Abstract
Purpose
This work aimed at investigating the adsorption of lead and cadmium onto Fe and Ag nanoparticles for use as a water contaminant removal agent as a function of particle type, sorbent concentration, and contact time.
Methods
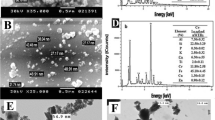
Fe and Ag spherical nanoparticles were prepared in water by the lab-made electro-exploding wire (EEW) system and were investigated for their structure properties. Adsorption experiments were carried out at room temperature and pH 8.3 water solutions.
Results
The removal/adsorption of both Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions was found to be dependent on adsorbent dosage and contact time. Pb(II) adsorption onto Fe and Ag nanoparticles showed more or less similar efficiency and behavior. The kinetic data for the adsorption process obeyed pseudo second-order rate equations. The calculated equilibrium adsorption capacities (q e) were 813 and 800 mg/g for Pb sorption onto Fe and Ag nanoparticles, respectively. Cd(II) ion adsorption onto Fe nanoparticles obeyed pseudo second-order rate equations with q e equal to 242 mg/g, while their adsorption onto Ag nanoparticles obeyed pseudo first-order rate equations with q e of 794 mg/g. The calculated q es are in quite agreement with the experimental values. The removal/uptake mechanisms of metal ions involved interaction between the metal ion and the oxide/hydroxyl layer around the spherical metallic core of the nanoparticle in water medium.
Conclusion
Fe and Ag nanoparticles prepared using the EEW technique exhibited high potentials for the removal of metal ions from water with very high adsorption capacities, suggesting that the EEW technique can be enlarged to generate nanoparticles with large quantities for field or site water purification.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmoneim MA, Khaled AM, Iskander MF (1994) A study on the levels of some heavy metals in El-Mex, West of Alexandria, Egypt. Bull Inst Oceanogr Fish ARE:155–174
Ali I, Gupta VK (2007) Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat Protoc 1(6):2661–2667
Alqudami A, Annapoorni S (2005) Fluorescent silver nanoparticles via exploding wire technique. Pramana–J Phys 65:815–819
Alqudami A, Annapoorni S (2007) Fluorescence from metallic silver and iron nanoparticles prepared by exploding wire technique. Plasmonics 2:5–13
Alqudami A, Annapoorni S, Lamba S, Kothari PC, Kotnala RK (2007) Magnetic properties of iron nanoparticles prepared by exploding wire technique. J Nanosci Nanotech 7:1898–1903
Alqudami A, Annapoorni S, Govind SSM (2008) Ag–Au alloy nanoparticles prepared by electro-exploding wire technique. J Nanopart Res 10:1027–1036
Atta IA, Abdul Razzak BI (2008) Chemical and physical analysis of some ground water sample in Al-Quti wells Hodiedah, Yemen. J Iran Chem Res 1:141–144
Azizian S (2004) Kinetic models of sorption: a theoretical analysis. J Colloid Interface Sci 276:47–52
Benguella B, Benaissa H (2002) Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by chitin: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Res 36:2463–2474
Colvin VL (2003) The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nature Biotech 21:1166–1170
David C (2004) Small water supplies, 1st edn. Cromwell Press, India
Dimitri M, Vladimir G, Abraham W (2000) Ion exchange. Marcel Dekker, New York
Dus R, Nowicka E (2003) Atomic deuterium (hydrogen) adsorption on thin silver films. Progress Surface Sci 74(1–8):39–56
Engates KE, Shipley HJ (2011) Adsorption of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, and Ni to titanium dioxide nanoparticles: effect of particle size, solid concentration, and exhaustion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:386–395
Esmail A, Abdul Rahim S, Wan Zuhairi WY, Alshaebi F, Nozaily F (2009) Leachate composition and groundwater pollution at municipal solid waste landfill of Ibb city, Yemen. Sains Malaysiana 38(3):295–304
Faghihian H, Ghannadi-Marageh M, Kazemian H (1999) The use of clinptilolite of radioactive cesium and strontium from nuclear waste water and lead, nickel, cadmium, barium from municipal waste water. Sep Sci Technol 34:2275–2292
Foppen JWA (2002) Impact of high-strength wastewater infiltration on groundwater quality and drinking water supply: the case of Sana’a, Yemen. J Hydrology 263:198–216
Foppen JWA, Naaman M, Schijven JF (2005) Managing water under stress in Sana’a-Yemen. Arab J Sci Eng 30(2C):69–83
Fryxell GE, Cao G (2007) Environmental applications of nanomaterials: synthesis, sorbents and sensors. Imperial College Press, London
Gupta VK, Ali I (2004) Removal of lead and chromium from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste. J Colloid Interface Sci 271(2):321–328
