Abstract
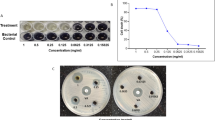
Extensive usage of antibiotics has led to the emergence of drug-resistant strains of pathogens and hence, there is an urgent need for alternative antimicrobial agents. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) of bacterial origin have shown the potential to replace some conventional antibiotics. In the present study, an AMP was isolated from Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii strain Ba49 present on the Allium cepa, the common onion and named as peptide-Ba49. The isolated AMP was purified and characterized. The purified peptide-Ba49, having a molecular weight of ~ 3.3 kDa as determined using mass spectroscopy, was stable up to 121 °C and in the pH range of 5–10. Its interaction with protein degrading enzymes confirmed the peptide nature of the molecule. The peptide exhibited low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against Staphylococcus aureus and its (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) MRSA strains (MIC, 2–16 µM/mL). Further, time kill kinetic assay was performed and analysis of the results of membrane depolarization and permeabilization assays (TEM, DiBAC4 (3) and PI) suggested peptide-Ba49 to be acting through the change in membrane potential leading to disruption of S. aureus membrane. Additionally, cytotoxicity studies of peptide-Ba49, carried out using three mammalian cell lines viz. HEK 293T, RAW 264.7, and L929, showed limited cytotoxicity on these cell lines at a concentration much higher than its MIC values. All these studies suggested that the AMP isolated from strain Ba49 (peptide-Ba49) has the potential to be an alternative to antibiotics in terms of eradicating the pathogenic as well as drug-resistant microorganisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMPs:
-
Antimicrobial peptides
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- DiBAC4 (3):
-
Bis-(1,3-dibutylbarbituric acid) trimethine oxonol
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer saline
- RP-HPLC:
-
Reverse phase-high-pressure liquid chromatography
- Tricine SDS-PAGE:
-
Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- MALDI-TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- CFU:
-
Colony forming unit
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthoazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- DMF:
-
Dimethylformamide
References
Abriouel H, Franz CM, Ben Omar N, Galvez A (2011) Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35(1):201–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00244.x
Adams DS, Levin M (2012) Measuring resting membrane potential using the fluorescent voltage reporters DiBAC4(3) and CC2-DMPE. Cold Spring Harbor Protoc 2012(4):459–464. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot067702
Al-Sahlany STG, Altemimi AB, Al-Manhel AJA, Niamah AK, Lakhssassi N, Ibrahim SA (2020) Purification of bioactive peptide with antimicrobial properties produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Foods. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030324
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19(5):455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Bansal K, Aqdas M, Kumar M, Bala R, Singh S, Agrewala JN, Katare OP, Sharma RK, Wangoo N (2018) A facile approach for synthesis and intracellular delivery of size tunable cationic peptide functionalized gold nanohybrids in cancer cells. Bioconjug Chem 29(4):1102–1110. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00772
Bizani D, Dominguez AP, Brandelli A (2005) Purification and partial chemical characterization of the antimicrobial peptide cerein 8A. Lett Appl Microbiol 41(3):269–273. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01748.x
Bushnell B (2014) BBMap: a fast, accurate, splice-aware aligner. Lawrence Berkeley National Lab.(LBNL), Berkeley
Cammue B, Thevissen K, Hendriks M, Eggermont K, Goderis IJ, Proost P, Van Damme J, Osborn RW, Guerbette F, Kader JC, Broekaert WF (1995) A potent antimicrobial protein from onion seeds showing sequence homology to plant lipid transfer proteins. Plant Physiol 109(2):445–455. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.2.445
Chalasani AG, Dhanarajan G, Nema S, Sen R, Roy U (2015) An antimicrobial metabolite from Bacillus sp.: significant activity against pathogenic bacteria including multidrug-resistant clinical strains. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01335
Chutani SK, Bordia A (1981) The effect of fried versus raw garlic on fibrinolytic activity in man. Atherosclerosis 38(3–4):417–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9150(81)90058-7
