Abstract
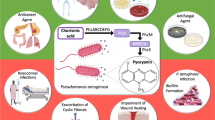
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic, Gram-negative bacterium and is one of the most commercially and biotechnologically valuable microorganisms. Strains of P. aeruginosa secrete a variety of redox-active phenazine compounds, the most well studied being pyocyanin. Pyocyanin is responsible for the blue-green colour characteristic of Pseudomonas spp. It is considered both as a virulence factor and a quorum sensing signalling molecule for P. aeruginosa. Pyocyanin is an electrochemically active metabolite, involved in a variety of significant biological activities including gene expression, maintaining fitness of bacterial cells and biofilm formation. It is also recognised as an electron shuttle for bacterial respiration and as an antibacterial and antifungal agent. This review summarises recent advances of pyocyanin production from P. aeruginosa with special attention to antagonistic property and bio-control activity. The review also covers the challenges and new insights into pyocyanin from P. aeruginosa.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja EG (2006) Towards elucidation of the phenazine biosynthesis pathway of pseudomonas with the structural and functional analysis of the enzymes PhzA, B, G and Bcep A. Thesis, Max Planck Institute for Molecular Physiology and Department of Chemistry, University of Dortmund, Germany, p 151
Al Hinai AH, Al Sadi AM, Al Bahry SN, Mothershaw AS, Al Said FA, Al Harthi SA, Deadman ML (2010) Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with antagonistic activity against Pythium aphani dermaturm. J Plant Pathol 92:653–660
Ali Siddiqui I, Ehetshamul-Haque S, Shahid Shaukat S (2001) Use of rhizobacteria in the control of root rot–root knot disease complex of mungbean. J Phytopathol 149:337–346
Angell S, Bench BJ, Williams H, Watanabe CM (2006) Pyocyanin isolated from a marine microbial population: synergistic production between two distinct bacterial species and mode of action. Chem Biol 13:1349–1359
Anjaiah V, Cornelis P, Koedam N (2003) Effect of genotype and root colonization in biological control of fusarium wilts in pigeon pea and chick pea by Pseudomonas aeruginos PNAI. Can J Microbiol 49:85–91
Audenaert K, Pattery T, Cornelis P, Hofte M (2002) Induction of systemic resistance to Botrytis Cinerea in tomato by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 7NSK2: role of salicylic acid, pyochelin and pyocyanin. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 115:1147–1156
Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilory S, Vivanco JM (2006) The role of root exudates in rhizosphere Interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:233–236
Bakthavatchalu S, Shivakumar S, Sullia SB (2013) Molecular detection of antibiotic related genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa FP6, an antagonist towards Rhizoctonia solani and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Turk J Biol 37:289–295
Baron SS, Rowe JJ (1981) Antibiotic action of pyocyanin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 20:814–820
Baron SS, Terranova G, Rowe JJ (1989) Molecular mechanism of the antimicrobial action of pyocyanin. Curr Microbiol 18:223–230
Bashan Y, Holguin G (1998) Proposal for the division of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in two classification: biocontrol PGPB (plant growth promoting bacteria) and PGPB. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1225–1228
Brown VI, Lowbury EJ (1965) Use of and improved cetrimide agar medium and other culture methods for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Pathol 18:752–756
Bryant S, Huerta V, Mihalik K, Crixell SH, Vattem DA (2008) Medicinal plants from Indian Subcontinent decrease quorum sensing dependent virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Nat Rem 8:138–150
Burton MO, Campbell JJ, Eagles BA (1948) The mineral requirements for pyocyanin production. Can J Res 26:15–22
Byng GS, Eustice DC, Jensen RA (1979) Biosynthesis of phenazine pigment in mutant and wild type cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 138:846–852
Caldwell CC, Chen Y, Goetzmann HS, Hao Y, Borchers MT, Hassett DJ, Young LR, Mavrodi D, Thomashow L, Lau GW (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin pyocyanin causes cystic fibrosis airway pathogenesis. Am J Pathol 175:2473–2488
Chang PC, Blackwood AC (1969) Simultaneous production of three phenazine pigments by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mac 436. Can J Microbiol 15:439–444
Clatworthy AE, Pierson E, Hung DT (2007) Targeting virulence: a new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat Chem Biol 3:541–548
Cook JR (1988) Biological control and holistic plant health care in agriculture. Am J Altern Agric 3:51–62