Gupta VK, Ali I (2008) Removal of endosulfan and methoxychlor from water on carbon slurry. Environ Sci Technol 42:766–770
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008a) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by green algae Spirogyra species: equilibrium and adsorption kinetics. J Hazard Mater 152(1):407–414
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008b) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium(II) biosorption by nonliving algal biomass Oedogonium sp. from aqueous phase. J Hazard Mater 153(1–2):759–766
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008c) Sorption and desorption studies of chromium(VI) from nonviable cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum biomass. J Hazard Mater 154(1–3):347–354
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008d) Biosorption of lead(II) from aqueous solutions by non-living algal biomass Oedogonium sp. and Nostoc sp.—a comparative study. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 64(2):170–178
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by raw and acid-treated green alga Oedogonium hatei from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 163(1):396–402
Gupta VK, Sharma S (2003) Removal of zinc from aqueous solutions using bagasse fly ash—a low cost adsorbent. Ind Eng Chem Res 42(25):6619–6624
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Dwivedi MK, Mohan D (1997) Process development for the removal of zinc and cadmium from wastewater using slag—a blast furnace waste material. Separation Sci Tech 32(17):2883–2912
Gupta VK, Mohan D, Sharma S (1998) Removal of lead from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste material. Separation Sci Tech 33(9):1331–1343
Gupta VK, Mohan D, Sharma S, Park KT (1999) Removal of chromium(VI) from electroplating industry wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste material. Environmentalist 19(2):129–136
Gupta VK, Srivastava SK, Tyagi R (2000) Design parameters for the treatment of phenolic wastes by carbon columns (obtained from fertilizer waste material). Water Res 34(5):1543–1550
Gupta VK, Gupta M, Sharma S (2001) Process development for the removal of lead and chromium from aqueous solutions using red mud—an aluminium industry waste. Water Res 35(5):1125–1134
Gupta VK, Singh P, Rahman N (2004) Adsorption behavior of Hg(II), Pb(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solution on Duolite C-433: a synthetic resin. J Colloid Interface Sci 275(2):398–402
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Gajbe V, Mittal J (2006) Removal and recovery of the hazardous azo dye acid orange 7 through adsorption over waste materials: bottom ash and de-oiled soya. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(4):1446–1453
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007a) Adsorption studies on the removal of Vertigo Blue 49 and Orange DNA13 from aqueous solutions using carbon slurry developed from a waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 315(1):87–93
Gupta VK, Jain R, Mittal A, Mathur M, Sikarwar S (2007b) Photochemical degradation of the hazardous dye Safranin-T using TiO2 catalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 309(2):464–469
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007c) Removal of Reactofix golden yellow 3 RFN from aqueous solution using wheat husk—an agricultural waste. J Hazard Mater 142(1–2):443–448
Gupta VK, Carrott PJM, Carrott MMLR (2009) Low cost adsorbents: growing approach to wastewater treatment—a review. Critical Rev Environ Sci Tech 39:783–842
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Nayak A (2010) Adsorption studies on the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using a low cost fertilizer industry waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 342(1):135–141
Harrison RM (ed) (1990) Pollution: causes, effects and control, 2nd edn. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Hewitt CN, Metcalfe PJ, Street RA (1991) Method for the sampling and removal of ionic alkyl-lead compounds from aqueous solution using ion-exchange media. Water Res 25:91–94
Ho YS (2004) Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 59:171–177
Ho YS (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136:681–689
Hu J, Lo Irene MC, Chen GH (2005) Fast removal and recovery of Cr(VI) using surface-modified jacobsite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles. Langmuir 21:11173–11179
Joo SH, Cheng IF (2006) Nanotechnology for environmental remediation. Springer, New York
Ju-Nam Y, Lead JR (2008) Manufactured nanoparticles: an overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Sci Total Env 400:396–414
Laumakis MT, Martin PJ, Pamucku S, Owens K (1995) Proceeding of the International Conference on Hazard Waste Management. ASCE, New York, pp 528–535
