Abstract
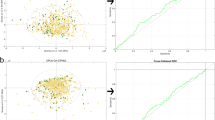
This study reports an accurate assignment of the resonance signals present in 1H-NMR spectra of human blood plasma. Hereto, blood plasma was spiked with 32 different metabolites in relevant concentrations since reported chemical shift values show quite some variability depending on the biofluid under study and the applied experimental measuring conditions. The resulting information was used to rationally divide the 1H-NMR spectrum in 110 well-defined integration regions for application in metabolomics. A case–control dataset of 53 breast cancer patients and 52 controls was investigated in order to demonstrate the proof of principle. After removal of noisy variables, i.e. variables exceeding a premised threshold for the coefficient of variation, the groups could be discriminated by OPLS-DA multivariate statistics with a sensitivity and specificity of 83 and 94 %, respectively. In addition, the classification was validated in a small but independent cohort. The proposed methodology might pave the way towards a better understanding of disturbances in disease-related biochemical pathways and so, to the clinical relevance of study findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1H:
-
Proton
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CPMG:
-
Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill
- ChEBI:
-
Chemical Entities of Biological Interest
- D2O:
-
Deuterium oxide
- DCIS:
-
Ductal carcinoma in situ
- DModX:
-
Distance to model
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- GC:
-
Gas chromatography
- IDA:
-
Invasive ductal adenocarcinoma
- ILA:
-
Invasive lobular adenocarcinoma
- IUPAC-IUB:
-
Nomenclature committee of the international union of biochemistry
- LC:
-
Liquid chromatography
- MHz:
-
Megahertz
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- OPLS-DA:
-
Orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- ppm:
-
Parts per million
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- RF:
-
Radio frequency
- S/N:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- TSP:
-
Trimethylsilyl-2,2,3,3-tetradeuteropropionic acid
References
Beckonert, O., Keun, H. C., Ebbels, T. M., Bundy, J., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., et al. (2007). Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nature Protocols, 2(11), 2692–2703.
Chang, D., Weljie, A., & Newton, J. (2007). Leveraging latent information in NMR spectra for robust predictive models. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, 12, 115–126.
Craig, A., Cloarec, O., Holmes, E., Nicholson, J. K., & Lindon, J. C. (2006). Scaling and normalization effects in NMR spectroscopic metabonomic data sets. Analytical Chemistry, 78(7), 2262–2267.
Engelke, U. F., Liebrand-van Sambeek, M. L., de Jong, J. G., Leroy, J. G., Morava, E., Smeitink, J. A., et al. (2004). N-acetylated metabolites in urine: proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study on patients with inborn errors of metabolism. Clinical Chemistry, 50(1), 58–66.
Fiehn, O. (2002). Metabolomics–the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Molecular Biology, 48(1–2), 155–171.
Garcia, E., Andrews, C., Hua, J., Kim, H. L., Sukumaran, D. K., Szyperski, T., et al. (2011). Diagnosis of early stage ovarian cancer by 1H-NMR metabonomics of serum explored by use of a microflow NMR probe. Journal of Proteome Research, 10(4), 1765–1771.
German, J. B., Hammock, B. D., & Watkins, S. M. (2005). Metabolomics: Building on a century of biochemistry to guide human health. Metabolomics, 1(1), 3–9.
Kohl, S. M., Klein, M. S., Hochrein, J., Oefner, P. J., Spang, R., & Gronwald, W. (2012). State-of-the art data normalization methods improve NMR-based metabolomic analysis. Metabolomics, 8(Suppl 1), 146–160.
Lindon, J. C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2008). Spectroscopic and statistical techniques for information recovery in metabonomics and metabolomics. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry (Palo Alto Calif), 1, 45–69.
Markley, J. L., Ulrich, E. L., Berman, H. M., Henrick, K., Nakamura, H., & Akutsu, H. (2008). BioMagResBank (BMRB) as a partner in the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB): New policies affecting biomolecular NMR depositions. Journal of Biomolecular NMR, 40(3), 153–155.
Nicholson, J. K., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (1999). ‘Metabonomics’: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica, 29(11), 1181–1189.
Nicholson, J. K., & Wilson, I. D. (2003). Opinion: Understanding ‘global’ systems biology: Metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2(8), 668–676.
O’Connell, T. M. (2012). Recent advances in metabolomics in oncology. Bioanalysis, 4(4), 431–451.
Oostendorp, M., Engelke, U. F., Willemsen, M. A., & Wevers, R. A. (2006). Diagnosing inborn errors of lipid metabolism with proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clinical Chemistry, 52(7), 1395–1405.
Salek, R. M., Maguire, M. L., Bentley, E., Rubtsov, D. V., Hough, T., Cheeseman, M., et al. (2007). A metabolomic comparison of urinary changes in type 2 diabetes in mouse, rat, and human. Physiological Genomics, 29(2), 99–108.
Staab, J. M., O’Connell, T. M., & Gomez, S. M. (2010). Enhancing metabolomic data analysis with Progressive Consensus Alignment of NMR Spectra (PCANS). BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 123.
van den Berg, R. A., Hoefsloot, H. C., Westerhuis, J. A., Smilde, A. K., & van der Werf, M. J. (2006). Centering, scaling, and transformations: improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics, 7, 142.
Wang, L., Chen, J., Chen, L., Deng, P., Bu, Q., Xiang, P., et al. (2013). 1H-NMR based metabonomic profiling of human esophageal cancer tissue. Molecular Cancer, 12, 25.
Wishart, D. S. (2008). Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27(3), 228–237.
Wishart, D. S., Jewison, T., Guo, A. C., Wilson, M., Knox, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2013). HMDB 3.0–The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Research, 41, D801–D807.
Wishart, D. S., Tzur, D., Knox, C., Eisner, R., Guo, A. C., Young, N., et al. (2007). HMDB: the Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, D521–D526.
Yang, W. J., Wang, Y. W., Zhou, Q. F., & Tang, H. R. (2008). Analysis of human urine metabolites using SPE and NMR spectroscopy. Science in China Series B-Chemistry, 51(3), 218–225.
Zheng, C., Zhang, S., Ragg, S., Raftery, D., & Vitek, O. (2011). Identification and quantification of metabolites in 1H-NMR spectra by Bayesian model selection. Bioinformatics, 27(12), 1637–1644.
Acknowledgments
This study is part of the Limburg Clinical Research Program UHasselt-ZOL-Jessa, supported by the foundation Limburg Sterk Merk, Hasselt University, Ziekenhuis Oost-Limburg and Jessa Hospital. We thank the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen) for their support via the MULTIMAR scientific research community project. We thank P. Degryse for his valuable contribution to the statistical discussions.
Ethical standards
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors Evelyne Louis and Liene Bervoets contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louis, E., Bervoets, L., Reekmans, G. et al. Phenotyping human blood plasma by 1H-NMR: a robust protocol based on metabolite spiking and its evaluation in breast cancer. Metabolomics 11, 225–236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0690-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0690-6