Abstract
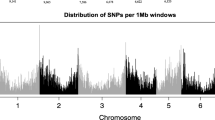
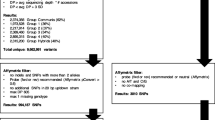
Pecan (Carya illinoinensis) is an outcrossing, highly heterozygous, and slow-to-mature tree native to North America. In order to better understand cultivar characteristics, appreciate regional adaptation, and improve selection in pecan breeding programs, improved genomic tools that are cost-effective and capable of high-throughput screening are necessary. A diverse panel of 108 cultivars and accessions from the National Collection of Genetic Resources for Pecans and Hickories (NCGR-Carya) was selected to represent regionally adapted native pecans, controlled cross progeny and their parents, selected wild relative species, and interspecific hybrids between those species and pecans. We implemented a genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) technique to discover 87,446 informative single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) throughout the pecan genome. SNPs were used to develop genomic profiles to confirm, refute, or inform questions of cultivar origin. Native accessions show strong genetic relationships by geographic region of origin. Matrices were developed to facilitate evaluation of pedigree relationships between cultivars. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) was performed to discover 17 SNPs from a contiguous region significantly associated with the expression of the simply inherited trait controlling flowering type (dichogamy). The information, techniques, and resources developed will benefit the pecan community by improving the ability to characterize germplasm and use marker data for marker-assisted breeding. This should reduce breeding time by facilitating more informed and efficient selection of parents and progeny.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida A, Loy A, Hofman H (2017) qqplotr: quantile-quantile plot extensions for ‘ggplot2’. R package version 0.0.3 initially funded by Google Summer of Code. https://github.com/aloy/qqplotr. Accessed 10 Sept 2018
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Beedanagari SR, Dove SK, Wood BW, Conner PJ (2005) A first linkage map of pecan cultivars based on RAPD and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 110(6):1127–1137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-1944-5
Bemmels JB, Dick CW (2018) Genomic evidence of a widespread southern distribution during the last glacial maximum for two eastern North American hickory species. J Biogeogr 45(8):1739–1750. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.13358
Bilton TP, McEwan JC, Clarke SM, Brauning R, van Stijn TC, Rowe SJ, Dodds KG (2018a) Linkage disequilibrium estimation in low coverage high-throughput sequencing data. Genetics 209(2):389–400. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.118.300831
Bilton TP, Schofield MR, Black MA, Chagne D, Wilcox PL, Dodds KG (2018b) Accounting for errors in low coverage high-throughput sequencing data when constructing genetic maps using biparental outcrossed populations. Genetics 209(1):65–76. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.117.300627
Bock CH, Grauke LJ, Conner P, Burrell SL, Hotchkiss MW, Boykin D, Wood BW (2016) Scab susceptibility of a provenance collection of pecan in three different seasons in the southeastern USA. Plant Dis 100(9):1937–1945. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-12-15-1398-RE
Brooks RM, Olmo HP (1951) Register of new fruit and nut varieties. List 6. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 58:386–404
Brooks RM, Olmo HP (1971) Register of new fruit and nut varieties. List 6. HortScience 6(5):439–442
Burkett JH (1925) The pecan in Texas. Texas Department of Agriculture Bulletin 81:1–218
Burkett JH (1932) The pecan in Texas. Texas Department of Agriculture Bulletin 111:1–239
Cohen JI, Williams JT, Plucknett DL, Shands H (1991) Ex situ conservation of plant genetic resources: global development and environmental concerns. Science 253(5022):866–872. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.253.5022.866
Conner PJ, Wood BW (2001) Identification of pecan cultivars and their genetic relatedness as determined by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126(4):474–480
Crane HL, Reed CA, Wood MN (1937) Nut breeding, vol 1937. USDA Yearbook of Agri, pp 827–889
Dodds KG, McEwan JC, Brauning R, Anderson RM, van Stijn TC, Kristjansson T, Clarke SM (2015) Construction of relatedness matrices using genotyping-by-sequencing data. BMC Genomics 16(1):1047. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2252-3
