Abstract
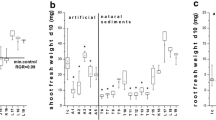
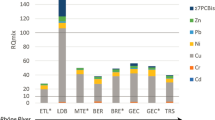
The purpose of the present study was to assess the hazard potentials of contaminated suspended particulate matter (SPM) sampled during a flood event for floodplain soils using in vitro bioassays and chemical analysis. Sediment-contact tests were performed to evaluate the direct exposure of organisms to native soils and SPM at two different trophic levels. For comparison, acetonic extracts were tested using both contact tests and additionally two cell-based biotests for cytotoxicity and Ah receptor-mediated activity (EROD-Assay). The sediment-contact tests were carried out with the dehydrogenase assay with Arthrobacter globiformis and the fish embryo assay with Danio rerio. The results of this study clearly document that native samples may well be significantly more effective than corresponding extracts in the bacteria contact assay or the fish embryo test. These results question the commonly accepted concept that acetonic extracts are likely to overestimate the toxicity of soil and SPM samples. Likewise, the priority organic compounds analyzed failed to fully explain the toxic potential of the samples. The outcomes of this study revealed the insufficient knowledge regarding the relationship between the different exposure pathways. Finally, there is concern about adverse effects by settling suspended particulate matter and remobilized sediments in frequently inundated floodplain soils due to an increase of the hazard potential, if compared with infrequently inundated floodplain soils. We showed that the settling of SPM and sediments revealed a significant impact on the dioxin-like potencies of riparian soils.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babich H, Borenfreund E (1992) Neutral red assay for toxicology in vitro. In: Watson RR (ed) In vitro methods of toxicology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 238–251
Baborowski E, Büttner O, Morgenstern P, Krüger F, Lobe I, Rupp H, von Tümpling W (2007) Spatial and temporal variability of sediment deposition on artificial-lawn traps in a floodplain of the River Elbe. Environ Pollut 148:770–778
Ballschmiter K, Zell M (1980) Analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) by glass capillary gas chromatography. Fresenius J Anal Chem 302:20–31
Behrens A, Schirmer K, Bols NC, Segner H (1998) Microassay for rapid measurement of 7-ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity in intact fish hepatocytes. Mar Environ Res 46:369–373
Boettcher G, Klose H (2003) Sedimentationsproblem Iffezheim. In: Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde (Hrsg.), Schwebstoffe und Schwebstofftransport in Binnenwasserstraßen. BfG-Veranstaltungen 03/2003. Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde, Koblenz, pp. 79–87
Bols NC, Schirmer K, Joyce EM, Dixon DG, Greenberg BM, Whyte JJ (1999) Ability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to induce 7-ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity in a trout liver cell line. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 44:118–128
Brack W (2003) Effect-directed analysis: a promising tool for the identification of organic toxicants in complex mixtures? Anal Bioanal Chem 377:397–407
Brack W, Schmitt-Jansen M, Machala M, Brix R, Barcelo D, Schymanski E, Streck G, Schulze T (2008) How to confirm identified toxicants in effect-directed analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:1959–1973
Brack W, Apitz SE, Borchardt D, Brils J, Cardoso AC, Foekema EM, van Gils J, Jansen S, Harris B, Hein M, Heise S, Hellsten S, de Maagd PG-J, Müller D, Panov VE, Posthuma L, Quevauviller P, Verdonschot PFM, von der Ohe PC (2009) Toward a holistic and risk-based management of European river basins. Integr Environ Assess Manag 5:5–10
Brack W, Dulio V, Slobodnik J (2012) The NORMAN Network and its activities on emerging environmental substances with a focus on effect-directed analysis of complex environmental contamination. Environ Sci Eur 24:1–5
