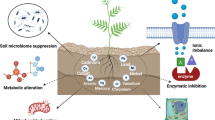
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution due to excessive use of chemical fertilizers (CF) causes major damage to the environment. Microbial biofilms, closely associated with the rhizosphere can remediate heavy metal-contaminated soil by reducing plant toxicity. Thus, this study was undertaken to examine the remedial effects of microbial biofilms against contaminated heavy metals. Fungi and bacteria isolated from soil were screened for their tolerance against Cd2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+. Three bacterial and two fungal isolates were selected upon the tolerance index (TI) percentage. Fungal-bacterial biofilms (FBBs) were developed with the most tolerant isolates and were further screened for their bioremediation capabilities against heavy metals. The best biofilm was evaluated for its rhizoremediation capability with different CF combinations using a pot experiment conducted under greenhouse conditions with potatoes. Significantly (P < 0.05), the highest metal removal percentage was observed in Trichoderma harzianum and Bacillus subtilis biofilm under in situ conditions. When compared to the 100% recommended CF, the biofilm with 50% of the recommended CF (50CB) significantly (P < 0.05) reduced soil available Pb2+ by 77%, Cd2+ by 78% and Zn2+ by 62%. In comparison to initial soil, it was 73%, 76%, and 57% lower of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+, respectively. In addition, 50CB treatment significantly (P < 0.05) reduced the metal penetration into the tuber tissues in comparison with 100 C. Thus, the function of the developed FBB with T. harzianum–B. subtilis can be used as a potential solution to remediate soil polluted with Pb2+ Cd2+ and Zn2+ metal contaminants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Shanab RA, Angle JS, Delorme TA, Chaney RL, van Berkum P, Moawad H, Ghanem K, Ghozlan HA (2003a) Rhizobacterial effects on nickel extraction from soil and uptake by Alyssum murale. New Phytol 158:219–224
Abtenh E (2017) Application of microorganisms in bioremediation-review. J Environ Microbiol 1:2–9
Afzal AM, Rasool MH, Waseem M, Aslam B (2017) Assessment of heavy metal tolerance and biosorptive potential of Klebsiella variicola isolated from industrial effluents. AMB Express 7:184
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang MQ (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9:42
AlKhader AMF (2015) The Impact of Phosphorus Fertilizers on Heavy Metals Content of Soils and Vegetables Grown on Selected Farms in Jordan. Agrotechnol 5:1–5
Alloway BJ (2013) Sources of Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Soils. Heavy Metals in Soils. Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and their Bioavailability; Alloway BJ. Ed.; Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 11–50
Alzahrani OM, Ahamed NT (2015) Ahamed Isolation and Characterization of Heavy Metal Resistant Bacillus subtilis spp. Collected from Water Sources of Taif Province of Saudi Arabia. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 4:350–357
Balzano S, Sardo A, Blasio M, Chahine TB, Dell’Anno F, Sansone C (2020) Microalgal metallothioneins and phytochelatins and their potential use in bioremediation. Front Microbiol 11:517
Bao Z, Ikunaga Y, Matsushita Y, Morimoto S, Takada-Hoshino Y (2012) Combined analyses of bacterial, fungal and nematode communities in Andosolic agricultural soils in Japan. Microbes and Environ 27:72–79
Casova K, Cerny J, Szakova J, Balík J, Tlustos P (2009) Cadmium balance in soils under different fertilization managements including sewage sludge application. Plant Soil Environ 55:353–361
Chellaiah ER (2018) Cadmium (heavy metals) bioremediation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a minireview. Appl Water Sci 8:1–10
Cheraghi M, Lorestani B, Merrikhpour H, Rouniasi N (2013) Heavy metal risk assessment for potatoes grown in overused phosphate-fertilized soils. Environ Monit Assess 185:1825–1831
Dixit R, Malaviya D, Pandiyan K, Singh UB, Sahu A, Shukla R, Singh BP, Rai JP, Sharma PK, Lade H, Paul D (2015) Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: an overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustainability 7:2189–2212
Doering M, Uehlinger U (2006) Biofilms in the Tagliamento. Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Sci Technol 60: 11–13
Fan Y, Li Y, Li H, Cheng F (2018) Evaluating heavy metal accumulation and potential risks in soil-plant systems applied with magnesium slag-based fertilizer. Chemosphere 197:382–388
Fazli MM, Soleimani N, Mehrasbi M, Darabian S, Mohammadi J, Ramazani A (2015) Highly cadmium tolerant fungi: their tolerance and removal potential. J Environ Health Sci Eng 13:1–9
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633
