Abstract
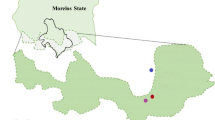
Effects of environmental chemical pollution can be observed at all levels of biological organization. At the population level, genetic structure and diversity may be affected by exposure to metal contamination. This study was conducted in Huautla, Morelos, Mexico in a mining district where the main contaminants are lead and arsenic. Peromyscus melanophrys is a small mammal species that inhabits Huautla mine tailings and has been considered as a sentinel species. Metal bioaccumulation levels were examined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and genetic analyses were performed using eight microsatellite loci in 100 P. melanophrys individuals from 3 mine tailings and 2 control sites. The effect of metal bioaccumulation levels on genetic parameters (population and individual genetic diversity, genetic structure) was analyzed. We found a tissue concentration gradient for each metal and for the bioaccumulation index. The highest values of genetic differentiation (Fst and Rst) and the lowest number of migrants per generation (Nm) were registered among the exposed populations. Genetic distance analyses showed that the most polluted population was the most genetically distant among the five populations examined. Moreover, a negative and significant relationship was detected between genetic diversity (expected heterozygosity and internal relatedness) and each metal concentration and for the bioaccumulation index in P. melanophrys. This study highlights that metal stress is a major factor affecting the distribution and genetic diversity levels of P. melanophrys populations living inside mine tailings. We suggest the use of genetic population changes at micro-geographical scales as a population level biomarker.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos W, Worthington W, Fullard K, Burger TM, Croxall JP, Bloch D, Coulson T (2001) The influence of parental relatedness on reproductive success. Proc R Soc Lond B 68:2021–2027
Antolin MF, Van Horne B, Berger MD, Holloway AK, Roach JL, Weeks RD (2001) Effective population size and genetic structure of a Piute ground squirrel (Spermophilus mollis) population. Can J Zool 79:26–34
Arif I, Khan H (2009) Molecular markers for biodiversity analysis of wildlife animals: a brief review. Animal Biodiv Conserv 32:9–17
Belfiore N, Anderson S (1998) Genetic patterns as a tool for monitoring and assessment of environmental impacts: the example of genetic ecotoxicology. Environ Monit Assess 51:465–479
Belfiore N, Anderson S (2001) Effects of contaminants on genetic patterns in aquatic organisms: a review. Mutat Res 489:97–122
Bengtsson G, Nordström S, Rundgren S (1983) Population density and tissue metal concentration of lumbricids in forest soils near a brass mill. Environ Pollut A 30:87–108
Benton M, Malott M, Trybula J, Dean D, Guttman S (2002) Genetic effects of mercury contamination on aquatic snail populations: allozyme genotypes and DNA strand breakage. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:584–589
Berckmoes V, Scheirs J, Jordaens K, Blust R, Backeljau T, Verhagen R (2005) Effects of environmental pollution on microsatellite DNA diversity in wood mouse (Apodemus Sylvaticus) populations. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2898–2907
Bernard A (2008) Biomarkers of metal toxicity in population studies: research potential and interpretation issues. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 71:1259–1265
Berthier K, Galan M, Foltete JC, Charbonnel N, Cosson JF (2005) Genetic structure of the cyclic fossorial water voles (Arvicola terrestris): landscape and demographic influences. Mol Ecol 14:2861–2871
Berthier K, Charbonnel N, Galan M, Cosson JF (2006) Migration and recovery of the genetic diversity during the increasing density phase in cyclic vole populations. Mol Ecol 15:2665–2676
Bervoets L, Blust R (2003) Metal concentrations in water, sediment and gudgeon (Gobio gobio) from a pollution gradient: relationship with fish condition factor. Environ Pollut 126:9–19
Bickham JW (2011) The four cornerstones of evolutionary toxicology. Ecotoxicology 20:497–502
Bickham J, Smolen M (1994) Somatic and heritable effects of environmental genotoxins and the emergence of evolutionary toxicology. Environ Health Persp 102:25–28
Bickham J, Sandhu S, Hebert P, Chikhi L, Athwal R (2000) Effects of chemical contaminants on genetic diversity in natural populations: implications for biomonitoring and ecotoxicology. Mutat Res 463:33–51
Bourret V, Couture P, Campbell P, Bernatchez L (2008) Evolutionary ecotoxicology of wild yellow perch (Percha flavescens) populations chronically exposed to a polymetallic gradient. Aquat Toxicol 86:76–90
Brooks S, Lyon B, Goodsir F, Bignell J, Thain J (2009) Biomarker responses in mussels, an integrated approach to biological effects measurements. J Toxicol Env Health A 72:196–208
Brown AR, Hosken DJ, Balloux F, Bickley LK, LePage G, Owen SF, Hetheridge MJ, Tyler CR (2009) Genetic variation, inbreeding and chemical exposure–combined effects in wildlife and critical considerations for ecotoxicology. Phil Trans R Soc B 364:3377–3390
Burger J (1995) Heavy metal and selenium levels in feathers of herring gulls (Larus argentatus): differences due to year, gender, and age at Captree, Long Island. Environ Monit Assess 38:37–50
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1996) Heavy metal and selenium levels in Franklin’s gull (Larus pipixcan): parents and their eggs. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 30:487–491
Cadena M (2003) Efecto de la perturbación y estacionalidad en la comunidad de roedores en una salva baja caducifolia en Morelos, México. Dissertation. Universidad de las Américas de Puebla.
