Abstract
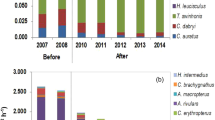
The Yangtze finless porpoise is a subspecies of narrow-ridged finless porpoise endemic to the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and the adjoining Poyang and Dongting Lakes. With the depletion of fish stocks in the Yangtze River in recent decades, food availability has become the most important factor affecting the survival of this subspecies. Despite this, the relationships between fish community and occurrences of porpoise are far from being fully understood. Therefore, during September 2013 to August 2014, the occurrences of porpoise were investigated in confluence of the Yangtze and Wanhe Rivers; fish community was also surveyed synchronously in confluence and two adjacent transects. The results showed that (1) the confluence had maximum fish species richness, and the main dominant species was upper fish, while the other two transects were mainly dominated by demersal fish. ANOVA analyses showed that individual number and yield of upper fish which can be eaten by porpoise (upper edible fish) in the confluence were significantly higher than other two transects. (2) Average group size of the porpoise was 3.7 ± 1.8 individuals. The occurrences of porpoise in different seasons had great differences, and the porpoise was more likely to be detected in autumn and winter. (3) Fish community had significant effects on occurrences of porpoise, and the main influencing factors were fish species richness, individual number, and yield of edible fish, especially the upper edible fish. The results of this study will have important implications for the conservation of porpoise.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appenzeller AR, Leggett WC (1992) Bias in hydroacoustic estimates of fish abundance due to acoustic shadowing: evidence from day-night surveys of vertically migrating fish. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49:2179–2189
Barnard CJ (2004) Animal behaviour: mechanism, development, function and evolution. Pearson Education Limited, Essex
Deng CY, Zhu R, Yan YZ (2013) Spatial and temporal patterns of fish diversity and assemblage structures in the Wuhu section of the Yangtze River. Freshw Fish 43:28–36 (in Chinese)
Fischer J, Paukert C, Daniels M (2012) Fish community response to habitat alteration: impacts of sand dredging in the Kansan River. T Am Fish Soc 141:1532–1544
Fu CZ, Wu JH, Chen JK, Wu QH, Lei GC (2003) Freshwater fish biodiversity in the Yangtze River basin of China: patterns, threats and conservation. Biodivers Conserv 12:1649–1685
Hastie GD, Wilson B, Wilson LJ, Parsons KM, Thompson PM (2004) Functional mechanisms underlying cetacean distribution patterns: hotspots for bottlenose dolphins are linked to foraging. Mar Biol 144:397–403
Hu J, Yao W (1996) Fishes in Yangtze River of Anhui region. J Anhui Univ 20:96–101 (in Chinese)
Jiao XS, Wu H (2012) Statistical analysis of the main hydrological parameters in the Wanhe basin. Jianghuai Water Resourc Sci Technol 4:34–36 (in Chinese)
Kimura S, Akamatsu T, Li S, Dong L, Wang K, Wang D, Arai N (2012) Seasonal changes in the local distribution of Yangtze finless porpoises related to fish presence. Mar Mammal Sci 28:308–324
Koopman HN (1998) Topographical distribution of the blubber of harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). J Mammal 79:260–270
Li J, Li X, Jia X, Li Y, He M, Tan X, Wang C, Jiang W (2010) Evolvement and diversity of fish community in Xijiang River. J Fish Sci China 17:298–311 (in Chinese)
Mei Z, Huang SL, Hao Y, Turvey ST, Gong W, Wang D (2012) Accelerating population decline of Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis). Biol Conserv 153:192–200
Mei Z, Zhang X, Huang SL, Zhao X, Hao Y, Zhang L, Qian Z, Zheng J, Wang K, Wang D (2014) The Yangtze finless porpoise: on an accelerating path to extinction? Biol Conserv 172:117–123
Partridge L (1978) Habitat selection. In: Krebs JR, Davies NB (eds) Behavioural ecology: an evolutionary approach. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 351–376
Paukert C, Schloesser J, Fischer J, Eitzmann J, Pitts K, Thornbrugh D (2008) Effect of instream sand dredging on fish communities in the Kansas River USA: current and historical perspectives. J Freshw Ecol 23:623–633
Richard S (2010) Last stand on the Yangtze. Science 329:378
Ru HJ, Liu XQ (2013) River-lake migration of fishes in the Dongting Lake area of the Yangtze floodplain. J Appl Ichthyol 29:594–601
