Abstract
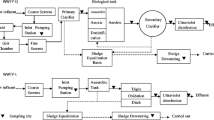
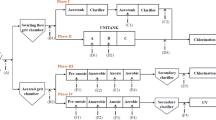
The variation of five antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs)—tetG, tetW, tetX, sul1, and intI1—in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant with A2O-MBR system was studied. The concentrations of five resistance genes both in influent and in membrane bioreactor (MBR) effluent decreased as sul1 > intI1 > tetX > tetG > tetW, and an abundance of sul1 was statistically higher than three other tetracycline resistance genes (tetG, tetW, and tetX) (p < 0.05). The concentrations of five ARGs in the influent were all higher in spring (median 105.81–107.32 copies mL−1) than they were in other seasons, and tetW, tetX, and sul1 reached its lowest concentration in autumn (104.61–106.81 copies mL−1). The concentration of ARGs in wastewater decreased in the anaerobic effluent and anoxic effluent, but increased in the aerobic effluent, and then sharply declined in the MBR effluent. The reduction of tetW, intI1, and sul1 was all significantly positively correlated with the reduction of 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) in the wastewater treatment process (p < 0.01). The concentration of ARGs (copies mg−1) in sludge samples increased along the treatment process, but the abundance of five ARGs (ratio of ARGs to 16S rDNA) remained the same from anaerobic to anoxic to aerobic basins, while an increment ratio in MBR was observed for all ARGs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarestrup FM, Agerso Y, Gerner–Smidt P, Madsen M, Jensen LB (2000) Comparison of antimicrobial resistance phenotypes and resistance genes in Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium from humans in the community, broilers, and pigs in Denmark. Diag Micr Infec Dis 37:127–137
Aminov RI, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Molecular ecology of tetracycline resistance: development and validation of primers for detection of tetracycline resistance genes encoding ribosomal protection proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:22–32
Auerbach EA, Seyfried EE, McMahon KD (2007) Tetracycline resistance genes in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 41:1143–1151
Baquero F, Martínez J-L, Cantón R (2008) Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:260–265
Börjesson S, Melin S, Matussek A, Lindgren PE (2009) A seasonal study of the mecA gene and Staphylococcus aureus including methicillin-resistant S. aureus in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 43:925–932
Börjesson S, Mattsson A, Lindgren P (2010) Genes encoding tetracycline resistance in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant investigated during 1 year. J Water Health 8:247–256
Breazeal MVR, Novak JT, Vikesland PJ, Pruden A (2013) Effect of wastewater colloids on membrane removal of antibiotic resistance genes. Water Res 47:130–140
Carabineiro SAC, Thavorn-Amornsri T, Pereira MFR, Figueiredo JL (2011) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin on surface-modified carbon materials. Water Res 45:4583–4591
Carabineiro SAC, Thavorn-amornsri T, Pereira MFR, Serp P, Figueiredo JL (2012) Comparison between activated carbon, carbon xerogel and carbon nanotubes for the adsorption of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Catal Today 186:29–34
Chen H, Zhang MM (2013) Effects of advanced treatment systems on the removal of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment plants from Hangzhou, China. Environ Sci Technol 47:8157–8163
Da Silva MF, Tiago I, Veríssimo A, Boaventura RA, Nunes OC, Manaia CM (2006) Antibiotic resistance of enterococci and related bacteria in an urban wastewater treatment plant. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55:322–329
Du J, Ren H, Geng J, Zhang Y, Xu K, Ding L (2014) Occurrence and abundance of tetracycline, sulfonamide resistance genes, and class 1 integron in five wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7276–7284
Environmental Protection Agency of China (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring methods, 4th edn. Chinese Environmental Science Publishing House, Beijing
Goossens H, Ferech M, Vander Stichele R, Elseviers M (2005) Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: a cross-national database study. Lancet 365:579–587
Heberer T (2002) Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: a review of recent research data. Toxicol Lett 131:5–17
Heuer H, Schmitt H, Smalla K (2011) Antibiotic resistance gene spread due to manure application on agricultural fields. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:236–243