Frey-Klett P, Burlinson P, Deveau A, Barret M, Tarkka M, Sarniguet A (2011) Bacterial-fungal interactions: hyphens between agricultural, clinical, environmental and food microbiologists. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75:583–609
Harrison JJ, Ceri H, Turner RJ (2007) Multi-metal resistance and tolerance in microbial biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:928–938
Hassen SHA, Gad Abskharon RNN, El-Rab SMF, Shoreit AAM (2008) Isolation, characterization of heavy metal resistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from polluted sites in Assiut city, Egypt. J Basic Microbiol 48:168–176
Henagamage AP (2019) Bioremediation of textile dyes by fungal-bacterial biofilms. Int J Environ Agric Biotech 4:635–642
Hennebel T, Boon N, Maes S, Lenz M (2015) Biotechnologies for critical raw material recovery from primary and secondary sources: R & D priorities and future perspectives. New Biotechnol 32:121–127
Herath HMLI, Rajapaksha AU, Vithanage M, Seneviratne G (2014) Developed fungal–bacterial biofilms as a novel tool for bioremoval of hexavelant chromium from wastewater. Chem Ecol 30:418–427
Hookoom M, Puchooa D (2013) Isolation and identification of heavy metals tolerant bacteria from industrial and agricultural areas in Mauritius. Curr Res Microbiol Biotechnol 1:119–123
Ibrahim UB, Yahaya S, Yusuf I, Kawo AH (2021) Optimization and simulation of process parameters in biosorption of heavy metals by Alcaligenes faecalis strain UBI (MT107249) isolated from soil of local mining area in North-West Nigeria. Soil Sediment Contam1 18
Idris R, Trifonova R, Puschenreiter M, Wenzel WW, Sessitsch A (2004) Bacterial communities associated with flowering plants of the Ni hyperaccumulator Thlaspigoesingense. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2667–2677
Iram S, Iftikhar A, Barira J, Saeeda Y (2009) Fungal tolerance to heavy metals. Pak J Bot 41:2583–2594
Javadi MA, Ghanbary MAT, Tazick Z (2012) Isolation and molecular identification of soil inhabitant Penicillia. Ann Biol Res 3:5758–5761
Kang SY, Lee JU, Kim KW (2007) Biosorption of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) onto the cell surface of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Eng J 36:54–58
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA, Oves M (2009) Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in the remediation of metal contaminated soils. Environ Chem Lett 7:1–19
Kisku GC, Pandey P, Singh MP, Misra NV (2011) Uptake and accumulation of potentially toxic metals (Zn, Cu and Pb) in soils and plants of Durgapur industrial belt. J Environ Biol 32:831–838
Lambert MTJ, Indraratne SP (2014) Cadmium and lead contents in paddy and uncultivated grumusols in murunkan, mannar district. Proc Peradeniya Univ Int Res Sess Sri Lanka 18:508
Landeweert R, Leeflang P, Kuyper TW, Hoffland E, Rosling A, Wernars K, Smit E (2003) Molecular identification of ectomycorrhizal mycelium in soil horizons. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:327–333
Lorito M, Woo SL, Harman GE, Monte E (2010) Translational research on Trichoderma: from ‘Omics’ to the field. Annu Rev Phytopathol 48:395–417
Lukowski A, Dec D (2018) Influence of Zn, Cd, and Cu fractions on enzymatic activity of arable soils. Environ Monit Assess 190:1–12
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Sa T (2007) Metal tolerating methylotrophic bacteria reduces nickel and cadmium toxicity and promotes plant growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Chemosphere 69:220–228
Meliani A, Bensoltane A (2016) Biofilm-Mediated Heavy Metals Bioremediation in PGPR Pseudomonas. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 7:1–9
Mishra A, Bhattacharya A, Mishra N (2019) Mycorrhizal symbiosis: An effective tool for metal bioremediation. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Singh JS, Ed; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands 113–128
Ogbuagu DH, Nwachukwu KN, Balogun BA (2017) Application of biofilms in removal of heavy metals from wastewater in static condition. Int J Microbiol Immunol Res 5:6–13
Ogbuagu DH, Okoli CG, Emereibeole EI, Anyanwu IC, Onuoha O, Ubah NO, Ndugbu CO, Okoroama ON, Okafor A, Ewa E, Ossai R, Ukah F (2011) Trace metals accumulation in biofilms of the upper and middle reaches of Otamiri River in Owerri. Nigeria J Biodivers Environ Sci 1:19–26
Oluwatosin GO, Olusegun OA, Akinyemi O, Cornelius CB, Mark SMR (2018) Heavy metal tolerance traits of filamentous fungi isolated from gold and gemstone mining sites. J Microbiol 49:29–37
Park D, Yun YS, Park JM (2005) Studies on hexavalent chromium biosorption by chemically-treated biomass of Ecklonia sp. Chemosphere 60:1356–1364
Premarathana HMPL, Hettiarachchi CM, Indraratne SP (2005) Accumulation of Cadmium in Intensive Vegetable Growing soils in the Up Country. Trop Agric Res 17:93–103