Cotter PD, Ross RP, Hill C (2013) Bacteriocins—a viable alternative to antibiotics? Nat Rev Microbiol 11(2):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2937
Dayan GH, Mohamed N, Scully IL, Cooper D, Begier E, Eiden J, Jansen KU, Gurtman A, Anderson AS (2016) Staphylococcus aureus: the current state of disease, pathophysiology and strategies for prevention. Expert Rev Vaccines 15(11):1373–1392. https://doi.org/10.1080/14760584.2016.1179583
DeLeo FR, Otto M, Kreiswirth BN, Chambers HF (2010) Community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 375(9725):1557–1568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61999-1
Elayaraja S, Annamalai N, Mayavu P, Balasubramanian T (2014) Production, purification and characterization of bacteriocin from Lactobacillus murinus AU06 and its broad antibacterial spectrum. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 4(Suppl 1):S305–S311. https://doi.org/10.12980/APJTB.4.2014C537
Field D, Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP (2015) Bioengineering lantibiotics for therapeutic success. Front Microbiol 6:1363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01363
Frank DN, Feazel LM, Bessesen MT, Price CS, Janoff EN, Pace NR (2010) The human nasal microbiota and Staphylococcus aureus carriage. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10598. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010598
Fuchs SW, Jaskolla TW, Bochmann S, Kotter P, Wichelhaus T, Karas M, Stein T, Entian KD (2011) Entianin, a novel subtilin-like lantibiotic from Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii DSM 15029T with high antimicrobial activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(5):1698–1707. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01962-10
Gabrielsen C, Brede DA, Nes IF, Diep DB (2014) Circular bacteriocins: biosynthesis and mode of action. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(22):6854–6862. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02284-14
Griffiths G, Trueman L, Crowther T, Thomas B, Smith B (2002) Onions–a global benefit to health. Phytother Res: PTR 16(7):603–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.1222
Gross E, Kiltz HH, Nebelin E (1973) [Subtilin, VI: the structure of subtilin (author’s transl)]. Hoppe-Seyler’s Zeitschrift fur physiologische Chemie 354(7):810–812
Guillamet CV, Kollef MH (2016) How to stratify patients at risk for resistant bugs in skin and soft tissue infections? . Curr Opin Infect Dis 29(2):116–123. https://doi.org/10.1097/QCO.0000000000000244
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29(8):1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Hancock RE, Rozek A (2002) Role of membranes in the activities of antimicrobial cationic peptides. FEMS Microbiol Lett 206(2):143–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11000.x
Hols P, Ledesma-Garcia L, Gabant P, Mignolet J (2019) Mobilization of microbiota commensals and their bacteriocins for therapeutics. Trends Microbiol 27(8):690–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2019.03.007
Howlin RP, Brayford MJ, Webb JS, Cooper JJ, Aiken SS, Stoodley P (2015) Antibiotic-loaded synthetic calcium sulfate beads for prevention of bacterial colonization and biofilm formation in periprosthetic infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59(1):111–120. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03676-14
Hu M, Zhao H, Zhang C, Yu J, Lu Z (2013) Purification and characterization of plantaricin 163, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum 163 isolated from traditional Chinese fermented vegetables. J Agric Food Chem 61(47):11676–11682. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf403370y
Jack RW, Bierbaum G, Sahl H-G (2013) Lantibiotics and related peptides. Springer, New York
Jangra M, Kaur M, Tambat R, Rana R, Maurya SK, Khatri N, Ghafur A, Nandanwar H (2019) Tridecaptin M, a new variant discovered in mud bacterium, shows activity against colistin- and extremely drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63:6. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00338-19
Kim S-Y, Lee N-K, Han EJ, Paik H-D (2012) Characterization of subtilin KU43 produced by Bacillus subtilis KU43 isolated from traditional Korean fermented foods. Food Sci Biotechnol 21(5):1433–1414
Kimura H, Matsusaki H, Sashihara T, Sonomoto K, Ishizaki A (1998) Purification and partial identification of bacteriocin ISK-1, a new lantibiotic produced by Pediococcus sp. ISK-1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62(12):2341–2345. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.62.2341