Brack W, Govender S, Schulze T, Krauss M, Hu M, Muz M, Hollender J, Schirmer K, Schollee J, Hidasi A, Slobodnik J, Rabova Z, Ait-Aissa S, Sonavane M, Carere M, Lamoree M, Leonards P, Tufi S, Ouyang X, Schriks M, Thomas K, De Almeida AC, Froment J, Hammers-Wirtz M, Ahel M, Koprivica S, Hollert H, Seiler TB, Di Paolo C, Tindall A, Spirhanzlova P (2013) EDA-EMERGE: an FP7 initial training network to equip the next generation of young scientists with the skills to address the complexity of environmental contamination with emerging pollutants. Environ Sci Eur 25:1–7
Braunbeck T, Böttcher M, Hollert H, Kosmehl T, Lammer E, Leist E, Rudolf M, Seitz N (2005) Towards an alternative for the acute fish LC50 test in chemical assessment: the fish embryo toxicity test goes multi-species—an update. ALTEX 22:87–102
Bundt J, Herbel W, Steinhart H, Franke S, Francke W (1991) Structure-type separation of diesel fuels by solid phase extraction and identification of the two- and three-ring aromatics by capillary GC-mass spectrometry. J High Resolut Chromatogr 14:91–98
Busche U, Hirner AV (1997) Mobilisierbarkeit von hydrophoben organischen Schadstoffen in Belasteten Böden und Abfällen. Teil II: Mobilsierbarkeit von PAK, PCB und Phenolen durch reale Wässer. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 25:248–252
Clemons JH, Dixon DG, Bols NC (1997) Derivation of 2,3,7,8-TCDD toxic equivalent factors (TEFs) for selected dioxins, furans and PCB with rainbow trout and rat liver cell lines and the influence of exposure time. Chemosphere 34:1105–1119
de Jonge J, Brils JM, Hendriks AJ, Ma WC (1999) Ecological and ecotoxicological surveys of moderately contaminated floodplain ecosystems in The Netherlands. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 2:9–18
Delpla I, Jung AV, Baures E, Clement M, Thomas O (2009) Impacts of climate change on surface water quality in relation to drinking water production. Environ Int 35:1225–1233
DIN 38412–48 (1998) Entwurf Deutsche Einheitsverfahren zur Wasser-, Abwasser- und Schlammuntersuchung-Testverfahren mit Wasserorganismen (Gruppe L)-Teil 48: Arthrobacter globiformis-Kontakttest für kontaminierte Feststoffe (L 48)
DIN 38414–24 (2000–10) German standard methods for the examination of water, waste water and sludge—Sludge and sediments (group S)—part 24: determination of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDD) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) (S 24)
DIN 38415–6 (2001) Draft German standard methods for the examination of water, waste water and sludge—subanimal testing (group T)—part 6: toxicity to fish; determination of the non-acute-poisonous effect of waste water to fish eggs by dilution limits (T 6)
Eichbaum K, Brinkmann M, Buchinger S, Hecker M, Engwall M, van Bavel B, Reifferscheid G, Hollert H (2013) The dioRAMA project: assessment of dioxin-like activity in sediments and fish (Rutilus rutilus) in support of the ecotoxicological characterization of sediments. J Soils Sediments 13:770–774
Ensenbach U (1998) Embryonic development of fish—a model to assess the toxicity of sediments to vertebrates. Fresenius Environ Bull 7:531–538
Fiedler H, Lau C, Kjeller LO, Rappe C (1996) Patterns and sources of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans found in soil and sediment samples in Southern Mississippi. Chemosphere 32:421–432
Förstner U (2004) Traceability of sediment analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 23:217–236
Franke S, Schwarzbauer J, Francke W (1998) Arylesters of alkylsulfonic acids in sediments. Part III of organic compounds as contaminants of the Elbe River and its tributaries. Fresenius J Anal Chem 360:580–588
Garke V (2003) Optimierung und anpassung eine in vitro bioassays mit RTL-W1- und RTG-2-Zellen zum Nachweis der cytotoxischen und Dioxin-ähnlichen Wirkung von komplexen Umweltproben. Staatsexamensarbeit, Ruprechts-Karls-Universität, Heidelberg, 62 pp
Gocht T, Moldenhauer K-M, Püttmann W (2001) Historical record of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and heavy metals in floodplain sediments from the Rhine River (Hessisches Ried, Germany). Appl Geochem 16:1707–1721