Doyle J (1991) DNA protocols for plants. In: Hewitt GM, Johnston AWB, Young JPW (eds) Molecular techniques in taxonomy. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 283–293
Grauke LJ (2010) Pecan seed stock selection—regional implications. Proc SE Pecan Grow Assoc 103:42–51
Grauke LJ, Starr JL (2014) Phenotypic screening of pecan seedling rootstocks in search of nematode resistance. Trees 28(5):1333–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1038-6
Grauke LJ, Thompson TE, Marquard RD (1995) Evaluation of pecan [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh) K Koch] germplasm collections and designation of a core subset. HortScience 30(5):950–954
Grauke LJ, Price HJ, Johnston JS (2001) Genome size of pecan as determined by flow cytometry. HortSci 36(4):814–814
Grauke LJ, Iqbal MJ, Reddy AS, Thompson TE (2003a) Developing microsatellite DNA markers in pecan. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 128(3):374–380
Grauke LJ, Storey J, Thompson TE, Wood B (2003b) Leaf structure and nutrient content varies in native pecan populations. Proc Tex Pecan Growers Assoc 70:59–60
Grauke LJ, Mendoza-Herrera MA, Loopstra C, Thomspon TE (2006) Microsatellite markers for verifying parentage of pecans. HortScience 41(3):515–515
Grauke LJ, Mendoza-Herrera MA, Binzel ML (2010) Plastid microsatellite markers in Carya. Acta Hortic (859):237–246. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2010.859.27
Grauke LJ, Mendoza-Herrera MA, Miller AJ, Wood BW (2011) Geographic patterns of genetic variation in native pecans. Tree Genet Genomes 7(5):917–932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0384-4
Grauke LJ, Klein R, Grusak MA, Klein P (2015) The forest and the trees: applications for molecular markers in the repository and pecan breeding program. Acta Hortic (1070):109–126. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2015.1070.12
Grauke LJ, Mendoza-Herrera MA, Stelly DM, Klein PE (2016a) ‘Jones hybrid’ hickory: a case study in Carya curation. Springerplus 5(1):1860. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3531-4
Grauke LJ, Wood BW, Harris MK (2016b) Crop vulnerability: Carya. HortScience 51(6):653–663
He C, Holme J, Anthony J (2014) SNP genotyping: the KASP assay. In: Fleury D, Whitford R (eds) Crop breeding: methods and protocols. Springer New York, New York, pp 75–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0446-4_7
Jenkins J, Wilson B, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Grauke LJ (2015) Towards a reference pecan genome sequence. Acta Hortic (1070):101–108
Kahle D, Wickham H (2013) ggmap: spatial visualization with ggplot2. R J 5(1):144–161
KenKnight G (1970) Pecan varieties “happen” in Jackson County, Mississippi. Pecan Q 4(3):6–7
Khoury CK, Greene SL, Williams KA, Sosa CC, Richards C (2017) Conservation priorities for tree crop wild relatives in the United States. In: Sniezko RA, Man G, Hipkins V, Woeste K, Gwaze D, Kliejunas JT, McTeague BA (Tech. Cords.) (eds) Gene conservation of tree species—banking on the future, Chicago, IL, 16–19 May 2017. pp 31–36
Kim C, Guo H, Kong W, Chandnani R, Shuang LS, Paterson AH (2016) Application of genotyping by sequencing technology to a variety of crop breeding programs. Plant Sci 242:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.04.016
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Li J, Zeng Y, Shen D, Xia G, Huang Y, Huang Y, Chang J, Huang J, Wang Z (2014) Development of SSR markers in Hickory (Carya cathayensis Sarg.) and their transferability to other species of Carya. Curr Genomics 15(5):357–379. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920291505141106103734
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ, Gore MA, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2012) GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 28(18):2397–2399. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts444
Marquard RD (1988) Outcrossing rates in pecan and the potential for increased yields. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 113(1):84–88
Marquard RD (1991) Inheritance of phosphoglucomutase isozymes in pecan. HortScience 26(9):1213–1214
Marquard RD, Grauke LJ, Thompson TE, Janos RS (1995) Identifying pecan cultivars by isozymes and inheritance of leucine aminopeptidase. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 120(4):661–666
Miller MR, Dunham JP, Amores A, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2007) Rapid and cost-effective polymorphism identification and genotyping using restriction site associated DNA (RAD) markers. Genome Res 17(2):240–248. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.5681207
