Abstract
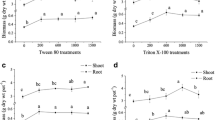
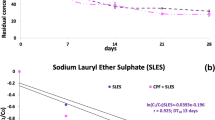
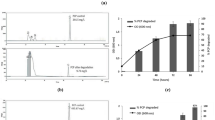
Endosulfan, a chlorinated cyclodiene insecticide is of environmental concern because of its apparent persistence and toxicity to many non target organisms. Endosulfan is hydrophobic and persists in soil for more than a year. To overcome the problem of hydrophobic and limited availability, surfactants play a major role in soil remediation. In the present study, the effect of Tween 80 added to the soil on the degradation of endosulfan by Pseudomonas aeruginosa at different pH (7.0 and 8.5) was studied. The addition of synthetic surfactant Tween 80 enhanced the solubility and degradation of endosulfan. A significant degradation (94%) was observed in pH 8.5 and Tween 80 added soil; the bacterial population in the treatment unit T8 was 75 × 109 CFU/g of soil. The unit T4 inoculated at pH 8.5 showed 86 % alpha and 60 % beta endosulfan degradation, the bacterial population was 73 × 108 CFU / g of soil. The degradation of both the isomers were observed and accompanied with formation of endodiol and endosulfan sulfate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angela link. (2000). Effect of non ionic surfactants on dissolution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from coal tar. Practice periodical of hazardous, Toxic Radio. Wast. Manag., 4, 78–81.
Aronstein, B.N., Alexander, M., (1993). Effect of non ionic surfactant added to the soil surface on the biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons within the soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 39, 386–390.
Atlas, R.M., Cerniglia, C.E., (1995). Bioremediation of petroleum pollutants. Bioscience, 45, 332–338.
Awasthi, N., Ahuja, R., Kumar, A., (2000). Factors influencing the degradation of soil applied endosulfan isomers. Soil Biol. Biochem., 32, 1697–1705.
Awasthi, N., Singh, A.K., Jain, R.K., Khangorat, B.S., Kumar, A., (2002). Degradation and detoxification of endosulfan isomers by a defined co-culture of two Bacillus strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 62, 279–283.
Ajay S., Jonathan, D., Van Hamme, Ward, O.P., (2006). Surfactants in Microbiology and biotechnology, part-2. Application aspects. Biotechnol. Adv., 21(1), 7–23.
Baar, D.P., Aust, S.A., (1987). Mineralization of recalcitrant environmental pollutants by white rot fungus. In: proceedings of the National conference on Hazardous materials. 146–151.
Bury, S.J., Miller, C.A, (1993). Effect of micellar solubilization on biodegradation rates of hydrocarbons. Environ. Sci. Technol. 27, 104–110.
Haigh, S.D., Alcock, R., (1996). A review of the interaction of surfactants with organic contaminants in sewage sludge. Lancaster University, U.K. 185, 161–170.
Hussain, S., Arsad, M., Saleem, M., Kalid, A., (2007). Biodegradation of alpha and beta endosulfan by soil bacteria. 1(25), 120–138.
Kovacs, M.F., (1965). Thin layer chromatography for pesticide residue analysis. J.Assoc. Agric. Chem., 48, 1018–1022.
Kullmann, S.W., Matsumura, F., (1996). Metabolic pathway utilized Phanerochaete Chrysosporium for degradation of the cyclodine pesticide endosulfan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 593–600.
Kumar, K., Devi, S.S., Krishnamurthy, K., Kanade, G.S., Chakrabarti, T., (2007). Enrichment isolation of endosulfan degrading and detoxifying bacteria. Chemosphere, 2, 89–96.
Kumar, M., Philip, L. (2006). Bioremediation of endosulfan contaminated soil and water optimization of operating conditions in laboratory scale reactors. J. Hazard. Mater., 21(2), 354–364.
Kumar, M., Philip, L., (2006). Enrichment and isolation of mixed bacterial culture for complete mineralization of endosulfan. J. Environ. Sci. Health B., 41(1), 81–96.
Kwon, G.S., Kim, J.E., Kim, T.K., Sohn, H.Y., Koh, S.C., Shin, K.S., D.G., (2002). Klebsiella pneumoniae KE-1 degrades endosulfan without formation of the toxic metabolite endosulfan sulfate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett, 215, 255–289.
Martens, R., (1976). Degradation of (8-9 14C) endosulfan by soil microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 31, 853–858.
Miller, R.M., Zhang, Y., (1997). Measurement of biosurfactant enhanced solubilization and biodegradation of hydrocarbons. Methods in Biotechnology, Bioremediation protocols, Sheeman human press, Totowa NJ. 2, 59–66.
Sethunathan, N., Megharaj, M., Chen, Z., Singh, N., Kookana, R.S., Naidu, R., (2002). Persistence of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate in soil as affected by moisture regime and organic matter addition. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 68, 725–731.
Shalini, S., Durga, P., Kumar, S., (2000). Biodegradation of alpha and beat isomers of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate in Indian soils. J. Environ. Sci. Health B., 35(3), 337–46.
Shivaramaiah, H.M., Kennedy, LR., (2006). Biodegradation of endosulfan by a soil bacterium. J. Environ. Sci. Health B., 41(6), 895–905.
Singer, M.E., Finnerty, W.R., (1984). Microbial metabolism of straight chain and branched alkanes. In R.M. Atlas (Ed) Petroleum microbiology, Macmillan pub. New York. 59.
Sutherland, T.D., Weir, K.M., Lacey, M.J., Horne, I., Russel, R.J., (2002). Gene cloning and molecular characterization of a two enzyme system catalyzing the oxidative detoxification of β-endosulfan. J. Appl. Microbiol., 92, 541–548.
Trivedy, R.K., Goel, P.K., (1986). Chemical and biological methods for water pollution studies. Environmental Publications. Karad.
Volkering, F., Breure, A.M., Anderi J.G., Rulkens, W.H., Andel, J.G., (1995). Influence of nonionic surfactants on bioavailability and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61, 1699–1705.
Wong, J.W.C., Fang, M., Zhao, Z., Xing, B., (2004). Effect of surfactants on solubilization and degradation of phenanthrene under thermophilic conditions. J. Environ. Qual., 33, 2015–2025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayashree, R., Vasudevan, N. Effect of tween 80 added to the soil on the degradation of endosulfan by Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 4, 203–210 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326275
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326275