Abstract
Purpose
In this cross-sectional study, we analyzed the potential association between sleep measures and blood pressure variability.
Methods
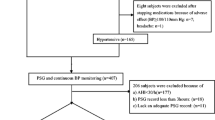
Ninety-three middle-aged hypertensive males, who underwent polysomnography and 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, were enrolled. Blood pressure variability was assessed by blood pressure standard deviation. Obstructive sleep apnea (apnea hypopnea index ≥ 15) was diagnosed in 52 (55.91%) patients. Mean body mass index and age were 27.77 ± 3.11 kg/m2 and 44.05 ± 8.07 years, respectively.
Results
Hypertensive males with obstructive sleep apnea showed significantly higher 24-h, diurnal, and nocturnal diastolic blood pressure variability, compared to those without obstructive sleep apnea. While total cohort was further divided into two groups using the median of oxygen desaturation index, another indicator for severity of OSA, significant differences were also observed in 24-h, diurnal, and nocturnal diastolic blood pressure variability between two groups with higher and lower oxygen desaturation index. While subjects were also divided into two groups via the mean of sleep stage 1, hypertensive males with sleep stage 1 ≥ 8.1% showed significantly higher diurnal diastolic blood pressure variability than those with sleep stage 1 < 8.1%. Apnea hypopnea index was independently associated with 24-h and nocturnal diastolic blood pressure variability; oxygen desaturation index of 3% with 24-h diastolic, diurnal, and nocturnal diastolic blood pressure; and sleep stage 1 was with 24-h and with diurnal diastolic blood pressure variability in all study subjects.
Conclusion
Effects of obstructive sleep apnea on blood pressure variability may not be limited nocturnally.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHI:
-
Apnea/hypopnea index
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- BPV:
-
Blood pressure variability
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- ESS:
-
Epworth sleepiness scale
- FBG:
-
Fasting blood glucose
- HbA1C:
-
hemoglobin A1C
- LSaO2 :
-
Lowest oxyhemoglobin saturation
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- N1:
-
Sleep 1 stage
- ODI3 :
-
oxygen desaturation index of 3%
- OSA:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
- PSG:
-
Polysomnography
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- CPAP:
-
Continuous positive airway pressure
References
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J (2005) Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 365:217–223
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Duran J, Esnaola S, Rubio R et al (2001) Obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea and related clinical features in a population-based sample of subjects aged 30 to 70 yr. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:685–689
Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK et al (2000) Association of sleep disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep Heart Health Study JAMA 283:1829–1836
Cano-Pumarega I, Duran-Cantolla J, Aizpuru F et al (2011) Obstructive sleep apnea and systemic hypertension: longitudinal study in the general population: the Vitoria Sleep Cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 184:1299–1304
Sega R, Corrao G, Bombelli M et al (2002) Blood pressure variability and organ damage in a general population: results from the PAMELA study (Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni). Hypertension 39:710–714
Mancia G, Parati G, Hennig M et al (2001) Relation between blood pressure variability and carotid artery damage in hypertension: baseline data from the European Lacidipine Study on Atherosclerosis (ELSA). J Hypertens 19:1981–1989
Steinhorst AP, Gonçalves SC, Oliveira AT et al (2014) Influence of sleep apnea severity on blood pressure variability of patients with hypertension. Sleep Breath 18:397–401
Walter LM, Yiallourou SR, Vlahandonis A et al (2013) Impaired blood pressure control in children with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 14:858–866
Leroy M, Van Surell C, Pilliere R et al (1996) Short-term variability of blood pressure during sleep in snorers with or without apnea. Hypertension 28:937–943
Shi J, Piao J, Liu B, Pan Y, Gong Y, Deng X, Sun W, Lu S, Li Y (2017) Obstructive sleep apnea increases systolic and diastolic blood pressure variability in hypertensive patients. Blood Press Monit 22(4):208–212. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBP.0000000000000259
Kohei N, Naohiko O, Minako S et al (2008) Diurnal blood pressure variation in patients with sleep apnea syndrome. Hypertens Res 31:185–191
Hedner JA, Wilcox I, Grunstein RR et al (1992) A potent pressor response in awake sleep apnea patients. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:1240–1245
Ian W, Ronald RG, Jan A (1993) Effect of nasal continuous positive airway pressure during sleep on 24-hour blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 16:539–544