Koch G, Yepes A, Forstner KU, Wermser C, Stengel ST, Modamio J, Ohlsen K, Foster KR, Lopez D (2014) Evolution of resistance to a last-resort antibiotic in Staphylococcus aureus via bacterial competition. Cell 158(5):1060–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.046
Kordel M, Schuller F, Sahl HG (1989) Interaction of the pore forming-peptide antibiotics Pep 5, nisin and subtilin with non-energized liposomes. FEMS Lett 244(1):99–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(89)81171-8
Laverty G, Gilmore B (2014) Cationic antimicrobial peptide cytotoxicity. SOJ Microbiol Infect Dis 2(1):1–8
Łoboda D, Kozłowski H, Rowińska-Żyrek M (2018) Antimicrobial peptide–metal ion interactions–a potential way of activity enhancement. New J Chem 42(10):7560–7568
Maldonado A, Ruiz-Barba JL, Jimenez-Diaz R (2003) Purification and genetic characterization of plantaricin NC8, a novel coculture-inducible two-peptide bacteriocin from Lactobacillus plantarum NC8. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(1):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.69.1.383-389.2003
Malhotra H, Patidar A, Boradia VM, Kumar R, Nimbalkar RD, Kumar A, Gani Z, Kaur R, Garg P, Raje M, Raje CI (2017) Mycobacterium tuberculosis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) functions as a receptor for human lactoferrin. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:245. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00245
Malmsten M (2014) Antimicrobial peptides. Ups J Med Sci 119(2):199–204. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009734.2014.899278
Marx R, Stein T, Entian KD, Glaser SJ (2001) Structure of the Bacillus subtilis peptide antibiotic subtilosin A determined by 1H-NMR and matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Protein Chem 20(6):501–506. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1012562631268
Meade E, Slattery MA, Garvey M (2020) Bacteriocins, potent antimicrobial peptides and the fight against multi drug resistant species: resistance is futile? Antibiotics. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010032
Mendoza N, Tyring SK (2010) Emerging drugs for complicated skin and skin-structure infections. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 15(3):509–520. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728214.2010.497486
Mookherjee N, Anderson MA, Haagsman HP, Davidson DJ (2020) Antimicrobial host defence peptides: functions and clinical potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov 19(5):311–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0058-8
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Perez RH, Zendo T, Sonomoto K (2014) Novel bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria (LAB): various structures and applications. Microb Cell Fact 13:S3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-13-S1-S3
Peterson LR, Schora DM (2016) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus control in the 21st century: laboratory involvement affecting disease impact and economic benefit from large population studies. J Clin Microbiol 54(11):2647–2654. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00698-16
Piper C, Draper LA, Cotter PD, Ross RP, Hill C (2009) A comparison of the activities of lacticin 3147 and nisin against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus species. J Antimicrob Chemother 64(3):546–551. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkp221
Qin Y, Wang Y, He Y, Zhang Y, She Q, Chai Y, Li P, Shang Q (2019) Characterization of subtilin L-Q11, a novel class I bacteriocin synthesized by Bacillus subtilis L-Q11 isolated from orchard soil. Front Microbiol 10:484. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00484
Rahman MS, Choi YH, Choi YS, Yoo JC (2017) Glycin-rich antimicrobial peptide YD1 from B. amyloliquefaciens, induced morphological alteration in and showed affinity for plasmid DNA of E. coli. AMB Express 7(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-016-0315-8
Santajit S, Indrawattana N (2016) Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Biomed Res Int 2016:2475067. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2475067
Schagger H (2006) Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat Protoc 1(1):16–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.4
Shanks RM, Dashiff A, Alster JS, Kadouri DE (2012) Isolation and identification of a bacteriocin with antibacterial and antibiofilm activity from Citrobacter freundii. Arch Microbiol 194(7):575–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-012-0793-2