Carleton MD, Musser GG (2005) Order Rodentia. In: Wilson DE, Reeder DM (eds) Mammal species of the world a taxonomic and geographic reference. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, pp 894–1531
Chirhart S, Honeycutt R, Greenbaum I (2000) Microsatellite markers for the deer mouse Peromyscus maniculatus. Mol Ecol 9:1661–1686
Chirhart S, Honeycutt R, Greenbaum I (2005) Microsatellite variation and evolution in the Peromyscus maniculatus species group. Molec Phylogenet Evol 34:408–415
Coues E (1874) Synopsis of the Muridae in North America. Proc Acad Nat Sci Phila 3:173–196
Dauwe T, Janssens E, Kempenaers B, Eens M (2004) The effect of heavy metal exposure on egg size, eggshell thickness and the number of spermatozoa in blue tit Parus caeruleus eggs. Environ Pollut 129:125–129
Deng J, Liao B, Ye M, Deng D, Lan C, Shu W (2007) The effects of heavy metal pollution on genetic diversity in zinc/cadmium hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii populations. Plant Soil 297:83–92
Dmowski K, Kozakiewicz M, Kozakiewicz A (1995) Ecological effects of heavy metal pollution (Pb, Cd, Zn) on small mammal populations and communities. B Pol Acad Biol Sci 43:1–10
Dorado O, Maldonado B, Arias D, Sorani V, Ramírez R, Leyva E (2005) Programa de conservación y manejo Reserva de la Biosfera Sierra de Huautla. Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales. Protegidas, México
EPA Environmental Protection Agency (2000). Innovative remediation technologies: Field scale demonstration projects in North America
Erry BV, Macnair MR, Meharg AA, Shore RF (2000) Arsenic contamination in wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus) and bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus) on abandoned mine sites in southwest Britain. Environ Pollut 110:179–187
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Folkeson L, Nyholm HEI, Tyler G (1990) Influence of acidity and other soil properties on metal concentrations in forest plants and animals. Sci Total Environ 96:211–233
Fratini S, Zane L, Ragionieri L, Vannini M, Cannicc S (2008) Relationship between heavy metal accumulation and genetic variability decrease in the intertidial crab Pachygrapsus marmoratus (Decapoda; Grapsidae). Estuar Coast Shelf S 79:679–686
Gardeström J, Dahl U, Kotsalainen O, Maxson A, Elfwing T, Grahn M, Bengtsson B, Breitholtz M (2008) Evidence of population genetic effects of long-term exposure to contaminated sediments: a multi-endpoint study with copepods. Aquat Toxicol 86:426–436
Gardner-Santana LC, Norris DE, Fornadel CM, Hinson ER, Klein SL, Glass GE (2009) Comensal ecology, urban landscapes and their influence on the genetic characteristics of city-dwelling Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus). Mol Ecol 18:2766–2778
Gauffre B, Estoup A, Bretagnolle V, Cosson F (2008) Spatial correlation structure of a small rodent in heterogeneous landscape. Mol Ecol 17:4619–4629
Hall ER (1981) The mammals of North America. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Hebert PM, Murdoch-Luiker M (1996) Genetic effects of contaminant exposure-towards an assessment of impacts on animal populations. Sci Total Environ 191:23–58
INEGI (2004) Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Información Geográfica del Estado de. Morelos, México
INEGI (2009) Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Información Geográfica del Estado de. Morelos, México
Jiang ZF, HuangSZ HYL, Zhao JZ, Fu JJ (2011) Physiological response of Cu mine tailing remediation of Paulownia fortunei (Seem) Hemsl. Ecotoxicology dpoi:. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0836-5
Kim S, Rodriguez M, Suh J, Song J (2003) Emergent effects of heavy metal pollution at a population level: Littorina brevicula a study case. Mar Pollut Bull 46:74–80
Klaper R, Rees CH, Drevnick P, Weber D, Sandheinrich M, Carvan M (2006) Gene expression changes related to endocrine function and decline in reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) after dietary methylmercury exposure. Environ Health Perspect 114:1337–1343
Lande R (1988) Genetics and demography in biological conservation. Science 241:455–1460