Grote M, Brack W, Walter HA, Altenburger R (2005) Confirmation of cause–effect relationships using effect-directed analysis for complex environmental samples. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1420–1427
Gustavsson L, Hollert H, Joensson S, van Bavel B, Engwall M (2007) Reed beds receiving industrial sludge containing nitroaromatic compounds—effects of outgoing water and bed material extracts in the umu-C genotoxicity assay, DR-CALUX assay and on early life stage development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Pollut Res 14:202–211
Hallare AV, Kosmehl T, Schulze T, Hollert H, Kohler H-R, Triebskorn R (2005) Assessing contamination levels of Laguna Lake sediments (Philippines) using a contact assay with zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Sci Total Environ 347:254–271
Hamers T, van den Berg JHJ, van Gestel CAM, van Schooten F-J, Murk AJ (2006) Risk assessment of metals and organic pollutants for herbivorous and carnivorous small mammal food chains in a polluted floodplain (Biesbosch, The Netherlands). Environ Pollut 144:581–595
Hecker M, Hollert H (2009) Effect-directed analysis (EDA) in aquatic ecotoxicology: state of the art and future challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:607–613
Heger S, Bluhm K, Agler MT, Maletz S, Schäffer A, Seiler TB, Angenent LT, Hollert H (2012) Biotests for hazard assessment of biofuel fermentation. Energy Eviron Sci 5:9778–9788
Heim S, Ricking M, Schwarzbauer J, Littke R (2005) Halogenated compounds in a dated sediment core of the Teltow Canal, Berlin: time related sediment contamination. Chemosphere 61:1427–1438
Heimann W, Sylvester M, Seiler T-B, Hollert H, Schulz R (2011) Sediment toxicity in a connected oxbow lake of the Upper Rhine (Germany): EROD induction in fish cells. J Soils Sediments 11:1279–1291
Heinisch E, Kettrup A, Bergheim W, Wenzel S (2006) Persistent chlorinated hydrocarbons (PCHC), source-oriented monitoring in aquatic media 5. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Fresenius Environ Bull 15:1344–1362
Heise S (2009) Sediments in river basins. J Soils Sediments 9:393–399
Hembrock-Heeger A (2011) Dioxine und PCB in Böden, Pflanzen, Futter- und Lebensmitteln in Überschwemmungsgebieten in NRW. Fachgespräch. Belastung der terrestrischen Umwelt mit Dioxinen und PCB des Umweltbundesamtes am 13./14.Oktober 2011 in Berlin
Hilscherova K, Kannan K, Kang Y-S, Holoubek I, Machala M, Masunaga S, Nakanishi J, Giesy JP (2001) Characterization of dioxin-like activity of sediments from a Czech river basin. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2768–2777
Hilscherova K, Kannan K, Nakata H, Hanari N, Yamashita N, Bradley PW, McCabe JM, Taylor AB, Giesy JP (2003) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran concentration profiles in sediments and flood-plain soils of the Tittabawassee River. Mich Environ Sci Technol 37:468–474
Hobbelen PHF, Koolhaas JE, van Gestel CAM (2004) Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution for detritivores in floodplain soils in the Biesbosch, The Netherlands, taking bioavailability into account. Environ Pollut 129:409–419
Hollert H, Dürr M, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T (2000) Cytotoxicity of settling particulate matter (SPM) and sediments of the Neckar River (Germany) during a winter flood. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:528–534
Hollert H, Dürr M, Olsman H, Halldin K, Van Bavel B, Brack W, Tysklind M, Engwall M, Braunbeck T (2002a) Biological and chemical determination of dioxin-like compounds in sediments by means of a sediment triad approach in the catchment area of the River Neckar. Ecotoxicology 11:323–336
Hollert H, Heise S, Pudenz S, Brüggemann R, Ahlf W, Braunbeck T (2002b) Application of a sediment quality triad and different statistical approaches (Hasse diagrams and fuzzy logic) for the comparative evaluation of small streams. Ecotoxicology 11:311–321