Miyamoto S, Riley T, Gobran G, Petticrew J (1986) Effects of saline water irrigation on soil-salinity, pecan tree growth and nut production. Irrig Sci 7(2):83–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00259425
Morishige DT, Klein PE, Hilley JL, Sahraeian SM, Sharma A, Mullet JE (2013) Digital genotyping of sorghum—a diverse plant species with a large repeat-rich genome. BMC Genomics 14(1):448. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-448
Muranty H, Jorge V, Bastien C, Lepoittevin C, Bouffier L, Sanchez L (2014) Potential for marker-assisted selection for forest tree breeding: lessons from 20 years of MAS in crops. Tree Genet Genomes 10(6):1491–1510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-014-0790-5
National Research Council (1993) Managing global genetic resources: agricultural crop issues and policies. National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Plomion C, Bastien C, Bogeat-Triboulot MB, Bouffier L, Déjardin A, Duplessis S, Fady B, Heuertz M, le Gac AL, le Provost G, Legué V, Lelu-Walter MA, Leplé JC, Maury S, Morel A, Oddou-Muratorio S, Pilate G, Sanchez L, Scotti I, Scotti-Saintagne C, Segura V, Trontin JF, Vacher C (2015) Forest tree genomics: 10 achievements from the past 10 years and future prospects. Ann For Sci 73(1):77–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-015-0488-3
Poland JA, Brown PJ, Sorrells ME, Jannink JL (2012) Development of high-density genetic maps for barley and wheat using a novel two-enzyme genotyping-by-sequencing approach. PLoS One 7(2):e32253. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032253
Postman J et al (2006) Fruit and nut genebanks in the US National Plant Germplasm System. HortScience 41(5):1188–1194
Risien EE (1904) Price list for 1903-1904. West Texas Pecan Nursery, San Saba. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.97697
Risien EE (1916) West Texas pecan nursery [catalog]. West Texas Pecan Nursery, San Saba. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.113179
Romberg L, Smith C (1946) Effects of cross-pollination, self-pollination, and sib-pollination on the dropping, the volume, and the kernel development of pecan nuts and on the vigor of the seedlings. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 47:130–138
Ruter B, Hamrick JL, Wood BW (1999) Genetic diversity within provenance and cultivar germplasm collections versus natural populations of pecan (Carya illinoinensis). J Hered 90(5):521–528. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/90.5.521
Rüter B, Hamrick JL, Wood BW (2000) Outcrossing rates and relatedness estimates in pecan (Carya illinoinensis) populations. J Hered 91(1):72–75
Sagaram M, Lombardini L, Grauke LJ (2011) Variation in anatomical characteristics in leaves of pecan seedstocks from Mexico and the United States. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 136(2):103–108
Sparks D (1995) Western-Schley pecan. Fruit Varieties J 49(2):70–74
Sparks D, Madden GD (1985) Pistillate flower and fruit abortion in pecan as a function of cultivar, time, and pollination. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 110(2):219–223
Stone DE (1962) Affinities of a Mexican endemic, Carya Palmeri, with American and Asian hickories. Am J Bot 49(3):199–212. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1962.tb14930.x
Taylor WA (1905) Promising new fruits. Pecans. Yearbook of the US Department of Agriculture, pp 504–508
Taylor WA (1906) Promising new fruits. Pecans Yearbook of the US Department of Agriculture, pp 365–370
Thompson TE (1990) 1990 update—pecan cultivars: current use and recommendations. Pecan South 24(1):12–17,20
Thompson TE, Grauke LJ (1991) Pecans and other hickories (Carya). Acta Hortic (290):839–906. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.1991.290.19
Thompson TE, Romberg LD (1985) Inheritance of heterodichogamy in pecan. J Hered 76(6):456–458. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110144
Thompson TE, Young F (1985) Pecan cultivars: past and present. Texas Pecan Growers Assoc, College Station
Vendrame WA, Kochert G, Wetzstein HY (1999) AFLP analysis of variation in pecan somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep 18(10):853–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050673
Vendrame WA, Kochert GD, Sparks D, Wetzstein HY (2000) Field performance and molecular evaluations of pecan trees regenerated from somatic embryogenic cultures. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 125(5):542–546
