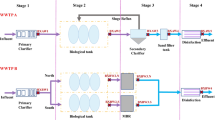
Abstract
A drinking water plant was surveyed to determine the bacterial composition of different drinking water treatment processes (DWTP). Water samples were collected from different processing steps in the plant (i.e., coagulation, sedimentation, sand filtration, and chloramine disinfection) and from distantly piped water. The samples were pyrosequensed using sample-specific oligonucleotide barcodes. The taxonomic composition of the microbial communities of different DWTP and piped water was dominated by the phylum Proteobacteria. Additionally, a large proportion of the sequences were assigned to the phyla Actinobacteria and Bacteroidetes. The piped water exhibited increasing taxonomic diversity, including human pathogens such as the Mycobacterium, which revealed a threat to the safety of drinking water. Surprisingly, we also found that a sister group of SAR11 (LD12) persisted throughout the DWTP, which was always detected in freshwater aquatic systems. Moreover, Polynucleobacter, Rhodoferax, and a group of Actinobacteria, hgcI clade, were relatively consistent throughout the processes. It is concluded that smaller-size microorganisms tended to survive against the present treatment procedure. More improvement should be made to ensure the long-distance transmission drinking water.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990) Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1919–1925
APHA, AWWA, WWF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Bai X, Wu F, Zhou B, Zhi X (2010) Biofilm bacterial communities and abundance in a full-scale drinking water distribution system in Shanghai. J Water Health 8:593–600
Bereschenko LA, Heilig GHJ, Nederlof MM, Van Loosdrecht MCM, Stams AJM, Euverink GJW (2008) Molecular characterization of the bacterial communities in the different compartments of a full-scale reverse-osmosis water purification plant. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5297–5304
Bibby K, Viau E, Peccia J (2010) Pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA gene to reveal bacterial pathogen diversity in biosolids. Water Res 44:4252–4260
Camper AK, LeChevallier MW, Broadaway SC, McFeters GA (1986) Bacteria associated with granular activated carbon particles in drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:434–438
Carter AM, Pacha RE, Clark GW, Williams EA (1987) Seasonal occurrence of Campylobacter spp. in surface waters and their correlation with standard indicator bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:523–526
Cui J, Meng H, Nie M, Chen X, Li Z, Bu N, Li B, Chen J, Quan Z, Fang C (2012) Bacterial succession during 500 years of soil development under agricultural use. Ecol Res 27:793–807
Duarte GF, Rosado AS, Seldin L, Keijzer-Wolters AC, van Elsas JD (1998) Extraction of ribosomal RNA and genomic DNA from soil for studying the diversity of the indigenous bacterial community. J Microbiol Methods 32:21–29
Eichler S, Christen R, Holtje C, Westphal P, Botel J, Brettar I, Mehling A, Hofle MG (2006) Composition and dynamics of bacterial communities of a drinking water supply system as assessed by RNA- and DNA-based 16S rRNA gene fingerprinting. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1858–1872
Falkinham JO III, Norton CD, LeChevallier MW (2001) Factors influencing numbers of Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium intracellulare, and other Mycobacteria in drinking water distribution systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1225–1231
Felföldi T, Heéger Z, Vargha M, Márialigeti K (2010) Detection of potentially pathogenic bacteria in the drinking water distribution system of a hospital in Hungary. Clin Microbiol Infec 16:89–92
Feng BW, Li XR, Wang JH, Hu ZY, Meng H, Xiang LY, Quan ZX (2009) Bacterial diversity of water and sediment in the Changjiang estuary and coastal area of the East China Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:80–92
Giovannoni SJ, Bibbs L, Cho JC, Stapels MD, Desiderio R, Vergin KL, Rappé MS, Laney S, Wilhelm LJ, Tripp HJ (2005) Proteorhodopsin in the ubiquitous marine bacterium SAR11. Nature 438:82–85
Glockner FO, Zaichikov E, Belkova N, Denissova L, Pernthaler J, Pernthaler A, Amann R (2000) Comparative 16S rRNA analysis of lake bacterioplankton reveals globally distributed phylogenetic clusters including an abundant group of actinobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5053–5065
Hamady M, Walker JJ, Harris JK, Gold NJ, Knight R (2008) Error-correcting barcoded primers for pyrosequencing hundreds of samples in multiplex. Nat Method 5:235–237
Heckmann K, Schmidt HJ (1987) Polynucleobacter necessarius gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately endosymbiotic bacterium living in the cytoplasm of Euplotes aediculatus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:456–457
Huber T (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20:2317–2319
Klausen C, Nicolaisen MH, Strobel BW, Warnecke F, Nielsen JL, Jørgensen NOG (2005) Abundance of actinobacteria and production of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in Danish streams and fish ponds. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:265–278
Kormas KA, Neofitou C, Pachiadaki M, Koufostathi E (2010) Changes of the bacterial assemblages throughout an urban drinking water distribution system. Environ Monit Assess 165:27–38
Kwon S, Moon E, Kim TS, Hong S, Park HD (2011) Pyrosequencing demonstrated complex microbial communities in a membrane filtration system for a drinking water treatment plant. Microbes Environ 26:149–155
Lane DJ, Pace B, Olsen GJ, Stahl DA, Sogin ML, Pace NR (1985) Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 82:6955–6959
LeChevallier MW, Au KK (2004) Water treatment and pathogen control: Process efficiency in achieving safe drinking water. IWA Pubishing, London