Hollert H, Haag I, Dürr M, Wetterauer B, Holtey-Weber R, Kern U, Westrich B, Färber H, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T (2003a) Untersuchungen zum ökotoxikologischen Schädigungspotenzial und Erosionsrisiko von kontaminierten Sedimenten in staugeregelten Flüssen. Umweltwiss Schadstoff Forsch 15:5–12
Hollert H, Keiter S, König N, Rudolf M, Ulrich M, Braunbeck T (2003b) A new sediment contact assay to assess particle-bound pollutants using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Soils Sediments 3:197–207
Hollert H, Heise S, Keiter S, Heininger P, Förstner U (2007) Wasserrahmenrichtlinie-Fortschritte und Defizite. Umweltwiss Schadstoff Forsch 19:58–70
Höss S, Ahlf W, Fahnenstich C, Gilberg D, Hollert H, Melbye K, Meller M, Hammers-Wirtz M, Heininger P, Neumann-Hensel H, Ottermanns R, Ratte HT, Seiler TB, Spira D, Weber J, Feiler U (2010) Variability of sediment-contact tests in freshwater sediments with low-level anthropogenic contamination—determination of toxicity thresholds. Environ Pollut 158:2999–3010
IKSR (2011) Rheinstoffliste 2011. IKSR-Bericht, 189d. Internationale Kommission zum Schutze des Rheines, Koblenz, 13 pp
ISO 7346–3 (1996) Water quality—part 3: flow-through method—determination of the acute lethal toxicity of substances to a freshwater fish [Rachydanio rerio Hamilton-Buchanan (Teleostei, Cyprinidae)]
Japenga J, Zschuppe KH, De Groot AJ, Salomons W (1990) Heavy metals and organic micropollutants in floodplains of the River Waal, a distributary of the River Rhine, 1958–1981. Neth J Agric Sci 38:381–397
Kammann U, Biselli S, Reineke N, Wosniok W, Danischewski D, Hühnerfuss H, Kinder A, Sierts-Herrmann A, Theobald N, Vahl H-H, Vobach M, Westendorf J, Steinhart H (2005) Bioassay-directed fractionation of organic extracts of marine surface sediments from the North and Baltic Sea—part II: results of the biotest battery and development of a biotest index. J Soils Sediments 5:225–232
Kamphues J, Schulz AJ, Gude K, Bruns-Weller E, Severin K, Appuhn H, Taube V (2011) Investigations concerning the use of dioxin exposed grassland along rivers by food producing ruminants with special regard to food safety. Organohalogen Compd 73:2040–2041
Kedziorek MAM, Dupuy A, Bourg ACM, Compère F (1998) Leaching of Cd and Pb from a polluted soil during the percolation of EDTA: laboratory column experiments modeled with a non-equilibrium solubilization step. Environ Sci Technol 32:1609–1614
Keiter S, Rastall A, Kosmehl T, Wurm K, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of sediment, suspended matter and water samples in the upper Danube River—a pilot study in search for the causes for the decline of fish catches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:308–319
Keiter S, Braunbeck T, Heise S, Pudenz S, Manz W, Hollert H (2009) A fuzzy logic-classification of sediments based on data from in vitro biotests. J Soils Sediments 9:168–179
Kennedy SW, Jones SP (1994) Simultaneous measurement of cytochrome P4501A catalytic activity and total protein concentration with a fluorescence plate reader. Anal Biochem 222:217–223
Klee N, Gustavsson L, Kosmehl T, Engwall M, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2004) Changes in toxicity and genotoxicity of industrial sewage sludge samples containing nitro- and amino-aromatic compounds following treatment in bioreactors with different oxygen regimes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 11:313–320
Klok C, Kraak MH (2008) Living in highly dynamic polluted river floodplains, do contaminants contribute to population and community effects? Sci Total Environ 406:455–461
Kühlers D, Bethge E, Hillebrand G, Hollert H, Fleig M, Lehmann B, Maier D, Maier M, Mohrlok U, Wölz J (2009) Contaminant transport to public water supply wells via flood water retention areas. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 9:1047–1058
Lake IR, Foxall CD, Fernandes A, Lewis M, White O, Mortimer D, Dowding A, Rose M (2014) The effects of river flooding on dioxin and PCBs in beef. Sci Total Environ 491–492:184–191
