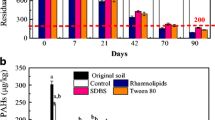
Abstract
In this work, an endosulfan-degrading strain was isolated from the aged soil contaminated by endosulfan, and identified as Ochrobactrum sp. EB-4 by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The microbial degradation characteristics of endosulfan in three eluents (Tween 80 + SDS, Tween 80 + Na2SiO3, Tween 80 + SDS + Na2SiO3) were investigated. The results showed that the degradation percents of α-, β-endosulfan in the three eluents were 86.83 %∼92.91 % and 88.90 %∼93.94 % in 15 days, respectively. The degradation process can be well described by the first-order kinetic model, and the half-times of α-endosulfan in eluent 1∼eluent 3 were 3.83, 5.29, and 4.53 days, while those of β-endosulfan were 3.35, 4.50 and 3.79 days, respectively. The endosulfan diol and endosulfan sulfate as main metabolites were detected, and the former can be further degraded by this strain, which revealed that the simultaneously happened hydrolysis and oxidation reactions were the main degradation processes, and dominated by hydrolysis reaction. After 5 days of washing with the eluents, 56.00∼84.33 % of α-endosulfan, and 46.49∼68.56 % of β-endosulfan in soil were eluted, respectively, and can be entirely biodegraded in 12 days, which indicated that the microbial degradation was the rate-determining step.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham J, Silambarasan S (2014a) Role of novel fungus Lasiodiplodia sp. JAS12 and plant growth promoting bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae JAS8 inmineralization of endosulfan and its metabolites. Ecol Eng 70:235–240
Abraham J, Silambarasan S (2014b) Biomineralization and formulation of endosulfan degrading bacterial and fungal consortiums. Pestic Biochem Physiol 116:24–31
Awasthi N, Kumar A, Makkar R, Cameotra SS (1999) Biodegradation of soil-applied endosulfan in the presence of a biosurfactant. J Environ Sci Health B 34:793–803
Chen W, Kan AT, Tomson MB (2000) Irreversible adsorption of chlorinated benzenes to natural sediments: implications for sediment quality criteria. Environ Sci Technol 34:385–392
Daher CF, Baroody GM, Howland RJ (2003) Effect of a surfactant, Tween 80, on the formation and secretion of chylomicrons in the rat. Food Chem Toxicol 41:575–582
Das AK, Saha S, Pal A, Maji SK (2009) Surfactant-modified alumina: an efficient adsorbent for malachite green removal from water environment. J Environ Sci Health A 44:896–905
Goswami S, Vig K, Singh DK (2009) Biodegradation of α and β endosulfan by Aspergillus sydoni. Chemosphere 75:883–888
Guerin TF (2005) Natural attenuation of metabolites of a chlorinated pesticide in soil. Int J Environ Stud 62:235–248
Hussain S, Arshad M, Saleem M, Khalid A (2007) Biodegradation of α- and β-endosulfan by soil bacteria. Biodegradation 18:731–740
Jayashree R, Vasudevan N (2007) Effect of Tween 80 added to the soil on the degradation of endosulfan by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4:203–210
Jayashree R, Vasudevan N (2009) Effect of Tween 80 and moisture regimes on endosulfan degradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Ecol Environ Res 7:35–44
Jayashree R, Vasudevan N, Chandrasekaran S (2006) Surfactants enhanced recovery of endosulfan from contaminated soils. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4:251–259
Jia H, Liu L, Sun Y, Sun B, Wang D, Su Y, Kannan K, Li YF (2010) Monitoring and modeling endosulfan in Chinese surface soil. Environ Sci Technol 44:9279–9284
Kataoka R, Takagi K, Sakakibara F (2011) Biodegradation of endosulfan by Mortieralla sp. strain W8 in soil: influence of different substrates on biodegradation. Chemosphere 85:548–552
Kathpal TS, Singh A, Dhankhar JS, Singh G (1997) Fate of endosulfan in cotton soil under subtropical conditions of northern India. Pestic Sci 50:21–27
Kong LF, Zhu SY, Zhu LS, Xie H, Su KC, Yan TX, Wang J, Wang JH, Wang FH, Sun FX (2013) Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticide endosulfan by bacterial strain Alcaligenes faecalis JBW4. J Environ Sci 25:2257–2264
Kong LF, Zhu SY, Zhu LS, Xie H, Wei K, Yan TX, Wang J, Wang JH, Wang FH, Sun FX (2014) Colonization of Alcaligenes faecalis strain JBW4 in natural soils and its detoxification of endosulfan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:1407–1416
Kumar K, Devi SS, Krishnamurthi K, Kanade GS, Chakrabarti T (2007) Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan degrading and detoxifying bacteria. Chemosphere 68:317–322
Kumar M, Lakshmi CV, Khanna S (2008) Biodegradation and bioremediation of endosulfan contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 99:3116–3122
Kumar A, Bhoot N, Soni I, John PJ (2014) Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis strain that degrades endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. 3. Biotech 4:467–475