Cook RJ (1993) Making greater use of introduced microorganisms for biological control of plant pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 31:53–80
Cox CD (1986) Role of pyocyanin in the acquisition of iron from transferring. Infect Immun 52:263–270
Das T, Manefield M (2012) Pyocyanin promotes extracellular DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS One 7(10):e46718
Das T, Kutty SK, Kumar N, Manefield M (2013) Pyocyanin facilitates extracellular DNA binding to Pseudomonas aeruginosa influencing cell surface properties and aggregation. PLoS One 8(3):e58299
De Vleesschauwer D, Cornelis P, Hofte M (2006) Redox active pyocyanin secreted by P. aeruginosa 7 NSK2 triggers systems resistance to Marnaporthe grisea but enhances Rhizoctoria solani susceptibility in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:1406–1419
Dilantha Fernando WG, Ramarthanam R, Krishnamoorth AS, Savchuk SC (2005) Identification and use of potential bacterial organic antifungal volatiles in bio control. Soil Biol Biochem 37:955–964
Driscoll JA, Brody SL, Kollef MH (2007) The epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs 67:351–368
El-Samerraie FT, Mohammed AR, Al Mosawi MA, Matloob SEA (1997) Treatment of Pseudomonas life threatening chronic suppurative otitis media by new conservative therapy—a prospective study. J Islam Acad Sci 10:109–112
Fontoura R, Spada JC, Silveira ST, Tsai SM, Brandelli A (2009) Purification and characterization of an antimicrobial peptide produced by Pseudomonas sp. strain 4B. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:205–213
Fordos MJ (1863) Recherches sur les matieres colorants des suppurations blues, pyocyaninet pyozanthos. ibid 56:1128–1131
Fothergill JL, Panagea S, Hart CA, Walshaw MJ, Pitt TL, Winstanley C (2007) Widespread pyocyanin over-production among isolates of a cystic fibrosis epidemic strain. BMC Microbiol 7:45
Frank LH, De Moss RD (1958) On the biosynthesis of pyocyanine. J Bacteriol 77:776–782
Gessard C (1984) Classics in infectious diseases. On the blue and green coloration that appears on bandages. Rev Infect Dis 6(3):775–776
Gibson J, Sood A, Hogan DA (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa–Candida albicans interactions: localization and fungal toxicity of a phenazine derivatives. App Environ Microbiol 75:504–513
Glazebrook JS, Campbell RS, Hutchinson GW, Stallman ND (1978) Rodent zoonoses in North Queensland: the occurrence and distribution of zoonotic infections in North Queensland rodents. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 56:147–156
Glick BR (1995) The enhancement of plant growth of free living bacteria. Can J Microbiol 41:109–117
Gohain N, Linda ST, Mavrodi DV, Wouf BF (2006) The purification, crystallization and preliminary structural characterization of PhzM, a phenzine modifying methyltransferase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62:887–890
Green SK, Schroth MN, Cho JJ, Kominos SK, Vitanza-Jack VB (1974) Agricultural plants and soil as a reservoir for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol 28:987–991
Hassan HM, Fridorich I (1980) Mechanism of the antibiotic action of pyocyanine. J Bacreriol 141:156–163
Hassanein WA, Awny NM, El-Mougith AA, Salah El-Dein SH (2009) Characterization and antagonistic activities of metabolite produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sha8. J Appl Sci Res 5:392–403
Hassani HH, Hasan HM, Al-Saadi A, Ali AM, Muhammad MH (2012) A comparative study on cytotoxicity and apoptotic activity of pyocyanin produced by wild type and mutant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Exp Biol 2:1389–1394
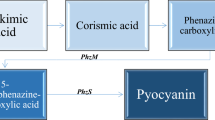
Herbert RB, Holliman FG, Sheridan JB (1974) Biosynthesis of iodine, incorporation of D-(1-14C), D-(6-14C) and D-(1,6,7-14C3)-shikimic acid. Tertrahedron Lett 48:4201–4204
Herbert RB, Holliman FG, Sheridan JB (1976) Biosynthesis of microbial phenazines: incorporation of shikmic acid. Tetrahedron Lett 8:639–642
Ho Sui SJ, Fedynak A, Hsiao WW, Langille MG, Brinkman FS (2009) The association of virulence factors with genomic islands. PLoS One 4:e8094
Ho Sui SJ, Lo R, Fernandes AR, Caulfield MDG, Lerman JA, Xie L, Bourne PE, Baillie DL, Brinkman FSL (2012) Raloxifene attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin production and virulence. Int J Antimicrob Agents 40:246–251
Hogan DA, Kolter R (2002) Pseudomonas–Candida interaction: an ecological role for virulence factors. Science 296:2229–2232
Hollstein U, Marshall LG (1972) Biosynthesis of phenazines. J Org Chem 37:3510–3514
Hollstein U, McCamey DA (1973) Biosynthesis of phenazines. II Incorporation of (6–14C)-d-shikimic acid into phenazine-1-carboxylic acid and iodinin. J Org Chem 38:3415–3417
Ingledew WM, Campbell JJ (1969) A new resuspension medium for pyocyanine production. Can J Microbiol 15:595–598