Wang GT, Zhang D, Li B, Dai H, Leal SM (2015) Collapsed haplotype pattern method for linkage analysis of next-generation sequence data. Eur J Hum Genet 23(12):1739–1743. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.64
Wells L (2014) Pecan planting trends in Georgia. HortTechnology 24(4):475–479
Wickham H (2016) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer, New York
Wilkinson JF (1913) Large pecan trees in Indiana and Kentucky. Proc Natl Nut Grow Assoc 12:41–42
Wood BW, Grauke LJ, Payne JA (1998) Provenance variation in pecan. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 123(6):1023–1028
Zedan D (2018) Crop overview 2017 pecan crop update. Presented at 2018 National Pecan Shellers Association Mid-Winter Meeting, March 14–15, San Antonio, Texas. http://www.nffonline.com/sites/default/files/2018%20NPSA%20Mid-Winter%20Meeting%20Presentation.pdf. Accessed 10 September 2018
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service (USDA ARS) CRIS project 6202-21000-036-00D (Management and Characterization of Pecan Genetics Resources and Related Wild Populations), USDA ARS CRIS project 6202-21000-035-00D (Pecan Improvement Through Breeding and Genetics), Specific Cooperative Agreement 58-6202-1-201 (Developing Molecular Markers for Carya), Specific Cooperative Agreement 58-3091-5-031 (Genomic Markers for Carya), USDA Hatch funds, and USDA-SCRI 58-6042-6009 (Coordinated Development of Genetic Tools for Pecan). The authors wish to thank Ms. Natalie Patterson for help in pecan DNA extraction and Illumina template preparation and Ms. Rory Tucker for help in DNA extraction protocol modification. Illumina sequencing was provided by Texas A&M AgriLife Research Genomics and Bioinformatics Services. The authors also thank Linwood Nursery for providing ramets of their proprietary clones. Questions regarding living inventories should be directed to Dr. L.J. Grauke at LJ.Grauke@ars.usda.gov.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.J. Grauke designed the diversity panel and contributed data regarding each accession. Nolan Bentley developed the modified pecan DNA extraction protocol. Patricia Klein analyzed and generated SNP calls from the sequence data. Nolan Bentley wrote the R scripts and performed the downstream analyses of the SNP data. Nolan Bentley wrote the manuscript with revisions and contributions to the interpretation from L.J. Grauke and Patricia Klein.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Troggio
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
Full calls and counts file for 87,446 SNPs (XLSX 126375 kb)
Table S2
Subset calls and counts file of the 40,586 SNPs used in the KGD and genetic distance analyses (XLSX 59027 kb)
Table S3
KGD relatedness value matrix (XLSX 138 kb)
Table S4
Tamura-Nei genetic distance value matrix (XLSX 124 kb)
Fig. S1
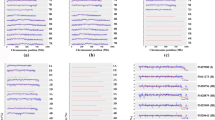
Two-dimensional histogram visualizing the distribution of the average absolute value of the difference in z-score adjusted read depths between adjacent SNPs on the same contig as a function of the bp difference in position measured between the SNPs being compared. The cyan bar shows the maximum value used to group SNPs if they were within 125 bp of each other and likely to represent the same mapped sequence associated with one side of a restriction enzyme site. Each square is a 1 bp difference wide and 0.016 y-unit tall bin with color indicating how many of 54,620 SNP comparisons shown are within its range (PNG 35 kb)
Fig. S2
PCA of KGD relatedness values between samples of pecan (right-side), bitternut hickory (C. cordiformis) (left-side), and bitternut x pecan interspecific hybrids (middle). Northern pecans include samples from MO, IL, IN, and KY. Intermediate pecans include OK and KS. The Mexican pecan is from Oaxaca, MX. San Felipe and Evers show evidence of admixture between Texan, Mexican, and Northern and Texan and Mexican germplasm, respectively. The two interspecific crosses cluster between the bitternut accession and the native pecan cluster that best matched that of their pecan parent (PDF 6 kb)
Fig. S3
Compilation and description of the historical documentation for Longfellow (PDF 2051 kb)
Data archiving statement
The sequences generated in this study have been submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) under the BioProject number PRJNA413769.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bentley, N., Grauke, L.J. & Klein, P. Genotyping by sequencing (GBS) and SNP marker analysis of diverse accessions of pecan (Carya illinoinensis). Tree Genetics & Genomes 15, 8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1314-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1314-5