Abstract
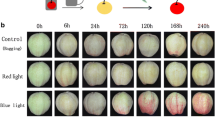
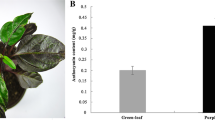
The usual red color of young leaves of peach (Prunus persica f. atropurpurea) is due to the accumulation of anthocyanin. Real-time PCR analysis revealed a strong correlation between the expression levels of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes and anthocyanin content in leaves at different developmental stages. The expression profiles of both anthocyanin biosynthetic genes and photorespiratory genes showed significant changes in leaves held in the dark or exposed to heat stress, compared with controls. The expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes dramatically decreased in peach red leaves following dark or heat treatments, resulting in a significant decrease of anthocyanin accumulation. However, the photorespiration-related genes GDCH and GOX exhibited increased expression in peach leaves after dark or heat treatment. Moreover, the expression levels of GDCH and GOX in the Arabidopsis chi/f3′h mutant that does not accumulate anthocyanins were higher than in the wild type. Overall, these results support the hypothesis that photorespiration-related genes might be involved in the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. This finding provides a new insight into our understanding of the mechanism underlying the control of anthocyanin biosynthesis in plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANS:
-
Anthocyanidin synthase
- bHLH:
-
Basic-helix-loop-helix
- CHI:
-
Chalcone isomerase
- CHS:
-
Chalcone synthase
- DFR:
-
Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
- F3H:
-
Flavanone 3-hydroxylase
- F3′H:
-
Flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase
- GDCH:
-
Glycine decarboxylase complex H protein
- GOX:
-
Glycolate oxidase
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine ammonialyase
- PGP:
-
Phosphoglycolate phosphatase
- Q-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
- RBCO:
-
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase
- RR:
-
Prunus persica f. atropurpurea
- TFs:
-
Transcription factors
- TPI:
-
Triosephosphate isomerase
- UFGT:
-
UDP-glucose:flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase
References
Aharoni A, De Vos CH, Wein M, Sun Z, Greco R, Kroon A, Mol JN, O’Connell AP (2001) The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant J 28:319–332
Ampomah-Dwamena C, McGhie T, Wibisono R, Montefiori M, Hellens RP, Allan AC (2009) The kiwifruit lycopene beta-cyclase plays a significant role in carotenoid accumulation in fruit. J Exp Bot 60:15
Azuma A, Kobayashi S, Mitani N, Shiraishi M, Yamada M, Ueno T, Kono A, Yakushiji H, Koshita Y (2008) Genomic and genetic analysis of Myb-related genes that regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape berry skin. Theor Appl Genet 117:1009–1019
Baudry A, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2006) TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 46:768–779
Baudry A, Heim MA, Dubreucq B, Caboche M, Weisshaar B, Lepiniec L (2004) TT2, TT8, and TTG1 synergistically specify the expression of BANYULS and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 39:366–380
Borevitz JO, Xia Y, Blount J, Dixon RA, Lamb C (2000) Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 12:2383–2394
Broun P (2005) Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis: a complex network of conserved regulators involved in multiple aspects of differentiation in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:8
Butelli E, Titta L, Giorgio M, Mock HP, Matros A, Peterek S, Schijlen EG, Hall RD, Bovy AG, Luo J, Martin C (2008) Enrichment of tomato fruit with health-promoting anthocyanins by expression of select transcription factors. Nat Biotechnol 26:1301–1308
Chang CS, Li YH, Chen LT, Chen WC, Hsieh WP, Shin J, Jane WN, Chou SJ, Choi G, Hu JM, Somerville S, Wu SH (2008) LZF1, a HY5-regulated transcriptional factor, functions in Arabidopsis de-etiolation. Plant J 54:205–219
Cazzonelli CI, Pogson BJ (2010) Source to sink: regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Trends Plant Sci 15:266–274
Chalker-Scott L (1999) Environmental significance of anthocyanins in plant stress responses. Photochem Photobiol 70:9
Coffman JA, Kirchhamer CV, Harrington MG, Davidson EH (1997) SpMyb functions as an intramodular repressor to regulate spatial expression of CyIIIa in sea urchin embryos. Development 124:4717–4727
