Abstract
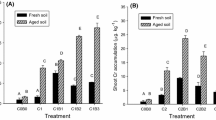
A greenhouse experiment was carried out to investigate the single effect of benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) or chromium (Cr) and the joint effect of Cr–B[a]P on the growth of Zea mays, its uptake and accumulation of Cr, and the dissipation of B[a]P over 60 days. Results showed that single or joint contamination of Cr and B[a]P did not affect the plant growth relative to control treatments. However, the occurrence of B[a]P had an enhancing effect on the accumulation and translocation of Cr. The accumulation of Cr in shoot of plant significantly increased by ≥ 79 % in 50 mg kg−1 Cr–B[a]P (1, 5, and 10 mg kg−1) treatments and by ≥ 86 % in 100 mg kg−1 Cr–B[a]P (1, 5, and 10 mg kg−1) treatments relative to control treatments. The presence of plants did not enhance the dissipation of B[a]P in lower (1and 5 mg kg−1) B[a]P contaminated soils; however, over 60 days of planting Z. mays seemed to enhance the dissipation of B[a]P by over 60 % in 10 mg kg−1 single contaminated soil and by 28 to 41 % in 10 mg kg−1B[a]P co-contaminated soil. This suggests that Z. mays might be a useful plant for the remediation of Cr–B[a]P co-contaminated soil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babu A, Kim J, Oh B (2013) Enhancement of heavy metal phytoremediation by Alnus firma with endophytic Bacillus thuringiensis GDB-1. J Hazard Mater 250–251:477–483
Bareen FE, Nazir A (2010) Metal decontamination of tannery solid waste using Tagetes patula in association with saprobic and mycorrhizal fungi. Environmentalist 30:45–53
Barnhart J (1997) Occurrence, uses and properties of chromium. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 26:s3–s7
Bonet A, Poschenrieder C, Barcelo J (1991) Chromium III-iron interaction in Fe-deficient and Fe-sufficient bean plants. I. Growth and nutrient content. J Plant Nutr 14:403–414
Chen YX, Lin Q, He YF, Tian GM (2004) Behaviour of Cu and Zn under combined pollution of 2, 4- dichlorophenol in the planted soil. Plant Soil 261:127–134
Gheju M, Balcu M, Gopec M (2009) Analysis of hexavalent chromium uptake by plants in polluted soils. Ovidus Univ Ann Chem 20(1):127–131
Han FX, Sridhar BBM, Monts DL, Su Y (2004) Phytoavailability and toxicity of trivalent and hexavalent chromium to Brassica juncea. New Phytol 162:189–199
Hossner L. R, Loeppert R. H, Newton R. J, Szaniszlo P. J and Attrep M (1998) Phytoaccumulation of chromium, uranium and plutonium in plant systems http://www.uraweb.org/reports/anrc9803.pdf. Accessed 21 Jan 2013
Jian Y, Yong L, Peter PF, Yu HT (2004) Photomutagenicity of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the US EPA priority pollutant list. Mutat Res 557:99–108
Juhasz A, Naidu R (2000) Bioremediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review of the microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 45:57–88
Khan S, Aisun L, Zhang S, Hu Q, Zhu Y (2008) Accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in lettuce grown in the soils contaminated with long-term waste water irrigation. J Hazard Mater 152:506–515
Khan S, Afzal M, Iqbal S, Khan QM (2013) Plant-bacteria partnerships for the remediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soils. Chemosphere 90:1317–1332
Knight BP, McGrath SP, Chaudri AM (1997) Biomass carbon measurements and substrate utilization patterns of microbial populations from soils amended with cadmium, copper, or zinc. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:39–43
Li H, Luo YM, Song J, Wu LH, Christie P (2006) Degradation of benzo (a) pyrenein an experimental contaminated paddy soil by vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanoides). Environ Geochem Health 28:183–188
Lin Q, Shen KL, Zhao HM, Li WH (2008) Growth response of Zea mays L. in pyrene-copper co-contaminated soil and the fate of pollutants. J Hazard Mater 150:515–521
Lin Q, Wang ZW, Ma S, Chen YX (2006) Evaluation of dissipation mechanisms of Lolium perenne L, and Raphanus sativus for pentachlorophenol (PCP) in copper co-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 368:814–822
Liu J, Zhou Q, Sun T, Ma L, Wang S (2008) Growth response of three ornamental plants to Cd and Cd-Pb stress and the metal accumulation characteristics. J Hazard Mater 151:261–267
Liu YT, Chen ZS, Hong CY (2011) Cadmium- induced physiological response and anti oxidant enzyme changes in the novel cadmium accumulator Tagetes patula. J Hazard Mater 189:724–731
Pandev V, Dixit V, Shyam R (2009) Chromium (VI) induced changes in growth and root plasma membrane redox activities in pea plants. Protoplasma 235(1–4):49–55
Shankar AK, Cervantes C, Loza- Tavera H, Avudainayagam S (2005) Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ Int 31:739–753
Shen GQ, Lu YT, Hong JB (2006) Combined effect of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on urease activity in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 63:474–480
Sun YB, Zhou QX, Diao CY (2008) Effects of cadmium and arsenic on growth and metal accumulation of Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Bioresour Technol 99:1103–1110
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Zu Y, Wang L, Liang X (2011) Phytoremediation for co- contaminated soils of benzo (a) pyrene and heavy metals using ornamental plant Tagetes patula. J Hazard Mater 186:2075–2082
Tappero R, Pleltier E, Grafe M, Heidel K, Ginder- Vogel M, Livi KJT, Rivers ML, Marcus MA, Chaney RL, Sparks DL (2007) Hyperaccumulator Alusum murale relies on a different metal storage mechanism for cobalt than for nickel. New Phytol 175:641–654
Vazquez MD, Poschenrieder CH, Barcelo J (1987) Chromium Vi induced structural and ultrastructural changes in bush bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Ann Bot 59:427–438
Watts AW, Ballestero TP, Gardner KH (2006) Uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in salt marsh plants Spartina alterniflora grown in contaminated sediments. Chemosphere 62:1253–1260
Wilcock RJ, Corban GA, Northcott GL, Wilkins AL, Langdon AG (1996) Persistence of polycyclic aromatic compounds of different molecular size and water solubility in surfcial sediment of intertidal sand flat. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:670–676
Wild E, Dent J, Barber JL, Thomas GO, Jones KC (2004) A novel analytical approach for visualizing and tracking organic chemicals in plants. Environ Sci Technol 38:4195–4199
Wild SR, Jones KC (1993) Biological and abiotic losses of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from soils freshly amended with sewage sludge. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:5–12
Xing B, Pignatello JJ (1998) Competitive sorption between 1,3- dichlorobenzene or 2,4-dichlorophenol and natural aromatic acids in soil organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 32:614–619
Xu SY, Chen YX, Lin KF, Chen XC, Lin Q, Li F, Wang ZW (2009) Removal of pyrene from contaminated soils by white clover. Pedosphere 19:265–272
Yu X, Gu J, Xing L (2008) Differences in uptake and translocation of hexavalent and trivalent chromium by two species of willow. Ecotoxicology 17:741–755
Zayed AC, Lytle M, Qian J, Terry N (1998) Chromium accumulation, translocation and chemical speciation in vegetable crops. Planta 206:293–299
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chigbo, C., Batty, L. Phytoremediation for co-contaminated soils of chromium and benzo[a]pyrene using Zea mays L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 3051–3059 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2254-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2254-0