Kaleli I, Cevahir N, Demir M, Yildrim U, Sahin R (2007) Anticandidal activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical specimens. Mycoses 50:74–78
Karatuna O, Yagci A (2010) Analysis of quorum sensing-dependent virulence factor production and its relationship with antimicrobial susceptibility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory isolates. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:1770–1775
Karpagam S, Sudhakar T, Lakshmipathy M (2013) Microbicidal response of pyocyanin produced by P. Aeruginosa toward clinical isolates of fungi. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5:870–873
Kerr JR (1994) Suppression of fungal growth exhibited by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol 32:525–527
Kerr JR, Taylor GW, Rutman A, Hoiby N, Cole PJ, Wilson R (1999) Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin and 1-hydroxyphenazine inhibit fungal growth. J Clin Pathol 52:385–387
Khamdan K, Suprapta DN (2011) Induction of plant resistance against soyabean stunt virus using some formulations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J ASSAAS 17:98–105
Khare E, Arora NK (2011) Dual activity of pyocyanin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa—antibiotic against phytopathogen and signal molecule for biofilm development by rhizobia. Can J Microbiol 57:708–713
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med 44:301–307
Krishnan T, Yin WF, Chan KG (2012) Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by ayurveda spice clove (Syzygium Aromaticum) bud extract. Sensors 12:4016–4030
Lau GW, Hassett DJ, Ran H, Kong F (2004) The role of pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Trends Mol Med 10:599–606
Liang H, Duan J, Sibley CD, Surette MG, Duan K (2011) Identification of mutants with altered phenazine production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol 60:22–34
Lilly HA, Lowbury EJL (1972) Cetrimide-nalidixic agar as a selective medium for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol 5:151–153
Lundgren BR, Thornton W, Dornan MH, Villegas-Peñaranda LR, Boddy CN, Nomura CT (2013) Gene PA2449 is essential for glycine metabolism and pyocyanin biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 195:2087–3000
Machan ZA, Pitt TL, White W, Watson D, Taylor GW, Cole PJ, Wilson R (1990) Interaction between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus: description of an anti-staphylococcal substance. J Med Microbiol 34:213–217
Mallesh SB (2008) Plant growth promoting rhizobactaria their characterization and mechanism in the suppression of soil borne pathogens of coleus and ashwaghandha. Ph.D. thesis, University of Agricultural Sciences, Dharwad, India
Mavrodi DV, Bonsall RF, Delaney SM, Soule MJ, Phillips G, Thomashow LS (2001) Functional analysis of genes for biosynthesis of pyocyanin and phenazine-1-carboxamide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 183:6454–6465
Mc Alester G, O’Gara F, Morrissey JP (2007) Signal-mediated interactions between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans. J Med Microbiol 57:563–569
Mercado-Blanco J, Bakker PA (2007) Interactions between plants and beneficial Pseudomonas sp.: exploiting beneficial traits for crop protection. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 92:367–389
Meyer JM (2000) Pyoverdines: pigments, siderophores and potential taxonomic markers of fluorescent Pseudomonas species. Arch Microbiol 174:135–142
Migula W (1984) Arbeiten aus clem Bakteriologischen Institute der Technischen Hoschschule. Zu Karlsruhe 1:235–238
Millican RC (1962) Biosynthesis of pyocyanine. Incorporation of C14 Shikimic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta 57:407–409
Moore ERB, Tindall BJ, Martins Dos Santos VAP, Pieper DH, Juan-Luis R, Palleroni NJ (2006) Nonmedical: Pseudomonas. Prokaryotes 6:646–703
Morkunas B, Galloway Warren RJD, Wright M, Ibbeson BM, Hodgkinson JT, O’Connell KMG, Bartolucci N, Valle MD, Welch M, Spring DR (2012) Inhibition of the production of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor pyocyanin in wild-type cells by quorum sensing autoinducer-mimics. Org Biomol Chem 10:8452–8464
Norman RS, Moeller P, Mc Donald TJ, Morris PJ (2004) Effect of pyocyanin on a crude oil degrading microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4004–4011
O’Malley YQ, Reszka KJ, Rasmussen GT, Abdalla MY, Denning GM, Britigan BE (2003) The Pseudomonas secretary product pyocyanin inhibits catalase activity in human lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285:1077–1086
Onbasli D, Aslim B (2008) Determination of antimicrobial activity and production of some metabolites by Pseudomanas aeruginosa B1 and B2 in sugar beet molasses. Afr J Biotechnol 7:4614–4619
Pal KK, Gardner BMS (2006) Biological control of plant pathogens. Plant Health Instr 1–25. doi:10.1094/PHI-A-2006-1117-02