Laurinolli M, Bendell-Young L (1996) Copper, zinc, and cadmium concentrations in Peromyscus maniculatus sampled near an abandoned copper mine. Environ Contam Toxicol 30:481–486
Layne JN (1968) Ontogeny. In: King JA (ed) Biology of Peromyscus (Rodentia). The American Society of Mammalogists, Provo, Utah, pp 148–253, Publication number 2
Lefèbvre C, Vernet P (1990) Microevolutionary processes on contaminated deposits. In: Shaw J (ed) Heavy metal tolerance in plants: evolutionary aspects. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 285–300
Levengood J, Heske E (2008) Heavy metal exposure, reproductive activity, and demographic patterns in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) inhabiting a contaminated wetland. Sci Total Environ 389:320–328
Lynch M, Conery J, Burger R (1995) Mutation accumulation and the extinction of small populations. Am Nat 146:489–518
Ma W, Denneman W, Faber J (1991) Hazardous exposure of ground-living small mammals to cadmium and lead in contaminated terrestrial ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:266–270
Maes GE, Raeymaekers JAM, Pampoulie C, Seynaeve A, Goemans G, Belpaire C, Volckaert FAM (2005) The catadromous European eel Anguilla anguilla (L.) as a model for freshwater evolutionary ecotoxicology: relationship between heavy metal bioaccumulation, condition and genetic variability. Aquat Toxicol 73:99–114
Mares MA, Ernest KA (1995) Population and community ecology of small mammals in a gallery forest of central Brazil. J Mammal 76:750–768
Matson C, Lambert M, McDonald T, Autenrieth R, Donnelly K, Islamzadeh A, Politov D, Bickham J (2006) Evolutionary toxicology: population-level effects of chronic contaminant exposure on the marsh frogs (Rana ridibunda) of Azerbaijan. Environ Health Persp 114:547–552
Medina M, Correa J, Barata C (2007) Micro-evolution due to pollution: possible consequences for ecosystem responses to toxic stress. Chemosphere 67:2105–2114
Miller MP (2000) Tools for populations genetic analyses (TFPGA) 1.3: A window program for the analyses of allozyme and molecular population genetic data computer software distributed by author.
Mills SL, Allendorf FW (1996) The one-migrant-per-generation rule in conservation and management. Coserv Biol 10:150–158
Morales EO, Carrillo FC (2010) Plan municipal de desarrollo de Tlaquiltenango, Morelos. H. Ayuntamiento de Tlaquiltenango, Morelos. http://www.tlaquiltenango.gob.mx/Transparencia/Obligaciones_Contable_Administrativas/OCA15_Plan_desarrollo_estatal%20doc.pdf. Accessed 19 September 2012
Morgan AJ, Kille P, Sturzenbaum SR (2007) Microevolution and ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates. Environ Sci Technol 41:1085–1096
Mossman CA, Waser PM (2001) Effects of habitat fragmentation on population genetic structure in the white-footed mouse (Peromyscus leucopus). Can J Zool 79:285–295
Mullen L, Hirschmann R, Prince K, Glenn T, Dewey M, Hoekstra H (2006) Sixty polymorphic microsatellite markers for the old field mouse developed in Peromyscus polionotus and Peromyscus maniculatus. Mol Ecol Notes 6:36–40
Mussali-Galante P (2008) Estudio sobre la inducción de daño al ADN en sangre periférica de individuos expuestos a metales en al agua de bebida, en la población de Huautla, Morelos. Dissertation, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México
Nacci D, Hoffman GR (2008) Genetic variation in population-level ecological risk assessment. In: Barnthouse LW, Munns WR, Sorensen MT Jr (eds) Population-level ecological risk assessment. Taylor and Francis, New York, pp 93–112
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
Page RDM (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pascoe GA, Blanchet RJ, Linder G, Lande R (1994) Bioavailability of metals and arsenic to small mammals at a mining waste-contaminated wetland. Genetics and demography in biological conservation. Science 241:455–1460
Peakall DB (1992) Animal biomarkers as pollution indicators, Ecotoxicological Series No.1. Chapman & Hall, London