Lee LE, Clemons JH, Bechtel DG, Caldwell SJ, Han KB, Pasitschniak-Arts M, Mosser DD, Bols NC (1993) Development and characterization of a rainbow trout liver cell line expressing cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase activity. Cell Biol Toxicol 9:279–294
Lerche D, Brüggemann R, Sørensen P, Carlsen L, Nielsen OJ (2002) Comparison of partial order technique with three methods of multi-criteria. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 42:1086–1098
Liß W, Ahlf W (1997) Evidence from whole-sediment, porewater, and elutriate testing in toxicity assessment of contaminated sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 36:140–147
LUBW (2011) Hochwasservorhersagezentrale Baden-Württemberg, http://www.hvz.badenwuerttemberg.de/ (accessed: 02.06.2011)
Maier D, Maier M, Fleig M (1997) Belastung von Grundwasseranreicherungsflächen mit Schadstoffen durch Schwebstoffeintrag, 2. Deutsch-Niederländischer Workshop Künstliche Grundwasseranreicherung, Schwerte, DVGW-Schriftenreihe Wasser Nr. 90, pp. 17–24
Maier M, Kühlers D, Brauch H-J, Fleig M, Jirka GH, Mohrlok U, Bethge E, Bernhart HH, Lehman B, Hillebrand G, Wölz J, Hollert H (2006) Flood retention and drinking water supply—preventing conflicts of interest. J Soils Sediments 6:113–114
Malmon DV, Dunne T, Reneau SL (2002) Predicting the fate of sediment and pollutants in river floodplains. Environ Sci Technol 36:2026–2032
Martin CW (1997) Heavy metal concentrations in floodplain surface soils, Lahn River. Germany Environ Geol 30:119–125
Martin C (2009) Recent changes in heavy metal storage in flood-plain soils of the Lahn River, central Germany. Environ Geol 58:803–814
Middelkoop H (2000) Heavy-metal pollution of the river Rhine and Meuse floodplains in The Netherlands. Geol Mijnb 79:411–428
Middelkoop H, Erkens G, van der Perk M (2010) The Rhine delta—a record of sediment trapping over time scales from millennia to decades. J Soils Sediments 10:628–639
Oetken M, Stachel B, Pfenninger M, Oehlmann J (2005) Impact of a flood disaster on sediment toxicity in a major river system—the Elbe flood 2002 as a case study. Environ Pollut 134:87–95
Pies C, Yang Y, Hofmann T (2007) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in floodplain soils of the Mosel and Saar River. J Soils Sediments 7:216–222
Power EA, Chapman PM (1992) Assessing sediment quality. In: Burton GA (ed) Sediment toxicity assessment. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 1–18
Prantner J, Korherr U, Weber R (2005) A groundwater treatment plant for remediation of DDT, halogenated organics, arsenic and mercury at the Lago Maggiore (North Italy). Proceedings of the 8th HCH and Pesticide Conference, Sofia
Rader BR, Nimmo DWR, Chapman PL (1997) Phytotoxicity of floodplain soils contaminated with trace metals along the Clark Fork River, Grant-Kohrs Ranch national historic site, Deer Lodge, Montana. USA Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1422–1432
Rice PM, Ray GJ (1985) Heavy metals in flood plain deposits along the upper Clark Fork River. Proceedings-Clark Fork Symposium, Montana Academy of Sciences, Montana College of Mineral Science and Technology, Butte
Ricking M, Terytze K (1999) Trace metals and organic compounds in sediment samples from the River Danube in Russe and Lake Srebarna (Bulgaria). Environ Geol 37:40–46
Rönnpagel K, Liß W, Ahlf W (1995) Microbial bioassays to assess the toxicity of solid-associated contaminants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 31:99–103
Sauvé S, Hendershot W, Allen HE (2000) Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 34:1125–1130
Schulz A-J, Wiesmüller T, Appuhn H, Stehr D, Severin K, Landmann D, Kamphues J (2005) Dioxin concentration in milk and tissues of cows and sheep related to feed and soil contamination. Anim Phys Anim Nutr 89:72–78
Schulze T, Ricking M, Schröter-Kermani C, Körner A, Denner H-D, Weinfurtner K, Winkler A, Pekdeger A (2007) The German Environmental Specimen Bank—sampling, processing, and archiving sediment and suspended particulate matter. J Soils Sediments 7:361–367