Lechevallier MW, Babcock TM, Lee RG (1987) Examination and characterization of distribution system biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2714–2724
Li D, Li Z, Yu JW, Cao N, Liu RY, Yang M (2010) Characterization of bacterial community structure in a drinking water distribution system during an occurrence of red water. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7171–7180
Liu W, Wu H, Wang Z, Ong SL, Hu JY, Ng WJ (2002) Investigation of assimilable organic carbon (AOC) and bacterial regrowth in drinking water distribution system. Water Res 36:891–898
Liu R, Li D, Gao Y, Zhang Y, Wu S, Ding R, Hesham AE-L, Yang M (2010) Microbial diversity in the anaerobic tank of a full-scale produced water treatment plant. Process Biochem 45:744–751
Logares R, Bråte J, Heinrich F, Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Bertilsson S (2010) Infrequent transitions between saline and fresh waters in one of the most abundant microbial lineages (SAR11). Mol Biol Evol 27:347–357
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228–8235
Mao DP, Zhou Q, Chen CY, Quan ZX (2012) Coverage evaluation of universal bacterial primers using the metagenomic datasets. BMC Microbiol 12:66
Miettinen IT, Vartiainen T, Nissinen T, Tuhkanen T, Martikainen PJ (1998) Microbial growth in drinking waters treated with ozone, ozone hydrogen peroxide or chlorine. Ozone Sci Eng 20:303–315
Nielsen JL, Klausen C, Nielsen PH, Burford M, Jørgensen NOG (2006) Detection of activity among uncultured Actinobacteria in a drinking water reservoir. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55:432–438
Nikitin DI, Strompl C, Oranskaya MS, Abraham W-R (2004) Phylogeny of the ring-forming bacterium Arcicella aquatica gen. nov., sp. nov. (ex Nikitin et al. 1994), from a freshwater neuston biofilm. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:681–684
Niquette P, Servais P, Savoir R (2000) Impacts of pipe materials on densities of fixed bacterial biomass in a drinking water distribution system. Water Res 34:1952–1956
Norton CD, LeChevallier MW (2000) A pilot study of bacteriological population changes through potable water treatment and distribution. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:268–276
Park SR, Mackay WG, Reid DC (2001) Helicobacter sp. recovered from drinking water biofilm sampled from a water distribution system. Water Res 35:1624–1626
Poitelon JB, Joyeux M, Welte B, Duguet JP, Prestel E, Lespinet O, Dubow MS (2009) Assessment of phylogenetic diversity of bacterial microflora in drinking water using serial analysis of ribosomal sequence tags. Water Res 43:4197–4206
Poitelon JB, Joyeux M, Welte B, Duguet JP, Prestel E, DuBow MS (2010) Variations of bacterial 16S rDNA phylotypes prior to and after chlorination for drinking water production from two surface water treatment plants. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:117–128
Rappe MS, Connon SA, Vergin KL, Giovannoni SJ (2002) Cultivation of the ubiquitous SAR11 marine bacterioplankton clade. Nature 418:630–633
Regan JM, Harrington GW, Baribeau H, De Leon R, Noguera DR (2003) Diversity of nitrifying bacteria in full-scale chloraminated distribution systems. Water Res 37:197–205
Revetta RP, Pemberton A, Lamendella R, Iker B, Domingo JWS (2010) Identification of bacterial populations in drinking water using 16S rRNA-based sequence analyses. Water Res 44:1353–1360
Salcher MM, Pernthaler J, Posch T (2011) Seasonal bloom dynamics and ecophysiology of the freshwater sister clade of SAR11 bacteria `that rule the waves’ (LD12). ISME J 5:1242–1252
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Schmidt TM, Delong EF, Pace NR (1991) Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S ribosomal-RNA gene cloning and sequencing. J Bacteriol 173:4371–4378
Sen K, Rodgers M (2004) Distribution of six virulence factors in Aeromonas species isolated from US drinking water utilities: a PCR identification. J Appl Microbiol 97:1077–1086
Suthar S, Chhimpa V, Singh S (2009) Bacterial contamination in drinking water: a case study in rural areas of northern Rajasthan, India. Environ Monit Assess 159:43–50
Symons JM (1978) Ozone, chlorine dioxide and chloramines as alternatives to chlorine for disinfection of drinking water. In: Jolley RL, Gorchev H, Hamilton DH Jr (eds) Water chlorination: environmental impact and health effects. Gatlinburg, Tennessee, pp 555–560
Vaerewijck MJM, Huys G, Palomino JC, Swings J, Portaels F (2005) Mycobacteria in drinking water distribution systems: ecology and significance for human health. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:911–934
Wagner R (1994) The regulation of ribosomal RNA synthesis and bacterial cell growth. Arch Microbiol 161:100–109
Ye L, Zhang T (2011) Pathogenic bacteria in sewage treatment plants as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. Environ Sci Technol 45:7173–7179
Zacheus OM, Iivanainen EK, Nissinen TK, Lehtola MJ, Martikainen PJ (2000) Bacterial biofilm formation on polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene and stainless steel exposed to ozonated water. Water Res 34:63–70
Zuma FN, Lin J, Jonnalagadda SB (2009) Kinetics of inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in aqueous solutions by ozone aeration. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 44:929–935
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2008AA062501) and the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (2006BAI19B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, DN., Fan, ZY., Chi, L. et al. Analysis of the bacterial communities associated with different drinking water treatment processes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 1573–1584 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1321-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1321-5