Abstract
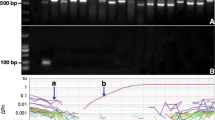
The occurrence of harmful algal blooms (HABs) throughout the world has increased and poses a large threat to human health, fishery resources and tourism industries. The genus Alexandrium includes a number of toxic species associated with HABs. Therefore, it is very important to rapidly detect and monitor the harmful algae, such as Alexandrium genus. In this study, a standard curve of plasmid containing 18S rDNA-28S rDNA region from Alexandrium catenella was constructed and 5.8S rDNA sequence served as the primer of the real-time PCR. Cultured A. catenella, Alexandrium affine, Alexandrium lusitanicum and Alexandrium minutum samples were analyzed by real-time PCR using the same set of primers simultaneously. Using microscopy cells counts, 5.8S rDNA copies per cell and total DNA per cell were estimated. This assay method is promising for rapid detection of large number of Alexandrium samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi M, Sake Y, Ishida Y (1996) Analysis of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species using sequences of the 5.8S ribosomal DNA and transcribed spacer regions. J Phycol 32:424–432
Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Sullivan JJ, Hall S, Lee C (1990) Dynamics and physiology of saxitoxin production by the dinoflagellates Alexandrium spp. Mar Biol 104:511–524
Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Qi YZ, Zheng L, Lu SH, Lin YT (1996) Paralytic shellfish poisoning in Southern China. Toxicon 34:579–590
Band-Schmidt CJ, Lilly EL, Anderson DM (2003) Identification of Alexandrium affine and A. margalefii (Dinophyceae) using DNA sequencing and LSU rDNA-based RFLP-PCR assays. Phycologia 42:261–268
Dyhrman ST, Erdner D, Du JL, Galac M, Anderson DM (2006) Molecular quantification of toxic Alexandrium fundyense in the gulf of maine using real-time PCR. Harmful Algae 5:242–250
Fontana F, Lanfredi M, Congiu L, Leis M, Chicca M, Rossi R (2003) Chromosomal mapping of 18S–28S and 5S rRNA genes by two-colour fluorescent in situ hybridization in six sturgeon species. Genome 46:473–477
Galluzzi L, Penna A, Bertozzini E, Vila M, Garcés E, Magnani M (2004) Development of a real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and quantification of Alexandrium minutum (a Dinoflagellate). Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1199–1206
Gescher C, Metfies K, Medlin LK (2008) The ALEX CHIP-development of a DNA chip for identification and monitoring of Alexandrium. Harmful Algae 7:485–494
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea cleve. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Hosoi-Tanabe S, Sako Y (2005) Rapid detection of natural cells of Alexandrium tamarense and A. catenella (Dinophyceae) by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Harmful Algae 4:319–328
Humbert JF, Quiblier C, Gugger M (2010) Molecular approaches for monitoring potentially toxic marine and freshwater phytoplankton species. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:1723–1732
Kamikawa R, Nagai S, Hosoi-Tanabe S, Itakura S, Yamaguchi M, Uchida Y, Baba T, Sako Y (2007) Application of real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of Alexandrium tamarense and Alexandrium catenella cysts from marine sediments. Harmful Algae 6:413–420
Lin S, Feinstein TN, Zhang H, Carpenter EJ (2003) Development of an immunofluorescence technique for detection Pfiesteria piscicida. Harmful Algae 2:223–231
Long EO, Dawid IB (1980) Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem 49:727–764
McCauley LAR, Erdner DL, Nagai S, Richlen M, Anderson DM (2009) Biogeographic analysis of the globally distributed harmful bloom species Alexandrium minutum (dinophyceae) based on rRNA gene sequences and microsatellite markers. J Phycol 45:454–463
Park TG, Bell EM, Pearce I, Rublee PA, Bolch CJS, Hallegraeff GM (2007) Detection of a novel ecotype of Pfiesteria piscicida (Dinophyceae) in an Antarctic saline lake by real-time PCR. Polar Biol 30:843–848
Penna A, Magnani M (1999) Identification of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species using PCR and rDNA-targeted probes. J Phycol 35:615–621
Saito K, Drgon T, Robledo JAF, Krupatkina DN, Vasta GR (2002) Characterization of the rRNA locus of Pfiesteria piscicida and development of standard and quantitative PCR-based detection assays targeted to the nontranscribed spacer. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5394–5407
Song XY, Huang LM, Zhang JL, Huang HH, Li T, Su Q (2009) Harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Daya Bay, China: an in situ study of primary production and environmental impacts. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1310–1318
Touzet N, Davidson K, Pete R, Flanagan K, McCoy GR, Amzil Z, Maher M, Chapelle A, Raine R (2010) Co-occurrence of the West European (Gr.III) and North American (Gr.I) ribotypes of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae) in Shetland, Scotland. Protist 161:370–384
Van Dolah FM (2000) Marine algal toxins: origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ Health Perspect 108:133–141
Wang JH, Wu JY (2009) Occurrence and potential risks of harmful algal blooms in the East China Sea. Sci Total Environ 407:4012–4021
Xin ZY, Yu ZG, Wang TC, Hui X, Gou WL, Sun J, Qi HG, Li RX (2005) Identification and quantification of the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium sp. with competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (cELISA). Harmful Algae 4:297–307
Yan T, Zhou MJ (2004) Environmental and health effects associated with harmful algal bloom and marine algal toxins in China. Biomed Environ Sci 17:165–176
Yeung PKK, Kong KF, Wong FTW, Wong JTY (1996) Sequence data for two large-subunit rRNA genes from an Asian strain of Alexandrium catenella. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4199–4201
Yoshida M, Mizushima K, Matsuoka K (2003) Alexandrium catenella (Gonyaulacales: Dinophyceae): morphological characteristics of vegetative cell and resting cyst. Plankton Biol Ecol 50:61–64
Zhang QC, Yu RC, Zhou MJ, Wang YF, Li J, Yan T (2005) Effects of different phosphorus substrates on growth and toxin generation of Alexandrium minutum. Oceanol Limnol Sin 36:465–474
Zhang B, Yan T, Chen TY, Zhou MJ (2008) The toxicity of non-PSP-producting Alexandrium affine. Oceanol Limnol Sin 39:419–426
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by fund from Key Laboratory of Integrated Marine Monitoring and Applied Technologies for Harmful Algal Blooms,S.O.A., MATHAB (No. MH200804). The authors thank Dr. Yuping Miao for providing Alexandrium minutum AMTK4 and Dr. Tinglin Yang for providing Alexandrium catenella ACDH 01, Alexandrium affine CCMP112 and Alexandrium lusitanicum CCMP1888.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Li, Z. Detection and quantification of cultured marine Alexandrium species by real-time PCR. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 3255–3260 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1136-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1136-9