Abstract
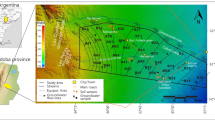
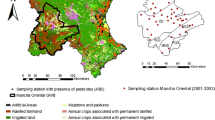
At present, some triazine herbicides occurrence in European groundwater, 13 years after their use ban in the European Union, remains of great concern and raises the question of their persistence in groundwater systems due to several factors such as storage and remobilization from soil and unsaturated zone, limited or absence of degradation, sorption in saturated zones, or to continuing illegal applications. In order to address this problem and to determine triazine distribution in the saturated zone, their occurrence is investigated in the light of the aquifer hydrodynamic on the basis of a geochemical approach using groundwater dating tracers (3H/3He). In this study, atrazine, simazine, terbuthylazine, deethylatrazine, deisopropylatrazine, and deethylterbuthylazine are measured in 66 samples collected between 2011 and 2013 from 21 sampling points, on the Vistrenque shallow alluvial aquifer (southern France), covered by a major agricultural land use. The frequencies of quantification range from 100 to 56 % for simazine and atrazine, respectively (LQ = 1 ng L−1). Total triazine concentrations vary between 15 and 350 ng L−1 and show three different patterns with depth below the water table: (1) low concentrations independent of depth but related to water origin, (2) an increase in concentrations with depth in the aquifer related to groundwater residence time and triazine use prior to their ban, and (3) relatively high concentrations at low depths in the saturated zone more likely related to a slow desorption of these compounds from the soil and unsaturated zone. The triazine attenuation rate varies between 0.3 for waters influenced by surface water infiltration and 4.8 for water showing longer residence times in the aquifer, suggesting an increase in these rates with water residence time in the saturated zone. Increasing triazine concentrations with depth is consistent with a significant decrease in the use of these pesticides for the last 10 years on this area and highlights the efficiency of their ban.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarado JAC, Purtschert R, Hinsby K, et al. (2005) 36Cl in modern groundwater dated by a multi-tracer approach (3H/3He, SF6, CFC-12 and 85Kr): a case study in quaternary sand aquifers in the Odense pilot River Basin, Denmark. Appl Geochem 20:599–609. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.09.018
Baran N, Mouvet C, Négrel P (2007) Hydrodynamic and geochemical constraints on pesticide concentrations in the groundwater of an agricultural catchment (Brévilles, France). Environ Pollut 148:729–738. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.01.033
Barbash J, Resek E (1996) Influence of pesticides properties, environmental setting, and study design on pesticide detections. In: pesticides in groundwater: distribution, trends, and governing factors. Ann Arbor Press, Inc.; CRC Press, Chelsea, MI; Boca Raton, FL, p. 590
Barriuso E, Houot S, Serra-Wittling C (1997) Influence of compost addition to soil on the behaviour of herbicides. Pestic Sci 49:65–75. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9063(199701)49:1<65::AID-PS488>3.0.CO;2-Z
Beltran J, Gerritse RG, Hernandez F (1998) Effect of flow rate on the adsorption and desorption of glyphosate, simazine and atrazine in columns of sandy soils. Eur J Soil Sci 49:149–156. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2389.1998.00132.x
Blume E, Bischoff M, Moorman TB, Turco RF (2004) Degradation and binding of atrazine in surface and subsurface soils. J Agric Food Chem 52:7382–7388. doi:10.1021/jf049830c
Burow K, Stork S, Bubrovsky N (1998) Nitrate and pesticides in ground water in the eastern San Joaquin Valley, California: occurrence and trends. USGS report. 33p
Castaneda AR, Bhuiyan SI (1996) Groundwater contamination by rice field pesticides and some influencing factors. J Environ Sci Heal Part A Environ Sci Eng Toxicol 31:83–99. doi:10.1080/10934529609376345
Celis R, Cornejo J, Hermosin M, Koskinen W (1998) Sorption of atrazine and simazine by model associations of soil collides. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:165–171
Cheng H, Koskinen WC (1986) Processes and factors affecting transport of pesticides to ground water. In: Evaluation of pesticides in ground water. 573 p, p 2–13
