Abstract
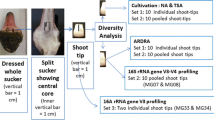
Genetic modification of maize with Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) cry proteins may predispose shifts in the bacterial endophytes’ community associated with maize shoots. In this study, the diversity of bacterial endophytes associated with a Bt maize genotype (Mon810) and its isogenic non-transgenic parental line were investigated at pre-flowering (50 days) and post-flowering (90 days) developmental stages. PCR-DGGE and high throughput sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq sequencer were used to characterize bacterial 16S rRNA gene diversity in leaves, stems, seeds and tassels. PCR-DGGE profile revealed similarity as well as differences between bacterial communities of shoots in both cultivars and at both developmental stages. A total of 1771 operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were obtained from the MiSeq and assigned into 14 phyla, 27 classes, 58 orders, 116 families and 247 genera. Differences in alpha and beta diversity measures of OTUs between the phyllospheres of both genotypes were not significant (P > .05) at all developmental stages. In all cultivars, OTU diversity reduced with plant development. OTUs belonging to the phyla Proteobacteria were dominant in all maize phyllospheres. The class Gammaproteobacteria was dominant in Bt maize while, Alphaproteobacteria and Actinobacteria were dominant in non-Bt maize phyllospheres. Differences in the abundance of some genera, including Acidovorax, Burkerholderia, Brachybacterium, Enterobacter and Rhodococcus, whose species are known beneficial endophytes were observed between cultivars. Hierarchical cluster analysis further suggests that the bacterial endophyte communities of both maize genotypes associate differently (are dissimilar). Overall, the results suggest that bacterial endophytes community differed more across developmental stages than between maize genotypes.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreote FD, de Araújo WL, de Azevedo JL, van Elsas JD, da Rocha UN, van Overbeek LS (2009) Endophytic colonization of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) by a novel competent bacterial endophyte, Pseudomonas putida strain P9, and its effect on associated bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3396–3406. doi:10.1128/AEM.00491-09
Andreote FD, da Rocha UN, Araújo WL, Azevedo JL, van Overbeek LS (2010) Effect of bacterial inoculation, plant genotype and developmental stage on root-associated and endophytic bacterial communities in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:389–399. doi:10.1007/s10482-010-9421-9
Berg G, Krechel A, Ditz M, Sikora RA, Ulrich A, Hallmann J (2005) Endophytic and ectophytic potato-associated bacterial communities differ in structure and antagonistic function against plant pathogenic fungi. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 51:215–229. doi:10.1016/j.femsec.2004.08.006
Bumunang EW, Jordaan K, Barros E, Bezuidenhout C, Babalola OO (2015) Analysis of rhizobacterial community in field grown GM and non-GM maize soil samples using PCR-DGGE. J Agric Technol 11:831–838
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK et al (2010a) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knigh R (2010b) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26(2):266–267. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp636
Castaldini M et al (2005) Impact of Bt corn on rhizospheric and soil eubacterial communities and on beneficial mycorrhizal symbiosis in experimental microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6719–6729. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.11.6719-6729.2005
Cavaglieri L, Orlando J, Etcheverry M (2009) Rhizosphere microbial community structure at different maize plant growth stages and root locations. Microbiol Res 164:391–399. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2007.03.006
Celador-Lera L, Menéndez E, Flores-Félix JD, Mateos PF, Rivas R (2016) Analysis of the PGPB potential of bacterial endophytes associated with maize. In: González-Andrés F, James E (eds) Biological nitrogen fixation and Beneficial plant–microbe interaction. Springer, Basel, pp 23–35
Chaparro JM, Badri DV, Vivanco JM (2014) Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development. ISME J 8:790–803. doi:10.1038/ismej.2013.196