Kay E, Vogel TM, Bertolla F, Nalin R, Simonet P (2002) In situ transfer of antibiotic resistance genes from transgenic (transplastomic) tobacco plants to bacteria. Appl Environ Microb 68:3345–3351
LaPara TM, Burch TR, McNamara PJ, Tan DT, Yan M, Eichmiller JJ (2011) Tertiary-treated municipal wastewater is a significant point source of antibiotic resistance genes into duluth-superior harbor. Environ Sci Technol 45:9543–9549
Ma LP, Zhang XX, Cheng SP, Zhang ZY, Shi P, Liu B, Wu B, Zhang Y (2011) Occurrence, abundance and elimination of class 1 integrons in one municipal sewage treatment plant. Ecotoxicology 20:968–973
Mokracka J, Koczura R, Kaznowski A (2012) Multiresistant enterobacteriaceae with class 1 and class 2 integrons in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 46:3353–3363
Monier J-M, Demanèche S, Delmont TO, Mathieu A, Vogel TM, Simonet P (2011) Metagenomic exploration of antibiotic resistance in soil. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:229–235
Munir M, Wong K, Xagoraraki I (2011) Release of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes in the effluent and biosolids of five wastewater utilities in Michigan. Water Res 45:681–693
Novo A, Andre S, Viana P, Nunes OC, Manaia CM (2013) Antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial residues and bacterial community composition in urban wastewater. Water Res 47:1875–188
Pei R, Cha J, Carlson KH, Pruden A (2007) Response of antibiotic resistance genes (ARG) to biological treatment in dairy lagoon water. Environ Sci Technol 41:5108–5113
Pruden A, Pei R, Storteboom H, Carlson KH (2006) Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: studies in northern Colorado. Environ Sci Technol 40:7445–7450
Schmitt H, Stoob K, Hamscher G, Smit E, Seinen W (2006) Tetracyclines and tetracycline resistance in agricultural soils: microcosm and field studies. Microb Ecol 51:267–276
Sui Q, Huang J, Deng S, Chen W, Yu G (2011) Seasonal variation in the occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in different biological wastewater treatment processes. Environ Sci Technol 45:3341–3348
Sun L, Klein EY, Laxminarayan R (2012) Seasonality and temporal correlation between community antibiotic use and resistance in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 55:687–694
Wilcks A, van Hoek AH, Joosten RG, Jacobsen BBL, Aarts HJM (2004) Persistence of DNA studied in different ex vivo and in vivo rat models simulating the human gut situation. Food Chem Toxicol 42:493–502
Yang Y, Zhang T, Zhang XX, Liang DW, Zhang M, Gao DW, Zhu HG, Huang QG, Fang HHP (2012) Quantification and characterization of beta-lactam resistance genes in 15 sewage treatment plants from East Asia and North America. Appl Microbiol Biot 95:1351–1358
Yang Y, Li B, Ju F, Zhang T (2013) Exploring variation of antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge over a 4 year period through a metagenomic approach. Environ Sci Technol 47:10197–10205
Yuan QB, Guo MT, Yang J (2014) Monitoring and assessing the impact of wastewater treatment on release of both antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their typical genes in a Chinese municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci: Processes Impacts 16:1930–1937
Zhang XX, Zhang T (2011) Occurrence, abundance, and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in 15 sewage treatment plants across China and other global locations. Environ Sci Technol 45:2598–2604
Zhang XX, Wu B, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Yang LY, Fang HHP, Ford T, Cheng SP (2009a) Class 1 integronase gene and tetracycline resistance genes tetA and tetC in different water environments of Jiangsu Province, China. Ecotoxicology 18:652–660
Zhang T, Zhang M, Zhang XX, Fang HHP (2009b) Tetracycline resistance genes and tetracycline resistant lactose-fermenting enterobacteriaceae in activated sludge of sewage treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 43:3455–3460
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 51278241) and the Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (No. BK2011016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, J., Geng, J., Ren, H. et al. Variation of antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater treatment plant with A2O-MBR system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 3715–3726 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3552-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3552-x