Kwon GS, Kim JE, Kim TK, Sohnc HY, Kohd SC, Shine KS, Kim DG (2002) Klebsiella pneumoniae KE-1 degrades endosulfan without formation of the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 215:255–259
Kwon GS, Sohn HY, Shin KS, Kim EB, Seo BI (2005) Biodegradation of the organochlorine insecticide, endosulfan, and the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate, by Klebsiella oxytoca KE-8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:845–850
Mani A, Hameed SS, Ramalingam S (2011) Effect of rhamnolipd potential on biodegradation of endosulfan by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in batch studies. J Biosci Technol 2:268–278
Mata-Sandoval JC, Karns J, Torrents A (2001) Influence of rhamnolipids and Triton X-100 on the biodegradation of three pesticides in aqueous phase and soil slurries. J Agric Food Chem 49:3296–3303
Oddukkathil G, Vasudevan N (2013) Enhanced biodegradation of endosulfan and its major metabolite endosulfate by a biosurfactant producing bacterium. J Environ Sci Health B 48:462–469
Oddukkathil G, Vasudevan N (2015) Biodegradation of endosulfan isomers and its metabolite endosulfate by two biosurfactant producing bacterial strains of Bordetella petrii. J Environ Sci Health B 50:81–89
Sachdev DP, Cameotra SS (2013) Biosurfactants in agriculture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1005–1016
Sarah S, Krishna MV, Riaz M (2012) Characterization of endosulfan and endosulfan sulphate degradation by strains of putida. Int J Environ Sci 3:859–869
Seralathan MV, Sivanesan S, Bafana A, Kashyap SM, Patrizio A, Krishnamurthi K, Chakrabarti T (2014) Cytochrome P450 BM3 of Bacillus megaterium: a possible endosulfan biotransforming gene. J Environ Sci 1–8
Singh NS, Singh DK (2011) Biodegradation of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain C8B in broth medium. Biodegradation 22:845–857
Singh V, Singh N (2014a) Uptake and accumulation of endosulfan isomers and its metabolite endosulfan sulfate in naturally growing plants of contaminated area. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:189–193
Singh M, Singh DK (2014b) Endosulfan induced alteration in bacterial protein profile and RNA yield of Klebsiella sp. M3, Achromobacter sp. M6, and Rhodococcus sp. M2. J Hazard Mater 265:233–241
Singh M, Singh DK (2014c) Biodegradation of endosulfan in broth medium and in soil microcosm by Klebsiella sp. M3. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:237–242
Thangadurai P, Suresh S (2014) Biodegradation of endosulfan by soil bacterial cultures. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 94:38–47
Tian QD, Wang GQ, Zhao X, Lin YS (2012) Effects of three surfactants remedying organochlorine polluted soils through enhanced elution. J Ecol Rural Environ 28:196–202 (in Chinese)
Tiehm A (1994) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the presence of synthetic surfactants. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:258–263
Verma K, Agrawal N, Farooq M, Misra RB, Hans RK (2006) Endosulfan degradation by a Rhodococcus strain isolated from earthworm gut. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:377–381
Verma A, Ali D, Farooq M, Pant AB, Ray RS, Hans RK (2011) Expression and inducibility of endosulfan metabolizing gene in Rhodococcus strain isolated from earthworm gut microflora for its application in bioremediation. Bioresour Technol 102:2979–2984
Weber J, Halsall CJ, Muir D, Teixeira C, Small J, Solomon K, Hermanson M, Hung H, Bidleman T (2010) Endosulfan, a global pesticide: a review of its fate in the environment and occurrence in the Arctic. Sci Total Environ 408:2966–2984
Weir KM, Sutherland TD, Horne I, Russell RJ, Oakeshott JG (2006) A single monooxygenase, ese, is involved in the sulfate in an Arthrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3524–3535
Xiong BL, Zheng GC, Zhang JZ, Xing Z, Xu WH (2013) Elution of endosulfan from contaminated soil by surfactants and their combination. Environ Sci 34:4649–4657 (in Chinese)
Zeng GM, Fu HY, Zhong H, Yuan XZ, Fu MX, Wang W, Huang GH (2007) Co-degradation with glucose of four surfactants, CTAB, Triton X-100, SDS and rhamnolipid, in liquid culture media and compost matrix. Biodegradation 18:303–310
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2012AA101405) and the National Public Service Sectors (Agriculture) Research Project of China (No. 2009030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 167 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, F., Xiong, B., Chen, B. et al. Microbial degradation of endosulfan in contaminated soil with the elution of surfactants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 13268–13275 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6523-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6523-6