Abstract
Purpose
[18F]ML-10 is the most advanced radiopharmaceutical for the clinical imaging of the apoptosis phenomenon by PET. The preparation of this radiopharmaceutical on a commercial radiosynthesis module and the requested quality controls for its release are presented herein.
Procedures
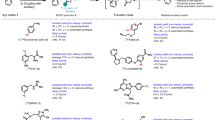
ML-10 as reference and its mesyloxy derivative as precursor for labelling with fluorine-18 were prepared. [18F]ML-10 was synthesized via a [18F]fluorine-de-mesyloxy aliphatic nucleophilic substitution via a GE TRACERLab® FX-FN module. Quality controls were performed.
Results
The labelling precursor was obtained in a four step synthesis in 28 % overall yield affording ML-10 in two steps (88 % yield). Pure [18F]ML-10 was obtained with a decay corrected yield of 39.8 % ± 8.4 % (n = 7) in 70 min and a specific activity of 235 ± 85 GBq/μmol at the end of synthesis.
Conclusions
[18F]ML-10 was prepared on a widely available automated module and passed the quality control. A LC/MS method was developed to measure specific radioactivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor RC, Cullen SP, Martin SJ (2008) Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:231–241
Faust A, Hermann S, Wagner S et al (2009) Molecular imaging of apoptosis in vivo with scintigraphic and optical biomarkers—a status report. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 9:968–985
Blankenberg FG (2008) In vivo imaging of apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1525–1532
Blankenberg FG (2008) In vivo detection of apoptosis [proceeding]. J Nucl Med 49(Suppl 2):81S–95S
De Saint-Hubert M, Prinsen K, Mortelmans L, Verbruggen A, Mottaghy FM (2009) Molecular imaging of cell death. Methods 48:178–187
Lahorte CM, Vanderheyden JL, Steinmetz N et al (2004) Apoptosis-detecting radioligands: current state of the art and future perspectives. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31:887–919
Nguyen QD, Aboagye EO (2010) Imaging the life and death of tumors in living subjects: preclinical PET imaging of proliferation and apoptosis. Integr Biol (Cambridge) 2:483–495
Michalski MH, Chen X (2011) Molecular imaging in cancer treatment. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:358–377
Haberkorn U, Markert A, Mier W, Askoxylakis V, Altmann A (2011) Molecular imaging of tumor metabolism and apoptosis. Oncogene 30:4141–4151
Aboagye EO (2010) The future of imaging: developing the tools for monitoring response to therapy in oncology: the 2009 Sir James MacKenzie Davidson Memorial lecture [proceeding]. Br J Radiol 83:814–822
Reshef A, Shirvan A, Akselrod-Ballin A, Wall A, Ziv I (2010) Small-molecule biomarkers for clinical PET imaging of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 51:837–840
Cohen A, Shirvan A, Levin G et al (2009) From the Gla domain to a novel small-molecule detector of apoptosis. Cell Res 19:625–637
Reshef A, Shirvan A, Waterhouse RN et al (2008) Molecular imaging of neurovascular cell death in experimental cerebral stroke by PET. J Nucl Med 49:1520–1528
Hoglund J, Shirvan A, Antoni G et al (2011) 18F-ML-10, a PET tracer for apoptosis: first human study. J Nucl Med 52:720–725
Larson S (2010) Newsline, oncology. J Nucl Med 51:19N–25N
Mock B, Winkle W, Vavrek M (1997) A color spot test for the detection of Kryptofix 2.2.2 in [18F]FDG preparations. Nucl Med Biol 24:193–195
Klok RP, Windhorst AD (2006) Residual solvent analysis by gas chromatography in radiopharmaceutical formulations containing up to 12 % ethanol. Nucl Med Biol 33:935–938
Mahidhar YV, Rajesh M, Chaudhuri A (2004) Spacer-arm modulated gene delivery efficacy of novel cationic glycolipids: design, synthesis, and in vitro transfection biology. J Med Chem 47:3938–3948
Ziv I, Shirvan A (2005) NST Neurosurvival technologies Ltd. Perturbed membrane-binding compounds and methods of using the same [patent]. WO/2005/067388
Acknowledgements
We thank O. Tirel for performing the cyclotron irradiation. This work was supported by the “Région de Basse-Normandie” and the “Commissariat à l’énergie atomique et aux énergies alternatives” (CEA).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sobrio, F., Médoc, M., Martial, L. et al. Automated Radiosynthesis of [18F]ML-10, a PET Radiotracer Dedicated to Apoptosis Imaging, on a TRACERLab FX-FN Module. Mol Imaging Biol 15, 12–18 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-012-0574-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-012-0574-y