Abstract
Purpose
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a risk factor for the development of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Apnea overloads the autonomic cardiovascular control system and may influence blood pressure variability, a risk for vascular damage independent of blood pressure levels. This study investigates the hypothesis that blood pressure variability is associated with OSA.
Methods
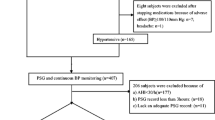
In a cross-sectional study, 107 patients with hypertension underwent 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and level III polysomnography to detect sleep apnea. Pressure variability was assessed by the first derivative of blood pressure over time, the time rate index, and by the standard deviation of blood pressure measurements. The association between the apnea–hypopnea index and blood pressure variability was tested by univariate and multivariate methods.
Results
The 57 patients with apnea were older, had higher blood pressure, and had longer duration of hypertension than the 50 patients without apnea. Patients with apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) ≥ 10 had higher blood pressure variability assessed by the standard deviation than patients with AHI < 10 during sleep (10.4 ± 0.7 versus 8.0 ± 0.7, P = 0.02) after adjustment for age, body mass, and blood pressure. Blood pressure variability assessed by the time rate index presented a trend for association during sleep (P = 0.07). Daytime blood pressure variability was not associated with the severity of sleep apnea.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea increases nighttime blood pressure variability in patients with hypertension and may be another pathway linking sleep abnormalities to cardiovascular disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tufik S, Santos-Silva R, Taddei JA, Bittencourt LR (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in the Sao Paulo Epidemiologic Sleep Study. Sleep Med 11:441–446
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J (2000) Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med 342:1378–1384
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee (2003) The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289:2560–2572
Yumino D, Redolfi S, Ruttanaumpawan P, Su MC, Smith S, Newton GE, Bradley TD (2010) Nocturnal rostral fluid shift: a unifying concept for the pathogenesis of obstructive and central sleep apnea in men with heart failure. Circulation 121:1598–1605
Yaggi HK, Concato J, Kernan WN, Lichtman JH, Brass LM, Mohsenin V (2005) Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N Engl J Med 353:2034–2041
Dempsey JA, Veasey SC, Morgan BJ, O'Donnell CP (2010) Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol Rev 90:47–112. doi:10.1152/physrev.00043.2008
Bradley TD, Floras JS (2009) Obstructive sleep apnoea and its cardiovascular consequences. Lancet 373:82–93
Floras JS, Hassan MO, Jones JV, Osikowska BA, Sever PS, Sleight P (1988) Factors influencing blood pressure and heart rate variability in hypertensive humans. Hypertension 11:273–81
Grassi G (2009) Assessment of sympathetic cardiovascular drive in human hypertension. Hypertension 54:690–97
Richter Y, Edelman ER (2006) Cardiology is flow. Circulation 113:2679–2682
Hansen TW, Thijs L, Li Y, Boggia J, Kikuya M, Björklund-Bodegård K, Richart T, Ohkubo T, Jeppesen J, Torp-Pedersen C, Dolan E, Kuznetsova T, Stolarz-Skrzypek K, Tikhonoff V, Malyutina S, Casiglia E, Nikitin Y, Lind L, Sandoya E, Kawecka-Jaszcz K, Imai Y, Wang J, Ibsen H, O'Brien E, Staessen JA, International Database on Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Relation to Cardiovascular Outcomes Investigators (2010) Prognostic value of reading-to-reading blood pressure variability over 24 hours in 8938 subjects from 11 populations. Hypertension 55:1049–1057
Hansen TW, Li Y, Staessen JA (2009) Blood pressure variability remains an elusive predictor of cardiovascular outcome. Am J Hypertens 22:3–4
Planès C, Leroy M, Fayet G, Aegerter P, Foucher A, Raffestin B (2002) Exacerbation of sleep-apnoea related nocturnal blood-pressure fluctuations in hypertensive subjects. Eur Respir J 20:151–157
