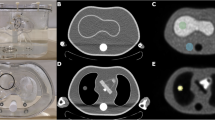
Abstract
Purpose
The presence of contrast materials on computed tomography (CT) images can cause problems in the attenuation correction of positron emission tomography (PET) images. These are because of errors converting the CT attenuation of contrast to 511-keV attenuation and by the change in tissue enhancement over the duration of the PET emission scan. Newer CT-based attenuation correction (CTAC) algorithms have been developed to reduce these errors.
Methods
To evaluate the effectiveness of the modified CTAC technique, we performed a retrospective analysis on 20 patients, comparing PET images using unenhanced and contrast-enhanced CT scans for attenuation correction. A phantom study was performed to simulate the effects of contrast on radiotracer concentration measurements.
Results
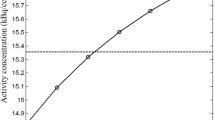
There was a maximum difference in calculated radiotracer concentrations of 5.9% within the retrospective data and 7% within the phantom data.
Conclusion
Using a CTAC algorithm that de-emphasizes high-density areas, contrast-enhanced CT can be used for attenuation mapping without significant errors in quantitation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kinahan PE, Hasegawa BH, Beyer T (2003) X-ray based attenuation correction for positron emission tomography/computed tomography scanners. Semin Nucl Med 33:166–179
Kinahan PE, Townsend DW, Beyer T, Sashin D (1998) Attenuation correction for a combined 3D PET/CT scanner. Med Phys 25:2046–2053 (Oct.)
LaCroix KJ, Tsui BMW, Hasegawa BH, Brown JK, et al. (1994) Investigation of the use of x-ray CT images for attenuation compensation in SPECT. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci NS-41:2793–2799
Burger C, Goerres G, Schoenes S, Buck A, et al. (2002) PET attenuation coefficients from CT images: experimental evaluation of the transformation of CT into PET 511 keV attenuation coefficients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag 29:922–927
Antoch G, Freudenberg LS, Egelhof T, Stattaus J, et al. (2002) Focal tracer uptake: A potential artifact in contrast enhanced dual-modality PET/CT scans. J Nucl Med 43:1339–1342
Visvikis D, Costa DC, Croasdale I, Lonn AHR, et al. (2003) CT-based attenuation correction in the calculation of semi-quantitative indices of [18F] FDG uptake in PET. Eur J Nucl Med 30:344–353
Nakamoto Y, Chin BB, Kraitchman DL, Lawler LP, et al. (2003) Effects of nonionic intravenous contrast agents at PET/CT imaging: phantom and canine studies. Radiology 227:817–824
Nehmeh SA, Erdi YE, Kalaigian H, Kolbert KS, et al. (2003) Correction for oral contrast artifacts in CT attenuation-corrected PET images obtained by combined PET/CT. J Nucl Med 44:1940–1944
Dizendorf E, Hany TF, Buck A, von Schulthess GK, et al. (2003) Cause and magnitude of the error induced by oral contrast agent in CT-based attenuation correction of PET emission studies. J Nucl Med 44:732–738
Antoch G, Jentzen W, Freudenberg LS, Stattaus J, et al. (2003) Effect of oral contrast on computed tomography based positron emission tomography attenuation correction in dual-modality positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging. Invest Radiol 38:784–789
Lonn AHR (2003) Evaluation of method to minimize the effect of X-ray contrast in PET-CT attenuation correction. Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record IEEE 3:2220–2221
Antoch G, Freudenberg LS, Stattaus J, Jentzen W, et al. (2002) Whole body positron emission tomography-CT: Optimized CT using oral and IV contrast materials. AJR 179:1555–1560
Yau YY, Chan WS, Tam YM, Vernon P, et al. (2005) Application of intravenous contrast in PET/CT: does it really introduce significant attenuation correction error? J Nucl Med 46:283–291
Berthelsen AK, Holm S, Loft A, Klausen TL, Andersen F, Hojgaard L (2005) PET/CT with intravenous contrast can be used for PET attenuation correction in cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:1167–1175
Yau YY, Chan WS, Tam YM, Vernon P, Wong S, Coel M, Chu SK (2005) Application of intravenous contrast in PET/CT: does it really introduce significant attenuation correction error? J Nucl Med 46:283–291
Mawlawi O, Erasmus JJ, Munden RF, Pan T, Knight AE, Macapinlac HA, Podoloff DA, Chasen M (2006) Quantifying the effect of IV contrast media on integrated PET/CT: clinical evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:308–319
Beyer T, Antoch G, Blodgett T, Freudenberg LF, et al. (2003) Dual-modality PET/CT imaging: the effect of respiratory motion on combined image quality in clinical oncology. Eur J Nucl Med 30:588–596
Pan T, Mawlawi O, Nehmeh SA, Erdi YE, Luo D, Liu HH, Castillo R, Mohan R, Liao Z, Macapinlac HA (2005) Attenuation correction of PET images with respiration-averaged CT images in PET/CT. J Nucl Med 46:1481–1487
Weber WA (2005) Use of PET for monitoring cancer therapy and for predicting outcome. J Nucl Med 46:983–995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bunyaviroch, T., Turkington, T.G., Wong, T.Z. et al. Quantitative Effects of Contrast Enhanced CT Attenuation Correction on PET SUV Measurements. Mol Imaging Biol 10, 107–113 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-007-0126-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-007-0126-z