Schulze T, Seiler T-B, Streck G, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2012) Comparison of different exhaustive and biomimetic extraction techniques for chemical and biological analysis of polycyclic aromatic compounds in river sediments. J Soils Sediments 12:1419–1434
Schüttrumpf H, Brinkmann M, Cofalla C, Frings RM, Gerbersdorf SU, Hecker M, Hudjetz S, Kammann U, Lennartz G, Roger S, Schaeffer A, Hollert H (2011) A new approach to investigate the interactions between sediment transport and ecotoxicological processes during flood events. Environ Sci Europe 23, 39-Article No.: 39
Schwartz R, Gerth J, Neumann-Hensel H, Bley S, Förstner U (2006) Assessment of high polluted fluvisol in the Spitelwasser floodplain. Based on national guideline value and MNA-criteria. J Soils Sediments 6:145–155
Schwarzbauer J (1997) Screening, identifizierung und quantitative analyse organischer substanzen in sediment und schwebstoff des elbesystems. Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, 282 pp
Stachel B, Jantzen E, Knoth W, Krüger F, Lepom P, Oetken M, Reincke H, Sawal G, Schwartz R, Uhlig S (2005) The Elbe flood in August 2002—organic contaminants in sediment samples taken after the flood event. J Environ Sci Health A Toxic Hazard Subst Environ Eng 40:265–287
Strecker R, Seiler T-B, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2011) Oxygen requirements of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos in embryo toxicity tests with environmental samples. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 153:318–327
Tockner K, Pusch M, Borchardt D, Lorang MS (2010) Multiple stressors in coupled river-floodplain ecosystems. Freshw Biol 55:135–151
Torres JPM, Leite C, Krauss T, Weber R (2013) Landfill mining from a deposit of the chlorine/organochlorine industry as source of dioxin contamination of animal feed and assessment of the responsible processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1958–1965
Tuikka AI, Schmitt C, Höss S, Bandow N, von der Ohe PC, de Zwart D, de Deckere E, Streck G, Mothes S, van Hattum B, Kocan A, Brix R, Brack W, Barceló D, Sormunen AJ, Kukkonen JVK (2011) Toxicity assessment of sediments from three European river basins using a sediment contact test battery. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:123–131
Ulrich M, Schulze T, Leist E, Glaß B, Maier M, Maier D, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2002) Abschätzung des Gefährdungspotenzials für Trinkwasser und Korrelation verschiedener Expositionspfade (Acetonischer Extrakt, Natives Sediment) im Bakterienkontakttest und Fischeitest. Umweltwiss Schadstoff Forsch 14:132–137
Umlauf G, Bidoglio G, Christoph EH, Kampheus J, Krüger F, Landmann D, Schulz AJ, Schwartz R, Severin K, Stachel B, Stehr D (2005) The situation of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs after the flooding of River Elbe and Mulde in 2002. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 33:543–554
van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93:223–241
van Gils J, van Hattum B, Westrich B (2009) Exposure modeling on a river basin scale in support of risk assessment for chemicals in European river basins. Integr Environ Assess Manag 5:80–85
Voigt K, Brüggemann R, Pudenz S (2006) A multi-criteria evaluation of environmental databases using the Hasse Diagram Technique (ProRank) software. Environ Model Softw 21:1587–1597
Weber R, Gaus C, Tysklind M, Johnston P, Forter M, Hollert H, Heinisch H, Holoubek I, Lloyd-Smith M, Masunaga S, Moccarelli P, Santillo D, Seike N, Symons R, Torres JPM, Verta M, Varbelow G, Vijgen J, Watson A, Costner P, Wölz J, Wycisk P, Zennegg M (2008a) Dioxin- and POP-contaminated sites—contemporary and future relevance and challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:363–393
Weber R, Tysklind M, Gaus C (2008b) Dioxin—contemporary and future challenges of historical legacies (editorial, dedicated to Otto Hutzinger). Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:96–100
Weber R, Watson A, Forter M, Oliaei F (2011) Persistent organic pollutants and landfills—a review of past experiences and future challenges. Waste Manag Res 29:107–121