Peakall R, Lindenmayer D (2006) Genetic insights into population recovery following experimental perturbation in a fragmented landscape. Biol Conserv 132:520–532
Peakall R, Ruibal M, Lindmeyer D (2003) Spatial correlation analysis offers new insights into gene flow in the Australian bush rat, Rattus fuscipes. Evolution 57:118–295
Phelps KL, McBee K (2009) Ecological characteristics of small mammal communities at a superfund site. Amer Midl Nat 161:57–68
Pra D, Rech-Frenke SI, Giulian R, Yoneama ML, Ferraz-Diaz J, Erdtmann B, Pegas-Henriques JA (2008) Genotoxicity and mutagenicity of iron and copper in mice. Biometals 21:289–297
Queller DC, Goodnight KF (1989) Estimating relatedness using genetic markers. Evolution 43:258–275
Ricketts HJ, Morgan AJ, Spurgeon DJ, Kille P (2004) Measurement of annetocin gene expression: a new reproductive biomarker in earthworm ecotoxicology. Ecotox Environ Safety 57:4–10
Rogstad S, Keane B, Collier M (2003) Minisatellite DNA mutation rate in dandelions increases with leaf-tissue concentrations of Cr, Fe, Mn, and Ni. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2093–2099
Rzedowski J (2006) Vegetación de México. Fondo de Cultura Económica, Mexico
Sánchez CH, Romero MLA (1992) Mastofauna silvestre del ejido el Limón, municipio de Tepalcingo, Morelos. Univ Cienc Tec 2:87–95
Scheirs J, Coan A, Covaci A, Beernaert J, Kayawe M, Caturla M, Wolf H, Baert P, Van Oostveldt P, Verhagen R, Blust R, Coen W (2006) Genotoxicity in wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus) along a pollution gradient: exposure age and gender-related effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2154–2162
Secretaría de Economía (2011) Panorama minero del Estado de Morelos. Servicio Geológico Mexicano, serie panorama minero de los estados, Mexico
Sheffield SR, Sawicka-Kapusta K, Cohen JB, Rattner BA (2001) Rodentia and Lagomorpha. In: Shore RF, Rattner BA (eds) Ecotoxicology of wild mammals. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 215–314
Shore RF, Douben PE (1994) Predicting ecotoxicological impacts of environmental contaminants on terrestrial small mammals. Rev Environ Contam T 134:49–89
Shugart L, Theodorakis C (1998) New trends in biological monitoring: application of biomarkers to genetic ecotoxicology. Biotherapy 11:119–127
Smith PN, Cobba GP, Harper FM, Adair BM, McMurry ST (2002) Comparison of white-footed mice and rice rats as biomonitors of polychlorinated biphenyl and metal contamination. Environ Pollut 119:261–268
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. The principles and practice of numerical classification. WH Freeman, San Francisco, 573 p
Sommer S (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation and changes of dispersal behavior after a recent population decline on the genetic variability of noncoding and coding DNA of a monogamous Malagasy rodent. Mol Ecol 12:2845–2851
Staton J, Schizas N, Chandler G, Coull B, Quattro J (2001) Ecotoxicology and population genetics: the emergence of “phylogeographic and evolutionary ecotoxicology”. Ecotoxicology 10:217–222
Statsoft (2000) Statistica for Windows, v. 5.1. Computer program manual. Tulsa, StatSoft Inc
Stockley P, Searle JB, Macdonald DW, Jones CS (1993) Female multiple mating behavior in the common shrew as a strategy to reduce inbreeding. Proc R Soc Lond B 254:173–179
Swofford DL, Olsen GJ (1990) Phylogeny reconstruction. In: Moritz C, Hillis DM (eds) Molecular systematics. Sinauer Associated Inc, Massachusetts, pp 411–501
Theodorakis C (2001) Integration of genotoxic and population genetic endpoints in biomonitoring and risk assessment. Ecotoxicology 10:245–256
Tovar-Sánchez E, Cervantes LT, Martínez C, Rojas E, Valverde M, Ortiz-Hernández ML, Mussali-Galante P (2012) Comparison of two wild rodent species as sentinels of environmental contamination by mine tailings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1677–1686
Ungherese G, Mengoni A, Somigli S, Baroni D, Focardi S, Ugolini A (2010) Relationship between heavy metals pollution and genetic diversity in Mediterranean population of the sandhopper Talitrus saltator (Montagu) (Crustaceae, Amphipoda). Environ Pollut 158:1638–1643