Cheeke TE, Darby H, Rosenstiel TN, Bever JD, Cruzan MB (2014) Effect of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) maize cultivation history on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal colonization, spore abundance and diversity, and plant growth. Agric Ecosyst Environ 195:29–35. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2014.05.019
Compant S, Clément C, Sessitsch A (2010) Plant growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizo-and endosphere of plants: their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization. Soil Biol Biochem 42:669–678. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.024
Cotta SR, Dias ACF, Marriel IE, Gomes EA, van Elsas JD, Seldin L (2013) Temporal dynamics of microbial communities in the rhizosphere of two genetically modified (GM) maize hybrids in tropical agrosystems. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:589–601. doi:10.1007/s10482-012-9843-7
Cotta SR, Dias ACF, Marriel IE, Andreote FD, Seldin L, van Elsas JD (2014) Different effects of transgenic maize and nontransgenic maize on nitrogen-transforming archaea and bacteria in tropical soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:6437–6445. doi:10.1128/AEM.01778-14
da Silva DAF, Cotta SR, Vollú RE, de Azevedo Jurelevicius D, Marques JM, Marriel IE, Seldin L (2014) Endophytic microbial community in two transgenic maize genotypes and in their near-isogenic non-transgenic maize genotype. BMC Microbiol 14:332. doi:10.1186/s12866-014-0332-1
Devare MH, Jones CM, Thies JE (2004) Effect of Cry3Bb transgenic corn and tefluthrin on the soil microbial community: biomass, activity, and diversity. J Environ Qual 33:837–843. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0837
Dohrmann AB, Küting M, Jünemann S, Jaenicke S, Schlüter A, Tebbe CC (2013) Importance of rare taxa for bacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of Bt-and conventional maize varieties. ISME J 7:37–49. doi:10.1038/ismej.2012.77
Donegan KK, Palm CJ, Fieland VJ, Porteous LA, Ganio LM, Schaller DL, Bucao LQ, Seidler RJ (1995) Changes in levels, species and DNA fingerprints of soil microorganisms associated with cotton expressing the Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki endotoxin. Appl Soil Ecol 2:111–124. doi:10.1016/0929-1393(94)00043-7
Dunfield KE, Germida JJ (2004) Impact of genetically modified crops on soil-and plant-associated microbial communities. J Environ Qual 33:806–815. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0806
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Egamberdiyeva D (2007) The effect of plant growth promoting bacteria on growth and nutrient uptake of maize in two different soils. Appl Soil Ecol 36:184–189. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2007.02.005
Ezeokoli OT, Gupta AK, Mienie C, Popoola TOS, Bezuidenhout CC (2016) PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of microbial community in soy-daddawa, a Nigerian fermented soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) condiment. Int J Food Microbiol 220:58–62. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.01.003
Felske A, Engelen B, Nübel U, Backhaus H (1996) Direct ribosome isolation from soil to extract bacterial rRNA for community analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4162–4167
Feng Y, Shen D, Song W (2006) Rice endophyte Pantoea agglomerans YS19 promotes host plant growth and affects allocations of host photosynthates. J Appl Microbiol 100:938–945. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02843.x
Ferreira A, Quecine MC, Lacava PT, Oda S, Azevedo JL, Araújo WL (2008) Diversity of endophytic bacteria from Eucalyptus species seeds and colonization of seedlings by Pantoea agglomerans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 287:8–14. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01258.x
Gafan GP, Lucas VS, Roberts GJ, Petrie A, Wilson M, Spratt DA (2005) Statistical analyses of complex denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles. J Clin Microbiol 43:3971–3978. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.8.3971-3978.2005
Garbeva P, Van Veen J, Van Elsas J (2003) Predominant Bacillus spp. in agricultural soil under different management regimes detected via PCR-DGGE. Microb Ecol 45:302–316. doi:10.1007/s00248-002-2034-8
Hails RS (2000) Genetically modified plants–the debate continues. Trends in Ecology Evolution 15:14–18. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(99)01751-6
Hardoim PR, Andreote FD, Reinhold-Hurek B, Sessitsch A, van Overbeek LS, van Elsas JD (2011) Rice root-associated bacteria: insights into community structures across 10 cultivars. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77:154–164. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01092.x