Dela G, Or E, Ovadia R, Nissim-Levi A, Weiss D, Oren-Shamir M (2003) Changes in anthocyanin concentration and composition in ‘Jaguar’ rose flowers due to transient high-temperature conditions. Plant Sci 164:8
Deshaies RJ, Meyerowitz E (2000) COP1 patrols the night beat. Nat Cell Biol 2:102–104
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1085–1097
Dooner HK, Robbins TP, Jorgensen RA (1991) Genetic and developmental control of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Genet 25:173–199
Dubos C, Le Gourrierec J, Baudry A, Huep G, Lanet E, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Alboresi A, Weisshaar B, Lepiniec L (2008) MYBL2 is a new regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 55:940–953
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty-Amma S, Allan AC (2007) Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J 49:414–427
Feild TS, Lee DW, Holbrook NM (2001) Why leaves turn red in autumn. The role of anthocyanins in senescing leaves of red-osier dogwood. Plant Physiol 127:566–574
Gould KS, Lister C (eds) (2006) Flavonoid functions in plants. CRC, Boca Raton
Grotewold E (2006) The genetics and biochemistry of floral pigments. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:761–780
Hernandez JM, Heine GF, Irani NG, Feller A, Kim MG, Matulnik T, Chandler VL, Grotewold E (2004) Different mechanisms participate in the R-dependent activity of the R2R3 MYB transcription factor C1. J Biol Chem 279:48205–48213
Hoch WA, Zeldin EL, McCown BH (2001) Physiological significance of anthocyanins during autumnal leaf senescence. Tree Physiol 21:1–8
Holton TA, Cornish EC (1995) Genetics and biochemistry of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:1071–1083
Jackson D, Culianez-Macia F, Prescott AG, Roberts K, Martin C (1991) Expression patterns of myb genes from Antirrhinum flowers. Plant Cell 3:115–125
Jang IC, Yang SW, Yang JY, Chua NH (2007) Independent and interdependent functions of LAF1 and HFR1 in phytochrome A signaling. Genes Dev 21:2100–2111
Jin H, Cominelli E, Bailey P, Parr A, Mehrtens F, Jones J, Tonelli C, Weisshaar B, Martin C (2000) Transcriptional repression by AtMYB4 controls production of UV-protecting sunscreens in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 19:6150–6161
Koes R, Verweij W, Quattrocchio F (2005) Flavonoids: a colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci 10:236–242
Lancaster JE (1992) Regulation of skin color in apples. Crit Rev Plant Sci 10:487–502
Leng P, Itamura H, Yamamura H (1995) Changes of phenylalanine ammonialyase activity in twig tissues of two Diospyros species during cold acclimation. Environ Control Biol 33:43–48
Leng P, Itamura H, Yamamura H, Deng XM (2000) Anthocyanin accumulation in apple and peach shoots during cold acclimation. Sci Hortic 83:43–50
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M (2006) Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:405–430
Leyva A, Jarillo JA, Salinas J, Martinez-Zapater JM (1995) Low temperature induces the accumulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase mRNAs of Arabidopsis thaliana in a light-dependent manner. Plant Physiol 108:8
Liu RH, Liu J, Chen B (2005) Apples prevent mammary tumors in rats. J Agric Food Chem 53:2341–2343
Lo Piero AR, Puglisi I, Rapisarda P, Petrone G (2005) Anthocyanins accumulation and related gene expression in red orange fruit induced by low temperature storage. J Agric Food Chem 53:9083–9088
Matsui K, Umemura Y, Ohme-Takagi M (2008) AtMYBL2, a protein with a single MYB domain, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 55:954–967
Mori K, Goto-Yamamoto N, Kitayama M, Hashizume K (2007) Loss of anthocyanins in red-wine grape under high temperature. J Exp Bot 58:1935–1945
Morita Y, Saitoh M, Hoshino A, Nitasaka E, Iida S (2006) Isolation of cDNAs for R2R3-MYB, bHLH and WDR transcriptional regulators and identification of c and ca mutations conferring white flowers in the Japanese morning glory. Plant Cell Physiol 47:457–470
Nijveldt RJ, van Nood E, van Hoorn DE, Boelens PG, van Norren K, van Leeuwen PA (2001) Flavonoids: a review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am J Clin Nutr 74:418–425
Niu SS, Xu CJ, Zhang WS, Zhang B, Li X, Lin-Wang K, Ferguson IB, Allan AC, Chen KS (2010) Coordinated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) fruit by a R2R3 MYB transcription factor. Planta 231:887–899