Frattola A, Parati G, Cuspidi C, Albini F, Mancia G (1993) Prognostic value of 24-h blood pressure variability. J Hypertens 11:1133–1137
Parati G, Casadei R, Gropelli A, di Rienzo M, Mancia G (1989) Comparison of finger and intra-arterial blood pressure monitoring at rest and during laboratory testing. Hypertension 13:747–755
Zakopoulos NA, Tsivgoulis G, Barlas G, Papamichael C, Spengos K, Manios E, Ikonomidis I, Kotsis V, Spiliopoulou I, Vemmos K, Mavrikakis M, Moulopoulos SD (2005) Time rate of blood pressure variation is associated with increased common carotid artery intima–media thickness. Hypertension 45:505–512
Kikuya M, Hozawa A, Ohokubo T, Tsuji I, Michimata M, Matsubara M, Ota M, Nagai K, Araki T, Satoh H, Ito S, Hisamichi S, Imai Y (2000) Prognostic significance of blood pressure and heart rate variabilities. Hypertension 36:901–906
Mena L, Pintos S, Queipo NV, Aizpurua JA, Maestre G, Sulbaran T (2005) A reliable index for the prognostic significance of blood pressure variability. J Hypertens 23:505–511
Stamatelopoulos KS, Manios E, Barlas G, Koroboki E, Zacharoulis A, Tsivgoulis G, Kollias G, Kyrkou K, Tsigas N, Papamichael CM, Zakopoulos NA (2010) Time rate of blood pressure variation is superior to central hemodynamics as an associate of carotid intima–media thickness. J Hypertens 28:51–58
Zakopoulos NA, Tsivgoulis G, Barlas G, Spengos K, Manios E, Ikonomidis I, Toumanidis S, Dolianitis K, Vemmos K, Vassilopoulos D, Moulopoulos SD (2006) Impact of the time rate of blood pressure variation on left ventricular mass. J Hypertens 24:2071–2077
Manios E, Tsagalis G, Tsivgoulis G, Barlas G, Koroboki E, Michas F, Alexaki E, Vemmos K, Zakopoulos N (2009) Time rate of blood pressure variation is associated with impaired renal function in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 27:2244–2248
Wittke E, Fuchs SC, Fuchs FD, Moreira LB, Ferlin E, Cichelero FT, Moreira CM, Neyeloff J, Moreira MB, Gus M (2010) Association between different measurements of blood pressure variability by ABP monitoring and ankle–brachial index. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 10–55
Gonçalves SC, Martinez D, Gus M, de Abreu-Silva EO, Bertoluci C, Dutra I, Branchi T, Moreira LB, Fuchs SC, de Oliveira AC, Fuchs FD (2007) Obstructive sleep apnea and resistant hypertension: a case–control study. Chest 132:1858–1862
Oliveira AT, Marinez D, Vasconcelos LFT, Gonçalves SC, Lenz MC, Fuchs SC, Gus M, Abreu-Silva EO, Moreira LB, Fuchs FD (2009) Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and its outcomes with home portable monitoring. Chest 135:330–336
Somers VK, Dyken ME, Clary MP, Abboud FM (1995) Sympathetic neural mechanisms in obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Invest 96:1897–1904
Gus M, Gonçalves SC, Martinez D, de Abreu Silva EO, Moreira LB, Fuchs SC, Fuchs FD (2008) Risk for obstructive sleep apnea by Berlin Questionnaire, but not daytime sleepiness, is associated with resistant hypertension: a case–control study. Am J Hypertens 21:832–835
Bianchi MT, Cash SS, Mietus J, Peng CK, Thomas R (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea alters sleep stage transition dynamics. PLoS One 5(6):e11356. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011356
Lenz MC, Martinez D (2007) Awakenings change results of nighttime ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Blood Press Monit 12:9–15
Eguchi K, Ishikawa J, Hoshide S, Pickering TG, Schwartz JE, Shimada K, Kario K (2009) Night time blood pressure variability is a strong predictor for cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Hypertens 22:46–51
Acknowledgment
This study was partially funded by Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa (CNPq), Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS), and Fundo de Incentivo a Pesquisa (FIPE), Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre.
Conflicts of interest
None to declare
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinhorst, A.P., Gonçalves, S.C., Oliveira, A.T. et al. Influence of sleep apnea severity on blood pressure variability of patients with hypertension. Sleep Breath 18, 397–401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-013-0899-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-013-0899-z