Weber R, Hollert H, Ballschmiter KH, Kamphues J, Blepp M (2013) Relevanz von PCB Quellen für Rindfleisch: Boden–Futter–Punktquellen. Vortrag UBA Fachgespräch “Belastung von Rindfleisch mit PCB aus extensiver Haltung” 5. Februar 2013, BMU, Bonn
Wetterauer B, Ricking M, Otte JC, Hallare AV, Rastall A, Erdinger L, Schwarzbauer J, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2012) Toxicity, dioxin-like activities, and endocrine effects of DDT metabolites-DDA, DDMU, DDMS, and DDCN. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:403–415
Witter B, Francke W, Franke S, Knauth H-D, Miehlich G (1998) Distribution and mobility of organic micropollutants in River Elbe floodplains. Chemosphere 37:63–78
Wölz J, Engwall M, Maletz S, Olsman Takner H, van Bavel B, Kammann U, Klempt M, Weber R, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2008) Changes in toxicity and Ah receptor agonist activity of suspended particulate matter during flood events at the rivers Neckar and Rhine—a mass balance approach using in vitro methods and chemical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:536–553
Wölz J, Brack W, Möhlenkamp C, Claus E, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2010a) Effect-directed analysis of Ah receptor-mediated activities caused by PAHs in suspended particulate matter sampled in flood events. Sci Total Environ 408:3327–3333
Wölz J, Fleig M, Schulze T, Maletz S, Lübcke-von Varel U, Reifferscheid G, Kühlers D, Braunbeck T, Brack W, Hollert H (2010b) Impact of contaminants bound to suspended particulate matter in the context of flood events. J Soils Sediments 10:1174–1185
Wölz J, Grosshans K, Streck G, Schulze T, Rastall A, Erdinger L, Brack W, Fleig M, Kühlers D, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2011a) Estrogen receptor mediated activity in bankside groundwater, with flood suspended particulate matter and floodplain soil—an approach combining tracer substance, bioassay and target analysis. Chemosphere 85:717–723
Wölz J, Schulze T, Lübcke-von Varel U, Fleig M, Reifferscheid G, Brack W, Kühlers D, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2011b) Investigation on soil contamination at recently inundated and non-inundated sites. J Soils Sediments 11:82–92
Wu L, Chen L, Hou J, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Gao H (2010) Assessment of sediment quality of Yangtze River estuary using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Toxicol 25:234–242
Zennegg M, Schmid P, Tremp J (2010) PCB fish contamination in Swiss rivers—tracing of point sources. Organohalogen Compd 72:362–365
Acknowledgments
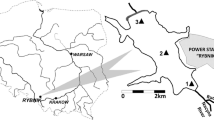
This study was supported by the Stadtwerke Karlsruhe (Germany) during the project «Ecotoxicological assessment of the Rhine sediments and suspended particulate matter in inundated areas». Volker Garke performed the cytotoxicity and EROD bioassays within his state examination thesis (Garke 2003) and friendly provided the raw data for publication. We are grateful to Mr. Beiser (Stadtwerke Karlsruhe) for technical support during the sampling as well as to Beate Kemink, L. Dunne, H. Johannsen, Dr. Anne Seebach, und Manuela Scholz for technical support of the laboratory analyses. Dr. Emma Schymanski (Eawag, Dübendorf, Switzerland) gave valuable comments to a previous version of the manuscript, which is part of the dissertation thesis of TS (urn:nbn:de:kobv:188-fudissthesis000000094124-8). Supplementary material is provided for download at the Springer website.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1788 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulze, T., Ulrich, M., Maier, D. et al. Evaluation of the hazard potentials of river suspended particulate matter and floodplain soils in the Rhine basin using chemical analysis and in vitro bioassays. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 14606–14620 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3707-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3707-9