Abstract
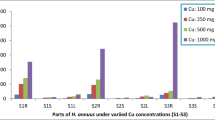
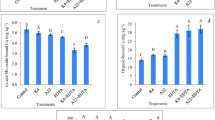
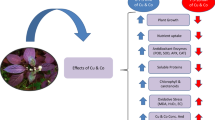
This study compares the efficiency of a synthetic chelate (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-EDTA), a natural low-molecular-weight organic acid (citric acid), and their combination for phytoremediation of Cu-pyrene co-contaminated soils. Zea mays was grown in each soil and amended with citric acid and/or EDTA to understand the effect of chelates during phytoremediation of contaminated soils. In Cu or pyrene-contaminated soil, plant growth was negatively affected by EDTA (43 %) and citric acid (44 %), respectively, while EDTA + citric acid promoted (41 %) plant growth in co-contaminated soil. EDTA and EDTA + citric acid increased the phytoextraction of Cu in Cu-contaminated and co-contaminated soils, respectively. In pyrene-contaminated soil, all tested chelates increased the dissipation of pyrene reaching 90.4 % for citric acid, while in co-contaminated soil, only citric acid or EDTA + citric acid enhanced pyrene dissipation. These results show that Z. mays can be effective with the help of chelates in phytoextraction of Cu and dissipation of pyrene in co-contaminated soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew, C., Thomas, B., Chloe, A., Smith, J., & Thompson, L. (2007). Phytoremediation of mixed contaminated soil using hyperaccumulator plant Alyssum lesbiacum: evidence of histidine as a measure of phytoextractable nickel. Environmental Pollution, 147, 74–82.
Baylock, M., Salt, D., Dushenkor, S., Zakharora, O., Gussman, C., Kapulnik, Y., Ensley, B., & Raskin, I. (1997). Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 860–865.
Binet, P., Portal, J., & Leyval, C. (2000). Dissipation of 3–6-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rhizosphere of ryegrass. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32, 2011–2017.
Chen, H., & Cutright, T. (2001). EDTA and HEDTA effects on Cd, Cr and Ni uptake by Helianthus annus. Chemosphere, 45, 21–28.
Chigbo, C., & Batty, L. (2013). Phytoremediation potential of B. juncea in Cu-pyrene co-contaminated soil: comparing freshly spiked soils with aged soils. Journal of Environmental Management, 129, 18–24.
Degryse, F., Smolders, E., & Merckx, R. (2006). Labile Cd complexes increase Cd availability to plants. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 830–836.
Ebbs, S., & Kochian, L. (1998). Phytoextraction of zinc by oat (Avena sativa), barley (Hordeum vulgare) and Indian mustard (Brassica juncea). Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 802–806.
Eibes, G., Chau, T., Feijoo, G., Moreira, M., & Lema, J. (2005). Complete degradation of anthracene by manganese peroxidase in organic solvent mixtures. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 37, 365–372.
Gao, Y., & Zhu, L. (2004). Plant uptake, accumulation and translocation of phenanthrene and pyrene in soils. Chemosphere, 55, 1169–1178.
Gramss, G., Voigt, K., & Bergmann, H. (2004). Plant availability and leaching of (heavy) metals from ammonium, calcium, carbohydrate and citric acid-treated uranium mine dump soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 167, 417–427.
Gunawardana, B., Singhal, N., & Johnson, A. (2010). Amendments and their combined application for enhanced copper, cadmium and lead uptake by Lolium perenne. Plant and Soil, 329, 283–294.
Gunawardana, B., Singhal, N., & Johnson, A. (2011). Effects of amendments on copper, cadmium and lead phytoextraction by Lolium perenne from multiple-metal contaminated solution. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 13, 215–232.
Jean, L., Gautier-, B. F., Moussard, C., Verney, P., Hitmi, A., & Bollinger, J. (2008). Effect of citric acid and EDTA on chromium and nickel uptake and translocation by Datura innoxia. Environmental Pollution, 153, 555–563.
Jiang, L., Yang, X., & He, Z. (2004). Growth response and phytoextraction of copper at different levels in soil by Elsholtzia splendens. Chemosphere, 55, 1179–1187.
Ke, L., Wong, T., Wong, A., Wong, Y., & Tam, N. (2003). Negative effects of humic acid addition on phytoremediation of pyrene-contaminated sediments by mangrove seedlings. Chemosphere, 52, 1581–1591.
Kim, S., & Li, I. (2010). Comparison of the ability of organic acids and EDTA to enhance the phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Bulletin in Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 84, 255–259.
Lee, J., Reeves, R., Brook, R., & Jaffre, T. (1977). Isolation and identification of a citrate-complex of nickel from nickel accumulating plants. Phytochemistry, 16, 1502–1505.