Li X, Zhang W (2007) Sequestration of metal cations with zerovalent iron nanoparticles: a study with high resolution x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). J Phys Chem C 111:6939–6946
Li X, Elliott DW, Zhang W (2006) Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: materials and engineering aspects. Cri Rev Solid State Mater Sci 31:111–121
Liang P, Shi T, Li J (2004) Nanometer-size titanium dioxide separation/pre-concentration and FAAS determination of trace Zn and Cd in water sample. Int J Environ Anal Chem 84:315–321
Mamadou SD, Savage N (2005) Nanoparticles and water quality. J Nano Res 7:325–330
Manahan S (1991) Environmental chemistry, 5th edn. Lewis Publishers, New York
Manahan S (2000) Environmental chemistry, 7th edn. Lewis Publishers, New York
Nabil Al-Shwafi (2002) Heavy metals concentration levels in some fish species in the red sea and gulf of Aden-Yemen. Qatar Univ Sci J 22:171–176
Ponder SM, Darab JG, Mallouk TE (2000) Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 34:2564–2569
Pradeep T, Anshup (2009) Noble metal nanoparticles for water purification: a critical review. Thin Solid Films 517:6441–6478
Quintelas C, Rocha Z, Silva B, Fonseca B, Figueiredo H, Tavares T (2009) Removal of Cd(II), Cr(VI), Fe(III) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by an E. coli biofilm supported on kaolin. Chem Eng J 149:319–324
Reed BE, Arunachalam S, Thomas B (1994) Removal of lead and cadmium from aqueous streams using granular activated carbon columns. Environ Prog 13:60–64
Saleh TA, Gupta VK (2012) Column with CNT/magnesium oxide composite for lead(II) removal from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0670-6
Schulte J (2005) Nanotechnology: global strategies, industry trends and applications. Wiley, England
Sen P, Ghosh J, Alqudami A, Kumar P, Vandana (2003) Novel process and apparatus for producing metal nanoparticles. Indian Patent 840/Del/03; (2004) PCT/IN2004/000067; (2004) International Publication No WO 2004/112997; World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Paris; (2007) US Patent Appl. No 20070101823
Shakweer LM, Abbas MM (1997) Heavy metals concentration levels in some fish species of Lake Mariut and the Nozha Hydrodrome, Egypt during 1974 and 1995. Bull Natl Inst Oceanogr Fish (Egypt) 23:167–186
Singh NK, Alqudami A, Annapoorni S (2010) ZnO nanoparticles prepared by an electroexploding wire technique. Phys Status Solidi A 207:2153–2158
Srivastava SK, Bhattacharjee G, Tyagi R, Pant N, Pal N (1988) Studies on the removal of some toxic metal ions from aqueous solutions and industrial waste part I—removal of lead and cadmium by hydrous iron and aluminium oxide. Environ Technol Lett 9:1173–1185
Srivastava SK, Tyagi R, Pant N, Pal N (1989) Studies on the removal of some toxic metal ions part II—removal of lead and cadmium by montmorillonite and kaolinite. Environ Technol Lett 10:275–282
Srivastava SK, Gupta VK, Mohan D (1997) Removal of lead and chromium by activated slag—a blast-furnace waste. J Environ Eng 123(5):461–468
Tarun KN, Ashim KB, Sudip KD (2009) Adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions on activated alumina. J Colloid Interface Sci 333:14–26
Theodore L, Kunz RG (2005) Nanotechnology: environmental implications and solutions. Wiley, Hoboken
Tien DC, Liao CY, Huang JC, Tseng KH, Lung JK, Tsung TT, Kao WS, Tsai TH, Cheng TW, Yu BS, Lin HM, Stobinski L (2008) Novel technique for preparing a nano-silver water suspension by the arc-discharge method. Rev Adv Mater Sci 18:750–756
Tiwari DK, Behari J, Sen P (2008) Application of nanoparticles in waste water treatment. World Appl Sci J 3:417–433
USEPA (2006) 2006 Edition of the drinking water standards and health advisories. USEPA, Washington, DC
Zhang H, Jin Z, Han L, Qin C (2006) Synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on exfoliated graphite for removal of nitrate. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 16(Supp. 1):s345–s349
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Yemeni Ministry of Higher Education & Scientific Research (President of the Republic Award, first period 2009). The authors thank the technicians of the Chemistry Department, Ibb University for their cooperative help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vinod Kumar Gupta
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alqudami, A., Alhemiary, N.A. & Munassar, S. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from water by Fe and Ag nanoparticles prepared using electro-exploding wire technique. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 2832–2841 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0788-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0788-1