Premarathna HMPL, Hettiarachchi GM, Indraratne SP (2011) Trace Metal Concentration in Crops and Soils Collected from Intensively Cultivated Areas of Sri Lanka. Pedologist 54:230–240
Quintelas C, Rocha Z, Silva B, Fonseca B, Figueiredo H, Tavares T (2009) Removal of Cd(II), Cr(VI), Fe(III) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by an E. coli biofilm supported on kaolin. Chem Eng J 149:319–324
Rajapaksha RMCP, Tobor-Kapłon MA, Baath (2004) Metal Toxicity Affects Fungal and Bacterial Activities in Soil Differently. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2966–2973
Rengel Z (2015) Availability of Mn, Zn and Fe in the rhizosphere. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 15:397–409
Roberts TL (2014) Cadmium and phosphorous fertilizers: the issues and the science. Procedia Eng 83:52–59
Saha JK, Selladurai R, Coumar MV, Dotaniya ML, Kundu S, Patra AK (2017) Status of soil pollution in India. Soil pollution-an emerging threat to agriculture. Springer, Singapore, pp 271–315
Selatnia A, Boukazoula A, Kechid N, Bakhti MZ, Chergui A, Kerchich Y (2004) Biosorption of lead (II) from aqueous solution by a bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Biochem Eng J 19:127–135
Seneviratne G, Indrasena IK (2006) Nitrogen fixation in lichens is important for improved rock weathering. J Biosci 31:639–643
Seneviratne G, Jayasinghearachchi HS (2003) Mycelial colonization by Bradyrhizobia and Azorhizobia. J Biosci 28: 243–247
Seneviratne G, Zavahir JS, Bandara WMMS, Weerasekara MLMAW (2008) Fungal-bacterial biofilms: their development for novel biotechnological applications. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:739–743
Sessitsch A, Kuffner M, Kidd P, Vangronsveld J, Wenzel WW, Fallmann K, Puschenreiter M (2013) The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 60:182–194
Sharma P (2021) Role and significance of biofilm-forming microbes in phytoremediation—A review.Environ Technol Innov102182
Shetty P, Acharya C, Veeresh N (2019) Effect of Urea Fertilizer on the Biochemical Characteristics of Soil. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 7:414–420
Suman J, Uhlik O, Viktorova J, Macek T (2018) Phytoextraction of heavy metals: a promising tool for clean-up of polluted environment. Front Plant Sci 9:1476
Syed S, Chinthala P (2015) Heavy metal detoxification by different Bacillus species isolated from solar salterns.Scientifica319760
Tanu FZ, Hoque S (2012) Bacterial Tolerance to Heavy Metal Contents Present in Contaminated and Uncontaminated Soils. Bangladesh J Microbiol 29:56–61
Teitzel GM, Parsek MR (2003) Heavy Metal Resistance of Biofilm and Planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2313–2320
Tharannum S, Krishnamurthy V, Mahmood R (2012) Characterization of chromium remediating bacterium Bacillus subtilis isolated from electroplating effluent. Int J Eng Res Appl 4:961–966
Usman ZU, Mukesh Y, Vandana S, Sharma JK, Sanjay P, Sidhartha D, Anil SK (2020) Microbial Bioremediation of Heavy Metals: Emerging Trends and Recent Advances. Res J Biotechnol 15:164–178
Verma P, Rawat S (2021) Rhizoremediation of Heavy Metaland Xenobiotic-Contaminated Soil: An Eco-Friendly Approach.Springer Nature Singapore95–113
Wang X, Liu W, Li Z, Teng Y, Christie P, Luo Y (2020) Effects of long-term fertilizer applications on peanut yield and quality and plant and soil heavy metal accumulation. Pedosphere 30:555–562
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, eds. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications. New York: Academic Press, Inc 315–322
Yan-de J, Zhen-li H, Xiao Y (2007) Role of soil rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 8:197–207
Yazdani M, Chee KY, Faridah A, Soon GT (2010) An in vitro study on the Adsorption, Absorption and uptake Capacity of Zn by the Bioremediator Trichoderma atroviride. Environ Asia 3:53–59
Zafar S, Aqil F, Ahmad I (2007) Metal tolerance and biosorption potential of filamentous fungi isolated from metal contaminated agricultural soil. Bioresour Technol 98:2557–2561
Zeng X, Su S, Jiang X, Li L, Bai L, Zhang Y (2010) Capability of pentavalent arsenic bioaccumulation and bio-volatilization of three fungal strains under laboratory conditions. Clean Soil Air Water 38:238–241
Zhang YJ, Zhang S, Liu XZ, Wen HA, Wang M (2010) A simple method of genomic DNA extraction suitable for analysis of bulk fungal strains. Lett Appl Microbiol 51:114–118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henagamage, A.P., Peries, C.M. & Seneviratne, G. Fungal-bacterial biofilm mediated heavy metal rhizo-remediation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 85 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03267-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03267-8