Liphadzi, M., Kirkaham, M., Mankin, K., & Paulsen, G. (2003). EDTA-assisted heavy-metal uptake by poplar and sunflower grown at a long-term sewage sludge farm. Plant and Soil, 257, 171–182.
Luo, C., Shen, Z., & Li, X. (2005). Enhanced phytoextraction of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd with EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere, 59, 1–11.
Marchiol, L., Assolari, S., Sacco, P., & Zerbi, G. (2004). Phytoextraction of heavy metals by canola (Brassica napus) and radish (Raphanus sativus) grown on multicontaminated soil. Environmental Pollution, 132, 21–27.
Marschner, B., Henke, U., & Wessolek, G. (1995). Effects of meliorative additives on the adsorption and binding forms of heavy metals in a contaminated top soil from a former sewage farm. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde, 158, 9–14.
Nowack, B., Schullin, R., & Robinson, B. (2006). Critical assessment of chelant-enhanced metal phytoextraction. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 5335–5232.
Romkens, P., Bouwman, L., Japenga, J., & Draaisma, C. (2002). Potentials and drawbacks of chelate-enhanced phytoremediation of soils. Environmental Pollution, 116, 109–121.
Schill, R., Gorlitz, H., & Kohler, H. (2003). Laboratory simulation of a mining accident: acute toxicity hsc/hsp70 response, and recovery from stress in Gammarus fossarum (Crustacea, Amphipoda) exposed to a pulse of cadmium. Biometals, 16, 391–401.
Shi, Z., Tao, S., Pan, B., Fan, W., He, X., Zuo, Q., Wu, S., Li, B., Cao, J., Liu, W., Xu, F., Wang, X., Shen, W., & Wong, P. (2005). Contamination of rivers in Tianjin, China by polycyclic hydrocarbons. Environmental Pollution, 134, 97–111.
Sinhal, V., Srivastava, A., & Singh, V. (2010). EDTA and citric acid-mediated phytoextraction of Zn, Cu, Pb and Cd through marigold (Tagetes erecta). Journal of Environmental Biology, 31, 255–259.
Ting, W., Yuan, S., Wu, J., & Chang, B. (2011). Biodegradation of phenanthrene and pyrene by Ganoderma lucidum. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 65, 238–242.
Turgut, C., Pepe, M., & Cutright, T. (2004). The effect of EDTA and citric acid on phytoremediation of Cd, Cr and Ni from soil using Helianthus annus. Environmental Pollution, 131, 147–154.
Vassil, A., Kapulnik, Y., Raskin, I., & Salt, D. (1998). The role of EDTA in lead transport and accumulation by Indian mustard. Plant Physiology, 117, 447–453.
Wang, M., Chen, Y., Chen, S., Chien, S., & Sunkara, S. (2012). Phytoremediation of pyrene-contaminated soils amended with compost and planted with ryegrass and alfalfa. Chemosphere, 87, 217–225.
Wasay, S., Barrington, S., & Tokunaga, S. (1998). Remediation of soils polluted by heavy metals using salts of organic acids and chelating agents. Environmental Technology, 19, 369–379.
Wei, X., Sang, L., Chen, J., Zhu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2009). The effects of LMWOAs on biodegradation of multicomponent PAHs in aqueous solution using dual-wavelength fluorimetry. Environmental Pollution, 157, 3150–3157.
Wenger, K., Gupter, S., Furrer, G., & Schulin, R. (2003). Heavy metals in the environment: the role of nitrilotriacetate in copper uptake by tobacco. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 1669–1678.
Wenzel, W., Unterbrunner, R., Sommer, P., & Sacco, P. (2003). Effects of EDTA and low molecular weight organic acids on soil solution properties of a heavy metal polluted soil. Chemosphere, 50, 819–822.
Wu, L., Luo, Y., Christie, P., & Wong, M. (2003). Effect of EDTA and low molecular weight organic acids in soil solution properties of a heavy metal polluted soil. Chemosphere, 50, 819–822.
Wu, L., Luo, Y., Xing, X., & Christie, P. (2004). EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil with Indian mustard and associated potential leaching risk. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 102, 307–318.
Wuana, R., & Okieimen, F. (2010). Phytoremediation potential of maize (Zea mays L.). A review. African Journal of General Agriculture, 6, 275–287.
Yan, J., Wang, I., Fu, P., & Yu, H. (2004). Photomutagenicity of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the US EPA priority pollutant list. Mutation Research, 557, 99–108.
Yang, C., Zhou, Q., Wei, S., Hu, Y., & Bao, Y. (2011). Chemical-assisted phytoremediation of Cd-PAHs contaminated soils using Solanum nigrum L. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 13, 818–833.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chigbo, C., Batty, L. Chelate-Assisted Phytoremediation of Cu-Pyrene-Contaminated Soil Using Z. mays . Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 74 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2277-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2277-2