Pal R, Revathi R (1998) Susceptibility of yeasts to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Indian J Med Microbiol 16:72–74
Palleroni NJ (2005) Pseudomonas. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 323–379
Parsons JF, Greenhagen BT, Shi K, Calabrese K, Robinson H, Ladner JE (2007) Structural and functional analysis of the pyocyanin biosynthetic protein Phz M from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochemistry 46:1821–1828
Pierson LS, Pierson EA (2010) Metabolism and function of phenazines in bacteria: impacts on the behavior of the bacteria in the environment and biotechnological process. Appl Micorbiol Biotechnol 18:1659–1670
Porter RC (2009) Studies in pigment production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. M.S. thesis, Texas Tech University, TX, 59 p
Rada B, Leto TL (2013) Pyocyanin effects on respiratory epithelium: relevance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway infections. Trends Microbiol 21:73–81
Rada B, Jendrysik MA, Pang L, Hayes CP, Yoo D-g, Park JJ, Moskowitz SM, Malech HL, Leto TL (2013) Pyocyanin-enhanced neutrophil extracellular trap formation requires the NADPH oxidase. PLoS One 8(1):e54205
Rahman PK, Pasirayi G, Auger V, Ali Z (2009) Development of simple and low cost micro–bioreactor for high throughput bio-processing. Biotechnol Lett 31:209–214
Ran H, Hassett DJ, Lau GW (2003) Human targets of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:14315–14320
Rane MR, Sarode PD, Chaudhari BL, Chincholkar SB (2007) Detection, isolation and identification of phenazine 1-carboxylic acid produced by biocontrol strains of Pseudomonas aeruiginosa. J Sci Ind Res 66:627–631
Raoof WM, Latif IAR (2010) In vitro study of the swarming phemomena and antimicrobial activity of pyocyanin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from different human infections. Eur J Sci Res 47:405–421
Reyes EA, Bale MJ, Cannon WH, Matsen JM (1981) Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by pyocyanin production on tech agar. J Clin Microbiol 13:456–458
Saha S, Thavasi R, Jayalakshmi S (2008) Phenazine pigments from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their application as antibacterial agent and food colourants. Res J Microbiol 3:122–128
Saosoong K, Wongphathanakul W, Paorsiri C, Ruangviriyachi C (2009) Isolation and analysis of antibacterial substance produced from Pseudomonas aeruginosa TISTR 781. KKU Sci J 37:163–172
Sheeba J (2007) Isolation, pigment production, antifungal activity and antibiogram pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa—a study. M.Phil., Thesis, Bharathidasan University, 39 p
Subramaniam L, Shriniwas B (1985) Rapid diagnosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection by demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescein. Indian J Med Res 81:561–566
Sudhakar T, Karpagam S, Shiyama S (2013) Antifungal efficacy of pyocyanin produced from bioindicators of nosocomial hazards. Int J ChemTech Res 5:1101–1106
Sunish Kumar R, Ayyadurai N, Pandiaraja P, Reddy AV, Venkateswarlu Y, Prakash O, Sakthivel N (2004) Characterization of anti-fungal metabolite produced by a new strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa PUPa3 that exhibits broad spectrum antifungal activity and biofertilizing traits. J Appl Microbiol 98:145–154
Suthar S, Chhimpa V, Singh S (2009) Bacterial contamination in drinking water: a case study in rural areas of northern Rajasthan, India. Environ Monit Asses 159:43–50
Sweden EG (2010) Study the effect of antibiotics on pyocyanin production from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and pyocyanin as antibiotic against different pathogenic bacteria. J Univ Anbar Pure Sci 4:15–18
Wahba AH, Darrel JH (1965) The identification of a typical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol 38:329–342
Waksman SA, Woodruff HB (1940) The soil as a source of microorganisms antagonistic to disease producing bacteria. J Bacteriol 40:581–600
Winstanley C, Fothergill JL (2008) The role of quorum sensing in chronic cystic fibrosis Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. FEMS Microbiol Lett 290:1–9
Young G (1947) Pigment production and antibiotic activity in cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 54:109–117
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to all the researchers whose papers have been used for this review. Greatest gratitude goes to Luigi Lucini, Ph.D., Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Institute of Environmental and Agricultural Chemistry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayaseelan, S., Ramaswamy, D. & Dharmaraj, S. Pyocyanin: production, applications, challenges and new insights. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 1159–1168 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1552-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1552-5