Ru H, Liu X, Huang X, Ning Y, Wang H (2008) Diversity of fish species and its spatio-temporal variations in Lake Dongting, a large Yangtze-connected lake. J Lake Sci 20:93–99 (in Chinese)
Ru H, Wang H, Zhao W, Shen Y, Wang Y, Zhang X (2010) Fishes in the mainstream of the Yellow River: assemblage characteristics and historical changes. Biodivers Sci 18:179–186 (in Chinese)
Tang J, Ye S, Li W, Liu J, Zhang T, Guo Z, Zhu F, Li Z (2013) Status and historical changes in the fish community in Erhai Lake. Chin J Oceanol Limn 31:712–723
Turvey S, Pitman R, Taylor B, Barlow J, Akamatsu T, Barrett L, Zhao X, Reeves R, Stewart B, Wang K, Wei Z, Zhang X, Pusser L, Richlen M, Brandon J, Wang D (2007) First human-caused extinction of a cetacean species? Biol Lett 3:537–540
Turvey ST, Risley CL, Barrett LA, Hao Y, Wang D (2012) River dolphins can act as population trend indicators in degraded freshwater systems. PLoS ONE 7:e37902
Wang D (2009) Population status, threats and conservation of the Yangtze finless porpoise. Chin Sci Bull 54:3473–3484
Wang D (2010) The last fifteen years to rescue the finless porpoise. Man Biosph 5:65 (in Chinese)
Wang Z, Akamatsu T, Mei Z, Dong L, Imaizumi T, Wang K, Wang D (2014a) Frequent and prolonged nocturnal occupation of port areas by Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis): forced choice for feeding? Integr Zool. doi:10.1111/1749-4877.12102
Wang Z, Akamatsu T, Wang K, Wang D (2014b) The diel rhythms of biosonar behavior in the Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis) in the port of the Yangtze River: the correlation between prey availability and boat traffic. PLoS ONE 9:e97907
Wei Z, Wang D, Kuang X, Wang K, Wang X, Xiao J, Zhao Q, Zhang X (2002) Observations on behavior and ecology of the Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis) group at Tian-E-Zhou Oxbow of the Yangtze River. Raffles B Zool 10:97–103
Wei Z, Zhang XF, Wang KX, Zhao QZ, Kuang XA, Wang XQ, Wang D (2003) Habitat use and preliminary evaluation of the habitat status of the Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis) in the Balijiang section of the Yangtze River, China. Acta Zool Sin 49:163–170 (in Chinese)
Ye S, Li Z, Lek-Ang S, Feng G, Lek S, Cao W (2006) Community structure of small fishes in a shallow macrophytic lake (Niushan Lake) along the middle reach of the Yangtze River, China. Aquat Living Resour 19:349–359
Yu Y, Zhang Q, Chen W, Xu Y (1986) A preliminary study on dominant fish species and their interspecific relations in waters of islands off the northern Zhejiang. J Fish China 10:l37–l49 (in Chinese)
Yu D, Dong M, Wang J, Zhang X (2001) Population status of Yangtze finless porpoise in the Yangtze River section from Hukou to Nanjing. Acta Theriol Sin 32:330–334 (in Chinese)
Yu D, Wang J, Yang G, Zhang X (2005) Primary analysis on habitat selection of Yangtze finless porpoise in spring in the section between Hukou and Digang. Acta Theriol Sin 25:302–306 (in Chinese)
Yu D, Huang M, Zhao K, Chen S (2012) Impact of river training on the population abundance of Yangtze finless porpoise in Dongliu section of the Yangtze River. Acta Theriol Sin 21:174–179 (in Chinese)
Zhang X, Liu R, Zhao Q, Zhang G, Wei Z, Wang X, Yang J (1993) The population of finless porpoise in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Acta Theriol Sin 13:260–270 (in Chinese)
Zhang M, Xu D, Liu K, Shi W (2006) Ichthyologic survey and primary studies on diversity of fishery species in Anqing section of the Yangtze River. J Lake Sci 18:670–676 (in Chinese)
Zhao X, Barlow J, Taylor BL, Pitman RL, Wang K, Wei Z, Stewart BS, Turvey ST, Akamatsu T, Reeves RR, Wang D (2008) Abundance and conservation status of the Yangtze finless porpoise in the Yangtze River, China. Biol Conserv 141:3006–3018
Zhao X, Wang D, Turvey S, Taylor B, Akamatsu T (2013) Distribution patterns of Yangtze finless porpoises in the Yangtze River: implications for reserve management. Anim Conserv 16:509–518
Acknowledgments
We thank Jingguo Wang and Jialei Li for their helps in fieldwork. This work was supported by the Ocean Park Conservation Foundation of Hong Kong (AW05_1341) and the Doctoral Research Foundation of Anqing Normal University, China (K05000130032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yu, D., Wang, H. et al. Effects of fish community on occurrences of Yangtze finless porpoise in confluence of the Yangtze and Wanhe Rivers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 9524–9533 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4102-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4102-x