Cook PG, Solomon DK (1997) Recent advances in dating young groundwater : chlorofluorocarbons, 3H/3He and 85Kr. J Hydrol 191:245–265
Darling WG, Gooddy DC (2007) Assessing the applicability of global CFC and SF(6) input functions to groundwater dating in the UK. Sci Total Environ 387:353–362. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.06.015
Domagalski JL, Dubrovsky NM (1992) Pesticide residues in ground water of the San Joaquin Valley, California. J Hydrol 130:299–338. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(92)90115-C
Dunkle S, Plummer L, Busenberg E, et al. (1993) Chlorofluorocarbons (CCl3F and CCl2F2) as dating tools and hydrologic tracers in shallow groundwater of the Delmarva peninsula, Atlantic coastal plain, United States. Water Resour Res 29:3837–3860
Garmouma M, Blanchoud H, Teil M, et al. (2001) Triazines in the Marne and the Seine rivers (France): longitudinal evolution and flows. Water Air Soil Pollut 132:1–17
Garmouma M, Chevreuil M (1998) Triazine dispersion and distribution in the unsaturated zone of drained soils in the brie (France). Water Air Soil Pollut 108:129–148
General Directorate of Health (2015) Bilan de la qualité de l’eau au robinet du consommateur vis-à-vis des pesticides en 2013. Ministère des affaires sociales, de la santé etd es droits de la femme. 14p. (In French)
Gevao B, Semple KT, Jones KC (2000) Bound pesticide residues in soils: a review. Environ Pollut 108:3–14
Gourcy L, Baran N, Vittecoq B (2009) Improving the knowledge of pesticide and nitrate transfer processes using age-dating tools (CFC, SF6, 3H) in a volcanic island (Martinique, French West Indies). J Contam Hydrol 108:107–117. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2009.06.004
Jean-Baptiste P, Fourré E, Dapoigny A, et al. (2010) (3)He mass spectrometry for very low-level measurement of organic tritium in environmental samples. J Environ Radioact 101:185–190. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2009.10.005
Jean-Baptiste P, Mantisi F, Dapoigny A, Stievenard M (1992) Design and performance of a mass spectrometric facility for measuring helium isotopes in natural waters and for low-level tritium determination by the 3He ingrowth method. Int J Rad Appl Instrum A 43:881–891
Kingsbury, JA (2003) Shallow ground-water quality in agricultural areas of Northern Alabama and Middle Tennessee, 2000–2001. USGS report. 45p
Köck-Schulmeyer M, Ginebreda A, Postigo C, et al. (2014) Four-year advanced monitoring program of polar pesticides in groundwater of Catalonia (NE-Spain). Sci Total Environ 470-471:1087–1098. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.079
Kolpin DW, Goolsby DA, Thurman EM (1995) Pesticides in near-surface aquifers—an assessment using highly sensitive analytical methods and tritium. J Environ Qual 24:1125–1132. doi:10.2134/jeq1995.00472425002400060011x
Kolpin DW, Kalkhoff SJ, Goolsby DA, et al. (1997) Occurrence of selected herbicides and herbicide degradation products in Iowa’s groundwater, 1995. Ground Water 35:679–688
Lange J (2010) Bilan de la qualité de l’eau des nappes Vistrenque et Costières. Au regard des nitrates et des pesticides. Master dissertation, University of Montpellier 2. 43 P. (In French)
Lapworth DJ, Gooddy DC (2006) Source and persistence of pesticides in a semi-confined chalk aquifer of Southeast England. Environ Pollut 144:1031–1044. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.055
Loos R, Locoro G, Comero S, et al. (2010) Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water. Water Res 44:4115–4126. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.032
Lopez B, Ollivier P, Togola A, et al. (2015) Screening of French groundwater for regulated and emerging contaminants. Sci Total Environ 518-519:562–573. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.110
Louchart X, Voltz M, Andrieux P, Moussa R (2001) Herbicide transport to surface waters at field and watershed scales in a Mediterranean vineyard area. J Environ Qual 30:982–991. doi:10.2134/jeq2001.303982x
Manning AH, Kip Solomon D, Thiros SA (2005) 3H/3He age data in assessing the susceptibility of wells to contamination. Ground Water 43:353–367. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.2005.0028.x