Hartmann A, Schmid M, van Tuinen D, Berg G (2009) Plant-driven selection of microbes. Plant Soil 321:235–257. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9814-y
Ibrahim MA, Griko N, Junker M, Bulla LA (2010) Bacillus thuringiensis: a genomics and proteomics perspective. Bioeng bugs 1:31–50. doi:10.4161/bbug.1.1.10519
Illumina (2016) 16 S Metagenomic sequencing library preparation. https://www.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-support/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b.pdf. Accessed 28 November 2016
Justé A, Thomma B, Lievens B (2008) Recent advances in molecular techniques to study microbial communities in food-associated matrices and processes. Food Microbiol 25:745–761. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2008.04.009
Kuklinsky-Sobral J, Araújo WL, Mendes R, Geraldi IO, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Azevedo JL (2004) Isolation and characterization of soybean-associated bacteria and their potential for plant growth promotion. Environ Microbiol 6:1244–1251. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00658.x
Lin L, Li Z, Hu C, Zhang X, Chang S, Yang L, Li Y, An Q (2012) Plant growth-promoting nitrogen-fixing enterobacteria are in association with sugarcane plants growing in Guangxi, China. Microbes Environ 27:391–398. doi:10.1264/jsme2.ME11275
Liu B, Zeng Q, Yan F, Xu H, Xu C (2005) Effects of transgenic plants on soil microorganisms. Plant Soil 271:1–13. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-1610-8
Ma B, Lv X, Warren A, Gong J (2013) Shifts in diversity and community structure of endophytic bacteria and archaea across root, stem and leaf tissues in the common reed, Phragmites australis, along a salinity gradient in a marine tidal wetland of northern China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:759–768. doi:10.1007/s10482-013-9984-3
Marques JM, da Silva TF, Vollú RE, de Lacerda JRM, Blank AF, Smalla K, Seldin L (2015) Bacterial endophytes of sweet potato tuberous roots affected by the plant genotype and growth stage. Appl Soil Ecol 96:273–281. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.08.020
Masella AP, Bartram AK, Truszkowski JM, Brown DG, Neufeld JD (2012) PANDAseq: paired-end assembler for Illumina sequences. BMC Bioinform 13:31. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-13-31
McInroy JA, Kloepper JW (1995) Survey of indigenous bacterial endophytes from cotton and sweet corn. Plant Soil 173:337–342. doi:10.1007/BF00011472
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16 S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Oliveros JC (2015) Venny. An interactive tool for computing lists with venn’s diagrams. http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html. Accessed 16 September 2016
Prasanna BM (2012) Diversity in global maize germplasm: characterization and utilization. J Biosci 37:843–855. doi:10.1007/s12038-012-9227-1
Prischl M, Hackl E, Pastar M, Pfeiffer S, Sessitsch A (2012) Genetically modified Bt maize lines containing cry3Bb1, cry1A105 or cry1Ab2 do not affect the structure and functioning of root-associated endophyte communities. Appl Soil Ecol 54:39–48. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.12.005
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–D596. doi:10.1093/nar/gks1219
R Core Team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Ranjekar P, Patankar A, Gupta V, Bhatnagar R (2003) Genetic engineering of crop plants for insect resistance. Current Science 84:321–329. doi:10.1016/S0261-2194(99)00028-9
Ranum P, Peña-Rosas JP, Garcia-Casal MN (2014) Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1312:105–112. doi:10.1111/nyas.12396
Redford AJ, Bowers RM, Knight R, Linhart Y, Fierer N (2010) The ecology of the phyllosphere: geographic and phylogenetic variability in the distribution of bacteria on tree leaves. Environ Microbiol 12:2885–2893. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02258.x
Rijavec T, Lapanje A, Dermastia M, Rupnik M (2007) Isolation of bacterial endophytes from germinated maize kernels. Can J Microbiol 53:802–808. doi:10.1139/W07-048
Robinson RJ, Fraaije BA, Clark IM, Jackson RW, Hirsch PR, Mauchline TH (2016) Endophytic bacterial community composition in wheat (Triticum aestivum) is determined by plant tissue type, developmental stage and soil nutrient availability. Plant Soil 405:381–396. doi:10.1007/s11104-015-2495-4