Sharma G, Dang S, Gupta S, Gabrani R (2018) Antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity, and the mechanism of action of bacteriocin from Bacillus subtilis GAS101. Medical principles and practice: international journal of the Kuwait University. Health Sci Centre 27(2):186–192. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487306
Silva FD, Rezende CA, Rossi DC, Esteves E, Dyszy FH, Schreier S, Gueiros-Filho F, Campos CB, Pires JR, Daffre S (2009) Structure and mode of action of microplusin, a copper II-chelating antimicrobial peptide from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. J Biol Chem 284(50):34735–34746. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.016410
Slimestad R, Fossen T, Vågen IM (2007) Onions: a source of unique dietary flavonoids. J Agric Food Chem 55(25):10067–10080
Sumi CD, Yang BW, Yeo IC, Hahm YT (2015) Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: a new era for antibiotics. Can J Microbiol 61(2):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2014-0613
Te Winkel JD, Gray DA, Seistrup KH, Hamoen LW, Strahl H (2016) Analysis of antimicrobial-triggered membrane depolarization using voltage sensitive dyes. Front Cell Dev Biol 4:29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2016.00029
Teng Y, Zhao W, Qian C, Li O, Zhu L, Wu X (2012) Gene cluster analysis for the biosynthesis of elgicins, novel lantibiotics produced by Paenibacillus elgii B69. BMC Microbiol 12:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-45
Walkenhorst WF, Sundrud JN, Laviolette JM (2014) Additivity and synergy between an antimicrobial peptide and inhibitory ions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1838(9):2234–2242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.05.005
Wang HX, Ng TB (2004) Isolation of allicepin, a novel antifungal peptide from onion (Allium cepa) bulbs. J Pept Sci 10(3):173–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.509
Weber T, Blin K, Duddela S, Krug D, Kim HU, Bruccoleri R, Lee SY, Fischbach MA, Muller R, Wohlleben W, Breitling R, Takano E, Medema MH (2015) antiSMASH 3.0—a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res 43(W1):W237–W243. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv437
Yamada A, Gaja N, Ohya S, Muraki K, Narita H, Ohwada T, Imaizumi Y (2001) Usefulness and limitation of DiBAC4(3), a voltage-sensitive fluorescent dye, for the measurement of membrane potentials regulated by recombinant large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels in HEK293 cells. Jpn J Pharmacol 86(3):342–350. https://doi.org/10.1254/jjp.86.342
Yasir M, Dutta D, Willcox MDP (2019) Comparative mode of action of the antimicrobial peptide melimine and its derivative Mel4 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 9(1):7063. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42440-2
Yi L, Luo L, Lu X (2018) Efficient exploitation of multiple novel bacteriocins by combination of complete genome and peptidome. Front Microbiol 9:1567. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01567
Zasloff M (1987) Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. PNAS 84(15):5449–5453. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.15.5449
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Director, CSIR- IMTECH, for providing all the institutional facilities. A special thanks to Mr. Sanpreet Singh (C/o Dr. Javed Agrewala lab) for helping in flow cytometry and mammalian cytotoxicity experiments and Mr. Randeep Sharma, CSIR-IMTECH, Chandigarh for helping to carry out TEM experiments. Financial support to RT as a recipient of DST INSPIRE Fellowship from Department of Science and Technology, Government of India is highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DKS, RT conceived the project. RT and MJ isolated, purified, and characterized the compound. RT performed the in vitro experiments with the assistance of AD. MJ performed the MIC experiments in MRSA strains. KB and PBP analysed the whole genome data of the microorganism. RT, MJ, DKS analysed the data. RT and DKS wrote and edited the manuscript, with input from all of the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they don’t have any conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taggar, R., Jangra, M., Dwivedi, A. et al. Bacteriocin isolated from the natural inhabitant of Allium cepa against Staphylococcus aureus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37, 20 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02989-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02989-x