McCallum JL, Cook PG, Simmons CT (2015) Limitations of the use of environmental tracers to infer groundwater age. Ground Water 53(Suppl 1):56–70. doi:10.1111/gwat.12237
McMahon PB, Chapelle FH, Jaguckl ML (1992) Atrazine mineralization potential of alluvial-aquifer sediments under aerobic conditions. Environ Sci Technol 26:1556–1559
Mills MS, Thurman EM (1994) Preferential dealkylation reactions of s-triazine herbicides in the unsaturated zone. Environ Sci Technol 28:600–605. doi:10.1021/es00053a011
Pedersen PG (2000) Pesticides degradability in groundwater : importance of redox conditions. PhD thesis. Technical University of Denmark. 79 p
Rodríguez CJ, Harkin JM (1997) Degradation of atrazine in subsoils, and groundwater mixed with aquifer sediments. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:728–735
Sannino F, Filazzola MT, Violante A, Gianfreda L (1999) Adsorption-desorption of simazine on montmorillonite coated by hydroxy aluminum species. Environ Sci Technol 33:4221–4225
Sassine L (2014) Occurrence of pesticides and emerging contaminants in an alluvial aquifer. Linking to groundwater origin and residence time. Case study of the Vistrenque aquifer. Aix-Marseille University, PhD dissertation, 127 p. (In French)
Sassine L, Khaska M, Ressouche S, et al. (2015) Coupling geochemical tracers and pesticides to determine recharge origins of a shallow alluvial aquifer: case study of the Vistrenque hydrogeosystem (SE France). Appl Geochem 56:11–22
Schlosser P, Stute M, Dörr H, et al. (1988) Tritium/3He dating of shallow groundwater. Earth Planet Sci Lett 89:353–362
Schlosser P, Stute M, Sonntag C, Münnich KO (1989) Tritiogenic 3He in shallow groundwater. Earth Planet Sci Lett 94:245–256
SMNVC (2002) Suivi des pesticides. Interprétations des résultats et premières conclusions. (In French)
Stackelberg PE, Barbash JE, Gilliom RJ, et al. (2012) Regression models for estimating concentrations of atrazine plus deethylatrazine in shallow groundwater in agricultural areas of the United States. J Environ Qual 41:479–494. doi:10.2134/jeq2011.0200
Steele GV, Johnson HM, Sandstrom MW, et al. (2008) Occurrence and fate of pesticides in four contrasting agricultural settings in the United States. J Environ Qual 37:1116–1132. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0166
Suckow A (2014) The age of groundwater—definitions, models and why we do not need this term. Appl Geochem. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.04.016
Tappe W, Groeneweg J, Jantsch B (2002) Diffuse atrazine pollution in German aquifers. Biodegradation 13:3–10
Tesoriero AJ, Saad DA, Burow KR, et al. (2007) Linking ground-water age and chemistry data along flow paths: implications for trends and transformations of nitrate and pesticides. J Contam Hydrol 94:139–155. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2007.05.007
Visser A, Fourré E, Barbecot F, et al. (2014) Intercomparison of tritium and noble gases analyses, 3H/3He ages and derived parameters excess air and recharge temperature. Appl Geochem. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.03.005
Vonberg D, Vanderborght J, Cremer N, et al. (2014) 20 years of long-term atrazine monitoring in a shallow aquifer in western Germany. Water Res 50:294–306. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.032
Acknowledgments
The PhD grant of L. Sassine was supported by the General Council of the Gard Department, the Urban Agglomeration of Nîmes Metropole, the University of Nîmes, and by the Joint Venture of the Vistrenque and the Costières Groundwaters. This work has been partially financed through the project funded by ONEMA, in the frame of the collaborative international consortium WATERJPI2013—PERSIST of the Water Challenges for a Changing World Joint Programming Initiative (Water JPI) Pilot Call.
The landowners and the stakeholders are gratefully thanked for giving us the access to the boreholes. The authors also wish to thank Marine Brogat and Amélie Sellier for their technical help in LC/MSMS analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sassine, L., Le Gal La Salle, C., Khaska, M. et al. Spatial distribution of triazine residues in a shallow alluvial aquifer linked to groundwater residence time. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 6878–6888 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7224-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7224-x