Valavanidis A, Vlachogianni T (2010) Metal pollution in ecosystems: ecotoxicology studies and risk assessment in the marine environment. Sci Adv Environ Toxicol Ecotox Issues. www.chem-tox-ecotox.org
Van de Zande L, Van Apeldoorn RC, Blijdenstein AF, De Jong D, Van Delden W, Bijlsma R (2000) Microsatellite analysis of population structure and genetic differentiation within and between population of the root vole, Microtus oeconomus in the Netherlands. Mol Ecol 9:1651–1656
Van Straalen N (1999) Genetic biodiversity in toxicant-stressed populations. Prog Environ Sci 1:195–201
Van Straalen N, Timmermans M (2002) Genetic variation in toxicant-stressed populations: an evaluation of the “genetic erosion” hypothesis. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 8:983–1002
Vargas V (2010) Estructura genética del roedor Baiomys musculus (Muridae) en la selva seca caducifolia en el estado de Morelos. Dissertation. Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos
Volke ST, Velasco TA, De la Rosa PA, Solórzano OG (2004) Evaluación de tecnologías de remediación para suelos contaminados con metales. Etapa I. Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales, Mexico
Volke ST, Velasco TA, De la Rosa PA, Solórzano OG (2005) Evaluación de tecnologías de remediación para suelos contaminados con metales. Etapa II. Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales, Mexico
Vucetich LM, Vucetich JA, Cleckner LB, Gorski PR, Peterson RO (2001) Mercury concentrations in deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) tissues from Isle Royale National Park. Environ Pollut 114:11–38
Weber JN, Peters M, Tsyusko O, Linnen C, Hagen C, Schable N, Tuberville T, Mckee A, Lance S, Jones K, Fisher H, Dewey M, Hoekstra H, Glenn C (2010) Five hundred microsatellite loci for Peromyscus. Conserv Genet 11:1243–1246
Weir BS (1996) Genetic data analysis II: methods for discrete population genetic data. Sinauer Associated Inc, Massachusetts
Werre F, Ortiz-Hernández L (2000) Monografía geologica-minera del estado de Morelos. Consejo de Recursos Minerales, Mexico
WHO World Health Organization (2007) Health risks of heavy metals from long range transboundary air pollution. WHO Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen
Yap CK, Tan SG, Ismail A, Omar H (2004) Allozyme polymorphisms and heavy metal levels in the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis (Linnaeus) collected from contaminated and uncontaminated sites in Malaysia. Environ Inter 30:39–46
Yap CK, Chua BH, Teh CH, Tan SG, Ismail A (2007) Primers of RAPD markers and heavy metal concentrations in Perna viridis (L.), collected from metal-contaminated and uncontaminated coastal waters: are they correlated with each other? Russian J Genet 43:544–550
Yap CK, Chong CM, Tan SG (2011) Allozyme polymorphism in the horseshoe crabs Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda collected from polluted intertidal area in Peninsular Malaysia. Environ Monit Assess 174:389–400
Yeh FC, Yang R, Boyle T (1999) PopGene Ver. 1.31. University of Alberta, Canada
Zar J (2010) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, New-Jersey
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a scolarship to P.M.G. (102684) by the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT).This paper constitutes a partial fulfillment of the Graduate Program in Biological Sciences of the National Autonomous University of México (UNAM). The authors thank the “Posgrado en Ciencias Biológicas, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM). We also thank Edith Rivas, Guillermo Sánchez, Evodio Rendon Alquicira, Guadalupe Rangel Altamirano and Laura Márquez for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Stuart Simpson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mussali-Galante, P., Tovar-Sánchez, E., Valverde, M. et al. Evidence of population genetic effects in Peromyscus melanophrys chronically exposed to mine tailings in Morelos, Mexico. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 7666–7679 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1263-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1263-8