystis bloom. Environ Toxicol 18:137–141
Molisch H (1937) Der Einfluss einer Pflanze auf die andere—Allelopathie. Fischer, Jena
Nübel U, Garcia-Pichel F, Muyzer G (1997) PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microb 63:3327–3332
Paerl H (2008) Nutrient and other environment controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms along the freshwater-marine continuum. Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Adv Exp Med Biol 619:217–237
Pawlik-Skowronska B, Skowronski T, Pirszel J, Adamczyk A (2004) Relationship between cyanobacterial bloom composition and anatoxin-a and microcystin occurrence in the eutrophic dam reservoir (Se Poland). Pol J Ecol 52:479–490
Qiao W, Li C, Fan LM (2014) Cross-talk between nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide in plant responses to abiotic stresses. Environ Exp Bot 100:84–93
Rasoul-Amini S, Ghasemi Y, Morowvat MH, Mohagheghzadeh A (2009) PCR amplification of 18S rRNA, single cell protein production and fatty acid evaluation of some naturally isolated microalgae. Food Chem 16:129–136
Reddy JK, Suga T, Mannaerts GP, Lazarow PB, Subramani S (1995) Peroxisomes: biology and role in toxicology and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci, New York, pp. 1–795
Reynolds CS (2006) The ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Ritchie RJ (2006) Consistent sets of spectrophotometric chlorophyll equations for acetone, methanol and ethanol solvents. Photosyn Res 89:27–41
Rzymski P, Poniedzialek B, Kokocinski M, Jurczk T, Lipski D, Wiktorowicz K (2014) Interspecific allelopathy in cyanobacteria: cylindrospermopsin and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii effect on the growth and metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 35:1–8
Torres MA, Barros MP, Campos SCG, Pinto E, Rajamani S, Sayre RT, Colepicolo P (2008) Biochemical markers in algae and marine pollution: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:1–15
Van de Waal DB, Verspagen JMH, Lurling M, Van Donk E, Visser PM, et al. (2009) The ecological stoichiometry of toxins produced by harmful cyanobacteria: an experimental test of the carbon-nutrient balance hypothesis. Ecol Letters 12:1326–1335
Willame R, Boutte C, Grubisic S, Willmotte A, Komárek J, Hoffmann L (2006) Morphological and molecular characterization of planktonic cyanobacteria from Belgium and Luxemburg. J Phycol 42:1312–1332
Acknowledgments
M.A. Chia and A.S. Lorenzi were supported by post-doctoral fellowships (FAPESP—2013/11306-3; 2013/15296-2; 2014/26898-6) and M. C Bittencourt-Oliveira by a research grant (FAPESP—2014/01934-0) from the Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chia, M.A., Cordeiro-Araújo, M.K., Lorenzi, A.S. et al. Does anatoxin-a influence the physiology of Microcystis aeruginosa and Acutodesmus acuminatus under different light and nitrogen conditions?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 23092–23102 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7538-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7538-8