Pattanaik S, Xie CH, Yuan L (2008) The interaction domains of the plant Myc-like bHLH transcription factors can regulate the transactivation strength. Planta 227:707–715
Quattrocchio F, Wing JF, Leppen H, Mol J, Koes RE (1993) Regulatory genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation are functionally conserved among plant species and have distinct sets of target genes. Plant Cell 5:1497–1512
Ramsay NA, Glover BJ (2005) MYB-bHLH-WD40 protein complex and the evolution of cellular diversity. Trends Plant Sci 10:63–70
Rasmussen SE, Frederiksen H, Struntze Krogholm K, Poulsen L (2005) Dietary proanthocyanidins: occurrence, dietary intake, bioavailability, and protection against cardiovascular disease. Mol Nutr Food Res 49:159–174
Regan BC, Julliot C, Simmen B, Vienot F, Charles-Dominique P, Mollon JD (2001) Fruits, foliage and the evolution of primate colour vision. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356:229–283
Romero I, Sanchez-Ballesta MT, Maldonado R, Escribano MI, Merodio C (2008) Anthocyanin, antioxidant activity and stress-induced gene expression in high CO2-treated table grapes stored at low temperature. Plant Physiol 165:522–530
Rowan DD, Cao M, Lin-Wang K (2009) Environmental regulation of leaf colour in red 35S:PAP1 Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 182:14
Sainz MB, Grotewold E, Chandler VL (1997) Evidence for direct activation of an anthocyanin promoter by the maize C1 protein and comparison of DNA binding by related Myb domain proteins. Plant Cell 9:611–625
Shvarts M, Borochov A, Weiss D (1997) Low temperature enhances petunia flower pigmentation and induces chalcone synthase gene expression. Physiol Plant 99:6
Steyn W, Holcroft D, Wand S, Jacobs G (2005) Red colour development and loss in pears. Acta Horticult 671:7
Steyn WJ, Wand SJ, Jacobs G, Rosecrance RC, Roberts SC (2009) Evidence for a photoprotective function of low-temperature-induced anthocyanin accumulation in apple and pear peel. Physiol Plant 136:12
Takos AM, Robinson SP, Walker AR (2006) Transcriptional regulation of the flavonoid pathway in the skin of dark-grown “Cripps’ Red” apples in response to sunlight. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 81:735–744
Tamagnone L, Merida A, Parr A, Mackay S, Culianez-Macia FA, Roberts K, Martin C (1998) The AmMYB308 and AmMYB330 transcription factors from antirrhinum regulate phenylpropanoid and lignin biosynthesis in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell 10:135–154
Tanaka Y, Sasaki N, Ohmiya A (2008) Biosynthesis of plant pigments: anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J 54:733–749
Ubi B, Honda C, Bessho H, Kondo S, Wada M, Kobayashi S, Moriguchi T (2006) Expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in apple skin: effect of UV-B and temperature. Plant Sci 170:8
Walker AR, Lee E, Bogs J, McDavid DA, Thomas MR, Robinson SP (2007) White grapes arose through the mutation of two similar and adjacent regulatory genes. Plant J 49:772–785
Winkel-Shirley B (2001) Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol 126:485–493
Wrolstand RE, Culbertson JD, Cornwell CJ, Mattick L (1982) Detection of adulteration in blackberry juice concentrates and wines. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 6:1417–1423
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by funds received from National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program) under grant no. 2011CB100600, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31101533), and 100 Talents program of the Chinese Academy of Science. Two mutant CHI/F3′H Arabidopsis of CS8586 was kindly offered by The Arabidopsis Information Resource. We would also like to express our gratitude to Juan Li for materials preparation and Dr. Yi Huang for critically reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Abbott
Ying Zhou and Dong Guo contributed to this paper equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Guo, D., Li, J. et al. Coordinated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis through photorespiration and temperature in peach (Prunus persica f. atropurpurea). Tree Genetics & Genomes 9, 265–278 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-012-0552-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-012-0552-1