Mayumi S, Kuniaki O, Christian G (1993) Long-term nasal continuous positive airway pressure administration can normalize hypertension in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep 16:545–549
Camilla M, Hoyos BJ, Yee KK, et al (2015) Treatment of Sleep Apnea With CPAP Lowers Central and Peripheral Blood Pressure Independent of the Time-of-Day: A Randomized Controlled Study. Am J Hypertens 28(10):1222–1228. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpv023
Nigam G, Camacho M, Riaz M (2017) Rapid Eye Movement (REM) rebound on initial exposure to CPAP therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Sci Pract 1:13
Cooper VL, Elliott MW, Pearson SB et al (2007) Daytime variability of baroreflex function in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: implications for hypertension. Exp Physiol 92:391–398
Toschi-Dias E, Trombetta IC, Dias da Silva VJ et al (2013) Time delay of baroreflex control and oscillatory pattern of sympathetic activity in patients with metabolic syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304:1038–1044
Wadhwa H, Gradinaru C, Gates GJ et al (2008) Impact of intermittent hypoxia on long-term facilitation of minute ventilation and heart rate variability in men and women: do sex differences exist? J Appl Physiol 104:1625–1633
Carlson J, Hedner JA, Elam M, Ejnell H, Wallin G (1991) Augmented sympathetic activity in awake patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Res 20A:297
Bao X, Nelesen RA, Loredo JS et al (2002) Blood pressure variability in obstructive sleep apnea: role of sympathetic nervous activity and effect of continuous positive airway pressure. Blood Press Monit 7(6):301–307
Li Y, Vgontzas AN, Fernandez-Mendoza J et al (2015) Insomnia with physiological hyperarousal is associated with hypertension. Hypertension 65:644–650
Chouchou F, Pichot V, Pépin JL, Tamisier R et al (2013) Sympathetic overactivity due to sleep fragmentation is associated with elevated diurnal systolic blood pressure in healthy elderly subjects: the PROOF-SYNAPSE study. Eur Heart J 34:2122–2131
Mokhlesi B, Finn LA, Hagen EW, Young T, Hla KM, Van Cauter E, Peppard PE (2014) Obstructive Sleep Apnea during REM Sleep and Hypertension Results of the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190(10):1158–1167
Carreras A, Zhang SX, Peris E et al (2014) Chronic sleep fragmentation induces endothelial dysfunction and structural vascular changes in mice. Sleep 37:1817–1824
Blasi A, Jo J, Valladares E et al (2003) Cardiovascular variability after arousal from sleep: time-varying spectral analysis. J Appl Physiol 95:1394–1404
Portaluppi F, Cortelli P, Avoni P et al (1994) Diurnal blood pressure variation and hormonal correlates in fatal familial insomnia. Hypertension 23:569–576
Liang S, Li N, Heizhati M et al (2014) What do changes in concentrations of serum surfactant proteins A and D in OSA mean? Sleep Breath. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1106-6
Kurtz TW, Lujan HL, DiCarlo SE (2014) The 24h pattern of arterial pressure in mice is determined mainly by heart rate-driven variation in cardiac output. Physiol Rep 2(11):e12223
Elstad M, Walløe L, Holme NL et al (2015) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia stabilizes mean arterial blood pressure at high-frequency interval in healthy humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 115:521–530
Fletcher EC, Lesske J, Qian W et al (1992) Repetitive, episodic hypoxia causes diurnal elevation of blood pressure in rats. Hypertension 19:555–561
Boudreau P, Yeh WH, Dumont GA et al (2013) Circadian variation of heart rate variability across sleep stages. Sleep 36:1919–1928
Scheer FA, Van Montfrans GA, van Someren EJ et al (2004) Daily nighttime melatonin reduces blood pressure in male patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 43:192–197
Sharma SK, Agrawal S, Damodaran D et al (2011) CPAP for the metabolic syndrome in patients with obstructive sleep apnea[J]. N Engl J Med 365:2277–2286
Noda A, Nakata S, Koike Y et al (2007) Continuous positive airway pressure improves daytime baroreflex sensitivity and nitric oxide production in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Hypertens Res 30:669–676
Silvani A, Calandra-Buonaura G, Benarroch EE et al (2015) Bidirectional interactions between the baroreceptor reflex and arousal: an update. Sleep Med 16:210–216
Funding
Government of China provided financial support in the form of National Natural Science Foundation (8,360,051 and 8,165,002). The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This study is in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or National Research Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, L., Heizhati, M., Yao, X. et al. Influences of obstructive sleep apnea on blood pressure variability might not be limited only nocturnally in middle-aged hypertensive males. Sleep Breath 22, 377–384 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-017-1571-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-017-1571-9