Rosenblueth M, Martínez-Romero E (2006) Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 19:827–837. doi:10.1094/MPMI-19-0827
Ryan RP, Germaine K, Franks A, Ryan DJ, Dowling DN (2008) Bacterial endophytes: recent developments and applications. FEMS Microbiol Lett 278:1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00918.x
Santhanam R, Groten K, Meldau DG, Baldwin IT (2014) Analysis of plant-bacteria interactions in their native habitat: bacterial communities associated with wild tobacco are independent of endogenous jasmonic acid levels and developmental stages. PLoS ONE 9:e94710. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094710
Seghers D, Wittebolle L, Top EM, Verstraete W, Siciliano SD (2004) Impact of agricultural practices on the Zea mays L. endophytic community. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1475–1482. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.3.1475-1482.2004
Shen RF, Cai H, Gong WH (2006) Transgenic Bt cotton has no apparent effect on enzymatic activities or functional diversity of microbial communities in rhizosphere soil. Plant Soil 285:149–159. doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9000-z
Siciliano S, Germida J (1999) Taxonomic diversity of bacteria associated with the roots of field-grown transgenic Brassica napus cv. Quest, compared to the non-transgenic B. napus cv. Excel and B. rapa cv. Parkland. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 29:263–272. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.1999.tb00617.x
Siciliano S, Theoret C, De Freitas J, Hucl P, Germida J (1998) Differences in the microbial communities associated with the roots of different cultivars of canola and wheat. Can J Microbiol 44:844–851. doi:10.1139/w98-075
Sims SR (1995) Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki [CryIA (c)] protein expressed in transgenic cotton: effects on beneficial and other non-target insects. Southwestern. Entomologist 20:493–506
Sun C, Geng L, Wang M, Shao G, Liu Y, Shu C, Zhang J (2016) No adverse effects of transgenic maize on population dynamics of endophytic Bacillus subtilis strain B916-gfp. MicrobiologyOpen 00:1–6. doi:10.1002/mbo3.404
Van Overbeek L, Van Elsas JD (2008) Effects of plant genotype and growth stage on the structure of bacterial communities associated with potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64:283–296. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00469.x
Wolfenbarger LL, Phifer PR (2000) The ecological risks and benefits of genetically engineered plants. Science 290:2088–2093. doi:10.1126/science.290.5499.2088
Yang JH, Liu HX, Zhu GM, Pan YL, Xu LP, Guo JH (2008) Diversity analysis of antagonists from rice-associated bacteria and their application in biocontrol of rice diseases. J Appl Microbiol 104:91–104. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03534.x
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF) through the Thuthuka grant (Grant No. 84168) awarded to RA Adeleke. The authors acknowledge the Agricultural Research Council’s sponsorship of Mashiane RA through the Professional development program. We sincerely thank Owen Rhode and members of the Microbiology and Environmental Biotechnology Research Group ARC-ISCW for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ramadimetja A. Mashiane and Obinna T. Ezeokoli have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11274_2017_2249_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 1 Fig S1. Rarefaction curve of OTUs species in maize phyllospheres. Rarefaction curve was constructed in R software by using the vegan package. (TIF 133 KB)
11274_2017_2249_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 2 Fig. S2. Heatmap of unweighted and weighted Bray-Curtis dissimilarity matrix between samples (a) Weighted (b) Unweighted. (TIF 45 KB)
11274_2017_2249_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 4 Fig. S3. Taxonomic diversity of OTUs in maize phyllospheres at order taxa level. “Others” indicate OTUs which were unclassified into phylum. Unassigned include OTUs which failed to align with any reference sequence. (TIF 103 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mashiane, R.A., Ezeokoli, O.T., Adeleke, R.A. et al. Metagenomic analyses of bacterial endophytes associated with the phyllosphere of a Bt maize cultivar and its isogenic parental line from South Africa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2249-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2249-y